| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
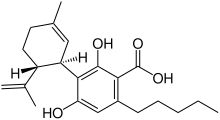
| Preferred IUPAC name
(1′R,2′R)-2,6-Dihydroxy-5′-methyl-4-pentyl-2′-(prop-1-en-2-yl)-1′,2′,3′,4′-tetrahydro[1,1′-biphenyl]-3-carboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3DMet | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H30O4 | |
| Molar mass | 358.478 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), is a cannabinoid found in cannabis plants.[1] It is most abundant in the glandular trichomes on the female seedless flowers or more accurately infructescence often colloquially referred to as buds.[2] CBDA is the chemical precursor to cannabidiol (CBD). Through the process of decarboxylation cannabidiol is derived via a loss of a carbon and two oxygen atoms from the 1 position of the benzoic acid ring. Cannabinoids are a class of compounds that are essentially unique to the cannabis genus. Both marijuana and hemp belong to this genus.