This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: "Cape" geography – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message)
This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: "Cape" geography – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2023)
(Learn how and when to remove this message)



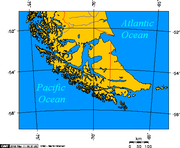
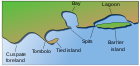
In geography, a cape is a headland, peninsula or promontory extending into a body of water, usually a sea.[1] A cape usually represents a marked change in trend of the coastline, often making them important landmarks in sea navigation. This also makes them prone to natural forms of erosion, mainly tidal actions, resulting in a relatively short geological lifespan. Capes can be formed by glaciers, volcanoes, and changes in sea level. Erosion plays a large role in each of these methods of formation.[citation needed]