| Ludic | |
|---|---|
| lyydin kiel', l'yyd'ikiel' | |
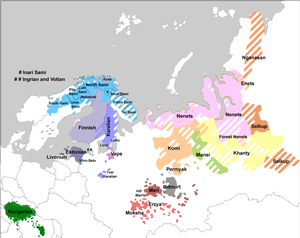
| Native to | Russia (Republic of Karelia) |
| Region | Near northwestern shore of Lake Onega |
Native speakers | 300 (2017)[1] |
| Latin (Karelian alphabet) | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | recognised as minority language in: Republic of Karelia[2] |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | lud |
| Glottolog | ludi1246 |
| ELP | Ludian |
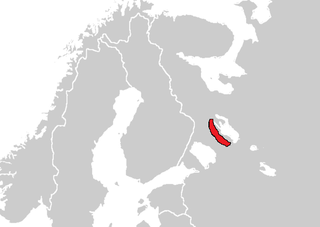 | |
 [image reference needed] Lude is classified as Severely Endangered by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger (2010) | |

Ludic, or Ludian, or Ludic Karelian (Luudi, Lyydi or lüüdi), is a Finnic language in the Uralic language family or a Karelian dialect. It is transitional between the Olonets Karelian language and the Veps language.[1] It is spoken by 300 Karelians in the Republic of Karelia in Russia, near the southwestern shore of Lake Onega, including a few children.[3]