The Frankish War (428) was a short military conflict between the Frankish people the Salians and the West Roman Empire under Emperor Valentinian III. The protagonists in this conflict were the captain of the Franks' king Clodio and the Roman general Aetius. The war ended in a Roman victory.
Background
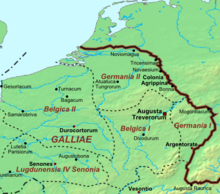
Around 400, the Frankish people consisted of two subgroups, the Salian Franks and the Ripuarian Franks, of which the Salians resided within the Roman Empire as foederati. In the
province Germania Secunda they delivered troops to the Limitanei in charge of guarding the Rhine border. During the crisis in which the Western Empire ended up as a result of the Rhine crossing and the civil war that broke out, they supported the British usurpator Constantine III[2] and after its decline the Gallic usurper Jovinus. The commander-in-Chief of the Western army Constantius III made an end to the civil war and restored central authority in Gaul. He concluded new treaties with the peoples on the Rhine border and thereby restored the bond with Emperor Honorius.
The invasion of the Franks
According to Sulpicius Alexander, Salic Franks were led by regales, little kings. No names of them are handed down from contemporary sources. Chlodio, is the first king that was written about. Taking advantage of the weakening of Roman power caused by the Roman Civil between 427 and 429, he invaded Belgica Secunda in northern Gaul and occupied the territory to the Somme. His armed forces crossed the Charcoal Forest and conquered the cities Tournai, Cambrai and Arras. His raid was successful because the Roman militias deployed against him were defeated or expelled. A real reaction from the Romans was not at first because the commander-in-chief of the Gallic field army had traveled to Ravenna, which is the most plausible reason why the Roman counterattack took some time.
The campaign of Aetius
Finally a Roman army was brought against him under the command of Aetius, the Gallic commander-in-chief , comes et magister militum per Gallias. He was a former general of the deposed emperor Joannes and previously successfully put an end to the rebellion of Theodoric I in 426. When a crisis broke out as a result of the revolt comes Africanae Bonifatius in North-Africa, he stayed in Italy.
Aetius army force and victory
In addition to the Comitatenses, the Gallic field army, Aetius had access to a large section Hun soldiers, who were famous for their skill as ridden archers. It was a logical decision to quickly send the ride army of Aetius to Gaul to stop the advance of the Franks in the far north. Aetius himself led the army against Chlodio and defeated the Salic Franks in 428. He then restored Roman power over part of the territory they had taken possession of. [8]
Sources and interpretation
The story of this war is extremely succinct. Only in three contemporary sources is the conflict mentioned: Philostorgius, Prosper and the Chronica Gallica of 452. Cassiodorus who also reports this war is a later source.[9] Except for the victory Aetius won over Cholodio, the further course of this war is unknown. No place has been reported handed where the fight against the Franks took place or it must have been Vicus Helenae.[10] Notwithstanding that, there is more evidence that the fight at Vicus Helenae took place later. It seems that despite his loss, Chlodio has nevertheless been granted an extension of his sphere of influence by the Romans, for the Salian Franks remained foederati of the empire and would still repeatedly fight for the cause of Rome.