This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: "Middle temporal gyrus" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this template message)
| Middle temporal gyrus | |
|---|---|
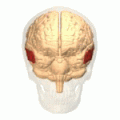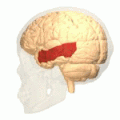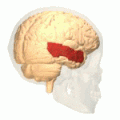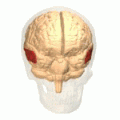
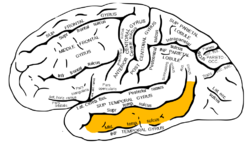 Lateral surface of left cerebral hemisphere, viewed from the side. (Middle temporal gyrus shown in orange.) | |
 Right temporal lobe (shown in green). Middle temporal gyrus is visible at the middle of the green area. | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Temporal lobe |
| Artery | Middle cerebra and Posterior cerebral |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Gyrus temporalis medius |
| NeuroNames | 137 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1653 |
| TA98 | A14.1.09.146 |
| TA2 | 5495 |
| FMA | 61906 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
Middle temporal gyrus is a gyrus in the brain on the temporal lobe. It is located between the superior temporal gyrus and inferior temporal gyrus. It corresponds largely to Brodmann area 21.
The middle temporal gyrus is bounded by:
- the superior temporal sulcus above;
- the inferior temporal sulcus below;
- an imaginary line drawn from the preoccipital notch to the lateral sulcus posteriorly.
It has been connected with processes as different as contemplating distance, recognition of known faces, audio-visual emotional recognition,[1] and accessing word meaning while reading.[2] Some studies indicate that lesions of the posterior region of the middle temporal gyrus, in the left cerebral hemisphere, may result in alexia and agraphia for kanji characters (characters of Chinese origin used in Japanese writing).[3] The left middle temporal gyrus is also activated during poem composition.[4]