
In geomorphology, drainage systems, also known as river systems, are the patterns formed by the streams, rivers, and lakes in a particular drainage basin. They are governed by the topography of land, whether a particular region is dominated by hard or soft rocks, and the gradient of the land. Geomorphologists and hydrologists often view streams as part of drainage basins (and sub-basins). This is the topographic region from which a stream receives runoff, throughflow, and its saturated equivalent, groundwater flow. The number, size, and shape of the drainage basins varies and the larger and more detailed the topographic map, the more information is available.[1]
Drainage patterns
[edit]Per the lie of channels, drainage systems can fall into one of several categories, known as drainage patterns. These depend on the topography and geology of the land.[2]
All forms of transitions can occur between parallel, dendritic, and trellis patterns.
Accordant versus discordant drainage patterns
[edit]A drainage system is described as accordant if its pattern correlates to the structure and relief of the landscape over which it flows.[2]
A discordant system or pattern does not correlate to the topography and geology of the area. Discordant drainage patterns are classified into two main types: antecedent and superimposed,[2] while ante position drainage patterns combine the two. In antecedent drainage, a river's vertical incision ability matches that of land uplift due to tectonic forces. Superimposed drainage develops differently: initially, a drainage system develops on a surface composed of 'younger' rocks, but due to denudation activities this surface of younger rocks is removed and the river continues to flow over a seemingly new surface, but one in fact made up of rocks of old geological formation.
Dendritic drainage pattern
[edit]
Dendritic drainage systems (from Greek δενδρίτης, dendrites, "of or like a tree") are not straight and are the most common form of the drainage system. In this, there are many sub-tributaries (analogous to the twigs of a tree), which merge into tributaries of the main river (the branches and the trunk of the tree, respectively). They are seen to feed a river channel that matches and is strongly accordant to the overriding gradient of the land. Truly dendritic systems form in V-shaped valleys; as a result, the rock types must be impervious and non-porous.[3]
Parallel drainage pattern
[edit]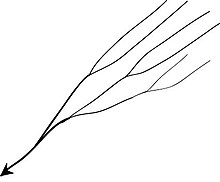
A parallel drainage system occurs on elongate landforms like outcropping resistant rock bands), typically following natural faults or erosion (such as prevailing wind scars). The watercourses run swift and straight, with very few tributaries, and all flow in the same direction. This system forms on very long, uniform slopes, for instance, high rivers flowing southeast from the Aberdare Mountains in Kenya and many rivers of Myanmar.
This sometimes indicates a major fault that cuts across an area of steeply folded bedrock.
Trellis drainage pattern
[edit]The geometry of a trellis drainage system is similar to that of a common garden trellis. Along a strike valley, smaller tributaries feed into the steep slopes of mountainsides. These tributaries enter the main river about perpendicular, causing a trellis-like appearance of the system. They form where hard and soft formations exist on both banks of the main river, and are reflective of height, accentuated by erosion. Trellis drainage is characteristic of folded mountains, such as the Appalachian Mountains in North America and in the north part of Trinidad.[2]
Rectangular drainage pattern
[edit]
Rectangular drainage develops on rocks that are of approximately uniform resistance to erosion, but which have two directions of jointing at approximately right angles or 90 degrees. The joints are usually less resistant to erosion than the bulk rock so erosion tends to preferentially open the joints and streams eventually develop along the joints. The result is a stream system in which streams consist mainly of straight line segments with right-angle bends and tributaries join larger streams at right angles.[2] This pattern can be found with the Arun River in Nepal.
Radial drainage pattern
[edit]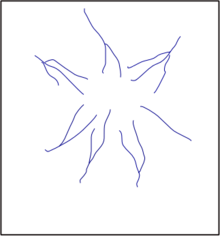

In a radial drainage system, the streams radiate outwards from a central high point. Volcanos usually have archetypal features on which this commonly develops are modest or hard domes pattern develops when streams flow in many general directions (meaning quite long-term)
In India, the Amarkantak range and Ramgarh crater are most archetypal; and Dogu'a Tembien in Ethiopia.[4]
Centripetal drainage pattern
[edit]When the streams converge at a point, which is generally a depression or a basin they form centripetal or inland drainage pattern.
Deranged drainage pattern
[edit]A deranged drainage system is a drainage system in drainage basins where there is no coherent pattern to the rivers and lakes. These can form in areas with extensive limestone deposits, where surface streams can disappear into the groundwater via caves and subterranean drainage routes.[5] They can also form in areas where there has been much geological disruption.
A classic example is the Canadian Shield. During the last ice age, the topsoil was scraped off, leaving mostly bare rock. The melting of the glaciers left land with many irregularities of elevation and a great deal of water to collect in the low points, resulting in the region's many lakes. The drainage basins are young and are still sorting themselves out; eventually the system will stabilize.[1]
Annular drainage pattern
[edit]
In an annular drainage pattern, streams trace a tangential or greater concentric path along a belt of weak rock so, with others, a roughly traced out ring can be seen. It is best displayed by streams draining a maturely dissected structural dome or basin where erosion has exposed rimming sedimentary strata of greatly varying degrees of hardness, as in the Red Valley, which nearly encircles the domal structure of the Black Hills of South Dakota.
Astroblemes and mud diapirs are also thought to be able to cause this kind of drainage pattern.[6]
Angular drainage pattern
[edit]Angular drainage patterns form where bedrock joints and faults intersect at angles other than rectangular drainage patterns. Angles can be more or less than 90 degrees.[7]
Integrated drainage
[edit]An integrated drainage is a mature drainage system characteristic of arid climates. It is formed by coalescing of individual basins formerly separated by high ground, such as mountains or ridges. Headward erosion from a lower basin may breach the barrier, as may spilling over from a higher basin due to aggradation (accumulation of sediments in the basin). The effect of integration of a drainage system is to replace local higher base levels with a single lower base level.[8]
An example of an integrated drainage is the area drained by the Rio Grande River. The sedimentary basins forming the modern Rio Grande Valley were not integrated into a single river system draining into the Gulf of Mexico until relatively recent geologic time. Instead, the basins formed by the opening of the Rio Grande rift were initially bolsons, with no external drainage and a central playa.[9] An axial river existed in the Espanola Basin as early as 13 million years ago, reaching the Santo Domingo Basin by 6.9 million years ago. However, at this time, the river drained into a playa in the southern Albuquerque Basin where it deposited the Popotosa Formation.[10] The upper reach of this river corresponded to the modern Rio Chama, but by 5 million years ago, an ancestral Rio Grande draining the eastern San Juan Mountains had joined the ancestral Rio Chama.[9]
The ancestral Rio Grande progressively integrated basins to the south, reaching the Palomas basin by 4.5 million years ago, the Mesilla basin by 3.1 million years, to Texas by 2.06 million years, and finally joining the Pecos River at 800,000 years to drain into the Gulf of Mexico. Volcanism in the Taos Plateau reduced drainage from the San Luis basin until a spillover event 440,000 years ago that drained Lake Alamosa and fully reintegrated the San Luis basin into the Rio Grande basin.[9]
Integrated drainages were widespread in western North America in the Paleocene and Eocene,[11] and there is evidence of integrated drainages on the surface of Mars.[12]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Pidwirny, M., (2006). "The Drainage Basin Concept". Fundamentals of Physical Geography, 2nd Edition.
- ^ a b c d e "Ritter, Michael E., The Physical Environment: an Introduction to Physical Geography. 2006". Archived from the original on 2017-09-02. Retrieved 2014-07-18.
- ^ Lambert, David (1998). The Field Guide to Geology. Checkmark Books. pp. 130–131. ISBN 0-8160-3823-6.
- ^ Amanuel Zenebe, and colleagues (2019). The Giba, Tanqwa and Tsaliet rivers in the headwaters of the Tekezze basin. In: Geo-trekking in Ethiopia's Tropical Mountains - The Dogu'a Tembien District. SpringerNature. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-04955-3_14. ISBN 978-3-030-04954-6.
- ^ "11 Water – An Introduction to Geology". Retrieved 2022-09-28.
- ^ Colucci, Sabrina; Fidani, Cristiano (2022). "Preliminary geomorphological and hydrographical characterization of a circular structure in the Marche Region (Central Italy) and its possible origin". Géomorphologie. 28 (2): 126–136. doi:10.4000/geomorphologie.17007.
- ^ Easterbrook, Don J (1969). Chapter 7, Origins of Stream Valleys and Drainage Patterns. Principles of Geomorphology. McGraw-Hill Book Company. pp. 148-153. ISBN 0-07-018780-0 (this author defines dendritic, trellis, rectangular, angular, radial, annular, centripetal and parallel drainage patterns)
- ^ Jackson, Julia A., ed. (1997). "Integrated drainage". Glossary of geology (Fourth ed.). Alexandria, Virginia: American Geological Institute. ISBN 0922152349.
- ^ a b c Repasch, Marisa; Karlstrom, Karl; Heizler, Matt; Pecha, Mark (May 2017). "Birth and evolution of the Rio Grande fluvial system in the past 8 Ma: Progressive downward integration and the influence of tectonics, volcanism, and climate". Earth-Science Reviews. 168: 113–164. Bibcode:2017ESRv..168..113R. doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.03.003.
- ^ Koning, Daniel J.; Jochems, Andy P.; Heizler, Matthew T. (2018). "Early Pliocene paleovalley incision during early Rio Grande evolution in southern New Mesico" (PDF). New Mexico Geological Society Field Conference Series. 69: 93–108. Retrieved 20 May 2020.
- ^ Mackey, G. N.; Horton, B. K.; Milliken, K. L. (2012-05-01). "Provenance of the Paleocene-Eocene Wilcox Group, western Gulf of Mexico basin: Evidence for integrated drainage of the southern Laramide Rocky Mountains and Cordilleran arc". Geological Society of America Bulletin. 124 (5–6): 1007–1024. Bibcode:2012GSAB..124.1007M. doi:10.1130/B30458.1.
- ^ Hynek, Brian M.; Phillips, Roger J. (2003). "New data reveal mature, integrated drainage systems on Mars indicative of past precipitation". Geology. 31 (9): 757. Bibcode:2003Geo....31..757H. doi:10.1130/G19607.1.
External links
[edit]| Large-scale features | |
|---|---|
| Alluvial rivers | |
| Bedrock river | |
| Bedforms | |
| Regional processes | |
| Mechanics | |