This article uses bare URLs, which are uninformative and vulnerable to link rot. Please consider converting them to full citations to ensure the article remains verifiable and maintains a consistent citation style. Several templates and tools are available to assist in formatting, such as reFill (documentation) and Citation bot (documentation). (August 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message)
 | |
| Original author(s) | Khronos Group |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Khronos Group |
| Stable release | 1.5[1]
/ March 19, 2014 |
| Written in | C |
| Operating system | Cross-platform |
| Platform | Cross-platform |
| Type | API |
| Website | www |
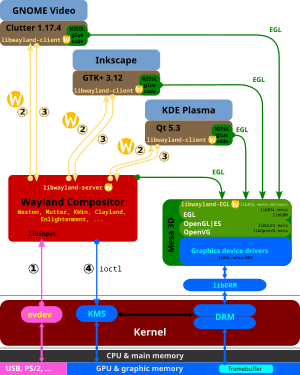
EGL is an interface between Khronos rendering APIs (such as OpenGL, OpenGL ES or OpenVG) and the underlying native platform windowing system. EGL handles graphics context management, surface/buffer binding, rendering synchronization, and enables "high-performance, accelerated, mixed-mode 2D and 3D rendering using other Khronos APIs."[2] EGL is managed by the non-profit technology consortium Khronos Group.
The acronym EGL is an initialism, which starting from EGL version 1.2 refers to Khronos Native Platform Graphics Interface.[3] Prior to version 1.2, the name of the EGL specification was OpenGL ES Native Platform Graphics Interface.[4] X.Org development documentation glossary defines EGL as "Embedded-System Graphics Library".[5]