.mw-parser-output .hidden-begin{box-sizing:border-box;width:100%;padding:5px;border:none;font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .hidden-title{font-weight:bold;line-height:1.6;text-align:left}.mw-parser-output .hidden-content{text-align:left}@media all and (max-width:500px){.mw-parser-output .hidden-begin{width:auto!important;clear:none!important;float:none!important))You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Polish. (November 2016) Click [show] for important translation instructions.
View a machine-translated version of the Polish article.
Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting machine-translated text into the English Wikipedia.
Consider adding a topic to this template: there are already 294 articles in the main category, and specifying|topic= will aid in categorization.
Do not translate text that appears unreliable or low-quality. If possible, verify the text with references provided in the foreign-language article.
You must provide copyright attribution in the edit summary accompanying your translation by providing an interlanguage link to the source of your translation. A model attribution edit summary is Content in this edit is translated from the existing Polish Wikipedia article at [[:pl:Kultura miłogradzka]]; see its history for attribution.
You may also add the template ((Translated|pl|Kultura miłogradzka)) to the talk page.
For more guidance, see Wikipedia:Translation.
This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: "Milograd culture" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this message)
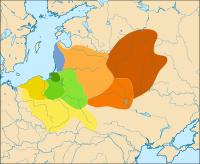
Sambian-Nothangian group
Western Masurian group (Galindians)
Eastern Masurian group (Yotvingians)
Lower Neman and West-Latvian group (Curonians)
Milograd culture
Plain-Pottery culture/Dnepr-Dvina culture
Bell-shaped burials group
The Milograd culture (also spelled Milahrad or Mylohrad, also known as Pidhirtsi culture on Ukrainian territory) is an archaeological culture, lasting from about the 7th century BC to the 1st century AD. Geographically, it corresponds to present day southern Belarus and northern Ukraine, in the area of the confluence of the Dnieper and the Pripyat, north of Kyiv. Their ethnic origin is uncertain, but likely to be either Baltic or Early Slavic.
The town of Milahrad (Belarusian: Мілаград), after which the culture is named, is located in the Gomel Region of Belarus.
