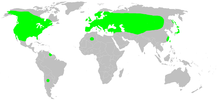
| Cyclosa conica | |
|---|---|

| |
| Female spiderling | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Subphylum: | Chelicerata |
| Class: | Arachnida |
| Order: | Araneae |
| Infraorder: | Araneomorphae |
| Family: | Araneidae |
| Genus: | Cyclosa |
| Species: | C. conica
|
| Binomial name | |
| Cyclosa conica Pallas, 1772
| |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Cyclosa conica is a small spider with no common name. It is an orb weaver, and it is easily recognized by the way it strings together the dead bodies of insects and other debris and hangs it near the center of its web. It hides on this string of debris, and its natural coloration makes it extremely difficult to see until it moves. One of its defenses against predators is to blend in with this debris and to feign death when disturbed. These spiders are small; the females range from 5.3 mm to 7.5 mm, and the males range from 3.6 mm to 4 mm.
The webs of these spiders are characterized by a vertical stripe running down the center. This stripe, or stabilimentum, is composed of dead prey and other debris and is used as a hiding place for the spider. The material in the stabilimentum may also serve as a decoy to mislead predators into attacking the debris, giving the spider time to escape.

Subspecies
[edit]- Cyclosa conica albifoliata Strand, 1907 (France)
- Cyclosa conica defoliata Strand, 1907 (Central Europe)
- Cyclosa conica dimidiata Simon, 1929 (France)
- Cyclosa conica leucomelas Strand, 1907 (Central Europe)
- Cyclosa conica pyrenaica Strand, 1907 (France)
- Cyclosa conica zamezai Franganillo, 1909 (España)
References
[edit]- Kaston, B.J. (1953). How to Know the Spiders. Pictured key nature series (1st ed.). Dubuque, IA: W.C. Brown Co. OCLC 681432632.
External links
[edit] Data related to Cyclosa conica at Wikispecies
Data related to Cyclosa conica at Wikispecies Media related to Cyclosa conica at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Cyclosa conica at Wikimedia Commons