Austrian Parliament Österreichisches Parlament | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Houses | Federal Council National Council |
| Leadership | |
Franz Ebner (ÖVP) since 1 July 2024 | |
| Structure | |
| Seats |
|
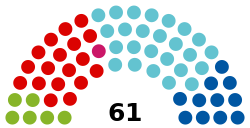 | |
Federal Council political groups | Government (31)
Opposition (30) |
 | |
National Council political groups | Government (97)
Opposition (86)
|
| Elections | |
| Appointment by State Landtage | |
| Proportional representation | |
Last National Council election | 29 September 2019 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Parliament Building Vienna, Austria | |
| Website | |
| parlament.gv.at | |
| This article is part of a series on the |
| Politics of Austria |
|---|
 |
The Austrian Parliament (German: Österreichisches Parlament) is the bicameral[1] federal legislature of Austria. It consists of two chambers – the National Council and the Federal Council. In specific cases, both houses convene as the Federal Assembly. The legislature meets in the Austrian Parliament Building in Vienna.
Overview
[edit]National Council
|
Federal Council
|
| Federal Assembly
(joint session of both houses) | |
The National Council is composed of 183 members elected through proportional representation in a general election. The legislative period lasts five years, elections are held earlier if the National Council prematurely moves for its own dissolution. The National Council is the dominant (albeit 'lower') house in the Austrian Parliament, and consequently the terms Parliament and National Council are commonly used synonymously.
The Federal Council is elected indirectly, through the provincial assemblies (Landtage) of the nine States of the Federal Republic, and reflects the distribution of seats in the Austrian Landtage. The states are represented in the Federal Council roughly in accordance to the size of their populations. Seats are redistributed among the states following each general census, and the overall size of the chamber varies slightly as a result. The current Federal Council is composed of 61 delegates. With regard to most issues, the Federal Council only possesses a dilatory right of veto which can be overridden by the National Council. However, the Federal Council enjoys absolute veto powers over bills intended to alter the powers of either the states, or of the Federal Council itself.
The Federal Assembly (Bundesversammlung) is a body whose function is mostly ceremonial in nature, and consists of the members of both houses of Parliament. The Federal Assembly convenes only rarely, for instance to witness the inauguration of the Federal President. It might be noted, however, that under exceptional circumstances the Austrian constitution endows the Federal Assembly with significant responsibilities. An example of this would be its pivotal role in the hypothetical impeachment of a Federal President.
Both houses of parliament, as well as the Federal Assembly, convene in the parliament building located on the Vienna Ring Road. From 2017 to 2022 they convened in the Redoute Wing of the Hofburg due to a renovation of the parliament building.
See also
[edit]- Constitution of Austria
- Austrian Parliament Building
- Imperial Council (Austria), the legislature between 1861 and 1918
- Imperial Diet (Austria), 1848–1849
References
[edit]- ^ "National Council, Federal Council and Federal Assembly". www.parlament.gv.at. Retrieved 2020-12-23.
External links
[edit]- The Austrian Parliament - Official Homepage (Engl. version)
- Austrian Parliament National Council Seating (DE version)
- Austrian Parliament Federal Council Seating (DE version)
National legislatures in Europe | |
|---|---|
| Sovereign states |
|
| States with limited recognition | |
| Dependencies and other entities | |
| Other entities | |

