Chemical compound
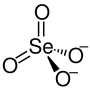
Nickel(II) selenate is a selenate of nickel with the chemical formula NiSeO4.
Preparation
Nickel(II) selenate can be produced by the reaction of nickel(II) carbonate and selenic acid.[4]

Properties
Nickel(II) selenate hexahydrate is a green solid.[1] It is tetragonal, space group P41212 (No. 92).[5] At 100 °C, nickel(II) selenate hexahydrate slowly loses water to the tetrahydrate, with space group P21/n (No. 14). At 510 °C, nickel(II) selenate decomposes directly into nickel selenite, which on further heating decomposes into nickel oxide and selenium dioxide.[6][2]
![{\displaystyle \mathrm {NiSeO_{4}\cdot 6H_{2}O\ {\xrightarrow[{-H_{2}O}]{100\,^{\circ }C))\ NiSeO_{4}\cdot 4H_{2}O\ {\xrightarrow[{-H_{2}O}]{300\,^{\circ }C))\ NiSeO_{4}\cdot H_{2}O\ {\xrightarrow[{-H_{2}O}]{390\,^{\circ }C))\ NiSeO_{4}\ {\xrightarrow[{-O_{2))]{510\,^{\circ }C))\ NiSeO_{3}\ {\xrightarrow[{-SeO_{2))]{690\,^{\circ }C))\ NiO} }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/4843a32541acbe56eb0f3968004c9a2a5ab74627)
It and potassium selenate are cooled and crystallized in hot aqueous solution to obtain the blue-green [Ni(H2O)6](SeO4)2.[7]
_{2)) }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/be3bdfe8bf1b42fa6a72f7973b3ca988ef509b9f)

![{\displaystyle \mathrm {NiSeO_{4}\cdot 6H_{2}O\ {\xrightarrow[{-H_{2}O}]{100\,^{\circ }C))\ NiSeO_{4}\cdot 4H_{2}O\ {\xrightarrow[{-H_{2}O}]{300\,^{\circ }C))\ NiSeO_{4}\cdot H_{2}O\ {\xrightarrow[{-H_{2}O}]{390\,^{\circ }C))\ NiSeO_{4}\ {\xrightarrow[{-O_{2))]{510\,^{\circ }C))\ NiSeO_{3}\ {\xrightarrow[{-SeO_{2))]{690\,^{\circ }C))\ NiO} }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/4843a32541acbe56eb0f3968004c9a2a5ab74627)
_{2)) }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/be3bdfe8bf1b42fa6a72f7973b3ca988ef509b9f)