Puget Sound region | |
|---|---|
| Country | United States |
| State | Washington |
| Core cities | Seattle Tacoma Bellevue Everett |
| Highest elevation | 14,411 ft (4,392 m) |
| Lowest elevation | 0 ft (0 m) |
| Time zone | UTC−08:00 (Pacific) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−07:00 (PDT) |
| Area codes | 206, 253, 360, 425, 564 |

The Puget Sound region is a coastal area of the Pacific Northwest in the U.S. state of Washington, including Puget Sound, the Puget Sound lowlands, and the surrounding region roughly west of the Cascade Range and east of the Olympic Mountains. It is characterized by a complex array of saltwater bays, islands, and peninsulas carved out by prehistoric glaciers.
Poet Robert Sund called the Puget Sound region "Ish River country", owing to its numerous rivers with names ending in "ish", such as the Duwamish, Samish, Sammamish, Skokomish, Skykomish, Snohomish, and the Stillaguamish.[1] The ish ending is from Salishan languages and means "people of".[2]

The Puget Sound region was formed by the collision and attachment of many terranes ("microcontinents") to the North American Plate between about 50 to 10 million years ago.[3] About 15,000 years ago during the Vashon Glaciation, the Puget Sound region was covered by a lobe of the Cordilleran Ice Sheet. The glacier that covered the area was about 3,000 feet (900 m) thick within the vicinity of Seattle.[4] By the time Captain George Vancouver found the Sound in 1792, early native people had already been there for over 5,000 years.
Logging started as early as 1853. In the 1880s logging railroads cut their way into Puget Sound. 1886 the St. Helens fire burned 300,000 acres (1,200 km2). Mount Rainier National Park started in 1899. The 1902 Yacolt Burn burned 600,000 acres (2,400 km2). Olympic National Park was established in 1938.[5]
George Vancouver explored Puget sound in 1792. Vancouver claimed it for Great Britain on June 4, 1792, naming it for one of his officers, Lieutenant Peter Puget. It became part of the Oregon Country, and became U.S. territory when the 1846 Oregon Treaty was signed.
After arriving along the Oregon Trail, many settlers wandered north to what is now Washington and settled the Puget Sound area. The first non-indigenous settlement was New Market (now known as Tumwater) in 1846. In 1853 Washington Territory was formed from part of Oregon Territory. In 1888 the Northern Pacific railroad line reached Puget Sound, linking the region to eastern states.
For a long period Tacoma was noted for its large smelters where gold, silver, copper and lead ores were treated. Seattle was the primary port for trade with Alaska and the rest of the country and for a time possessed a large shipbuilding industry. The region around eastern Puget Sound developed heavy industry during the period including World War I and World War II, and the Boeing Company became established in the area.
During World War II the Puget Sound area became a focus for the war industry, with Boeing producing many of the nation's heavy bombers and the ports of Seattle, Bremerton and Tacoma available for shipbuilding. The most important yards in the Sound during World War II were Seattle-Tacoma Shipbuilding's Seattle and Tacoma yards, also known as Todd Pacific, Todd Seattle and Todd Tacoma and the Puget Sound Navy Yard. They produced a significant portion of destroyers and escort carriers. Smaller operations included Winslow, Associated Shipbuilders and the Lake Washington Shipyard.
Since 1995, Puget Sound has been recognized as an American Viticultural Area by the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau.[6]
|
Main article: Seattle metropolitan area |
The urban region designated the Puget Sound Region is centered on Seattle and consists of nine counties, two urban center cities and four satellite cities making up what has been dubbed "Pugetopolis."[7] Both urban core cities have large industrial areas and seaports plus a high-rise central business district. The satellite cities are primarily suburban, featuring a small downtown core and a small industrial area or port. The suburbs consist mostly of residences, strip malls, and shopping centers. The region is also home to numerous ports. The two largest and busiest are the Port of Seattle and Port of Tacoma, which, if combined, comprise the third largest container port in North America after Los Angeles/Long Beach and New York/New Jersey.[8]
As defined by the U.S. Census Bureau and the Office of Management and Budget, the Seattle metropolitan area is officially the Seattle–Tacoma–Bellevue, WA metropolitan statistical area (MSA) and consists of:[9][10]
Based on commuting patterns, the adjacent metropolitan areas of Olympia, Bremerton, and Mount Vernon, along with a few smaller satellite urban areas, are grouped together in a wider labor market region known as the Seattle–Tacoma combined statistical area (CSA), which encompasses most of the Puget Sound region.[10][11] The population of this wider region is 4,269,349—almost two-thirds of Washington's population—as of 2012[update].[12] The Seattle CSA is the 12th largest CSA, and the 13th largest primary census statistical area in the country. The additional metropolitan and micropolitan areas included are:[10]
A state-run ferry system, Washington State Ferries, connects the larger islands to the Washington mainland, as well as both sides of the sound, allowing cars and people to move about the greater Puget Sound region.
The region has a Csb (warm summer mediterranean) climate with some areas in the far east (western foothills of the Cascades) having an oceanic (Cfb) climate when the 30 millimetres (1.2 in) isotherm is used. The wet season is from October to April and is due to the Aleutian Low coming in from the northwest, and variation in winter rain from year to year is mostly due to variation in the strength of the Aleutian Low (strong = dry and weak = wet). The dry season (May-Sep) is caused by a subtropical high moving north from California. The driest part of the region is in the rain shadow of the Olympic Mountains around Sequim and Whidbey Island, receiving 40-75 cm of precipitation per year. The wettest part is in the foothills of both the Cascade and the Olympic Mts, and on the west side of the Sound, receiving 125-1000+ cm of precipitation per year.[13][14]
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Record high °F (°C) | 67 (19) |
70 (21) |
79 (26) |
89 (32) |
93 (34) |
108 (42) |
103 (39) |
99 (37) |
98 (37) |
89 (32) |
74 (23) |
66 (19) |
108 (42) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 57.0 (13.9) |
59.1 (15.1) |
66.4 (19.1) |
74.3 (23.5) |
81.9 (27.7) |
85.8 (29.9) |
91.2 (32.9) |
89.9 (32.2) |
84.1 (28.9) |
72.0 (22.2) |
61.6 (16.4) |
56.8 (13.8) |
94.1 (34.5) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 48.0 (8.9) |
50.3 (10.2) |
54.2 (12.3) |
59.3 (15.2) |
66.3 (19.1) |
71.1 (21.7) |
77.4 (25.2) |
77.6 (25.3) |
71.6 (22.0) |
60.5 (15.8) |
52.1 (11.2) |
47.0 (8.3) |
61.3 (16.3) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 42.8 (6.0) |
44.0 (6.7) |
47.1 (8.4) |
51.3 (10.7) |
57.5 (14.2) |
62.0 (16.7) |
67.1 (19.5) |
67.4 (19.7) |
62.6 (17.0) |
53.8 (12.1) |
46.5 (8.1) |
42.0 (5.6) |
53.7 (12.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 37.7 (3.2) |
37.7 (3.2) |
39.9 (4.4) |
43.3 (6.3) |
48.7 (9.3) |
53.0 (11.7) |
56.8 (13.8) |
57.2 (14.0) |
53.6 (12.0) |
47.0 (8.3) |
40.9 (4.9) |
37.1 (2.8) |
46.1 (7.8) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 26.1 (−3.3) |
27.3 (−2.6) |
31.3 (−0.4) |
35.6 (2.0) |
40.6 (4.8) |
46.6 (8.1) |
51.5 (10.8) |
51.7 (10.9) |
45.8 (7.7) |
36.8 (2.7) |
29.2 (−1.6) |
25.4 (−3.7) |
21.5 (−5.8) |
| Record low °F (°C) | 0 (−18) |
1 (−17) |
11 (−12) |
29 (−2) |
28 (−2) |
38 (3) |
43 (6) |
44 (7) |
35 (2) |
28 (−2) |
6 (−14) |
6 (−14) |
0 (−18) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 5.78 (147) |
3.76 (96) |
4.17 (106) |
3.18 (81) |
1.88 (48) |
1.45 (37) |
0.60 (15) |
0.97 (25) |
1.61 (41) |
3.91 (99) |
6.31 (160) |
5.72 (145) |
39.34 (999) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 1.8 (4.6) |
2.2 (5.6) |
0.4 (1.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.2 (0.51) |
1.7 (4.3) |
6.3 (16) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 18.7 | 15.9 | 17.1 | 15.0 | 11.3 | 9.2 | 4.7 | 4.9 | 8.3 | 14.3 | 18.4 | 18.4 | 156.2 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 1.4 | 1.2 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 1.5 | 4.7 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 78.0 | 75.2 | 73.6 | 71.4 | 68.9 | 67.1 | 65.4 | 68.2 | 73.2 | 78.6 | 79.8 | 80.1 | 73.3 |
| Average dew point °F (°C) | 33.1 (0.6) |
35.1 (1.7) |
36.3 (2.4) |
38.8 (3.8) |
43.5 (6.4) |
48.2 (9.0) |
51.4 (10.8) |
52.7 (11.5) |
50.2 (10.1) |
45.1 (7.3) |
38.8 (3.8) |
34.3 (1.3) |
42.3 (5.7) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 69.8 | 108.8 | 178.4 | 207.3 | 253.7 | 268.4 | 312.0 | 281.4 | 221.7 | 142.6 | 72.7 | 52.9 | 2,169.7 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 25 | 38 | 48 | 51 | 54 | 56 | 65 | 64 | 59 | 42 | 26 | 20 | 49 |
| Average ultraviolet index | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| Source 1: NOAA (relative humidity, dew point and sun 1961–1990)[16][17][18] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Weather Atlas (UV)[19] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Olympia Regional Airport, Washington (1991−2020 normals, extremes 1948−present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 64 (18) |
73 (23) |
79 (26) |
88 (31) |
96 (36) |
110 (43) |
104 (40) |
104 (40) |
98 (37) |
90 (32) |
74 (23) |
64 (18) |
110 (43) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 56.3 (13.5) |
59.4 (15.2) |
67.9 (19.9) |
76.2 (24.6) |
83.9 (28.8) |
87.9 (31.1) |
93.6 (34.2) |
92.2 (33.4) |
86.3 (30.2) |
73.7 (23.2) |
61.5 (16.4) |
55.5 (13.1) |
96.0 (35.6) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 46.0 (7.8) |
49.1 (9.5) |
53.7 (12.1) |
58.9 (14.9) |
66.1 (18.9) |
70.8 (21.6) |
77.6 (25.3) |
78.0 (25.6) |
72.1 (22.3) |
60.2 (15.7) |
50.6 (10.3) |
44.9 (7.2) |
60.7 (15.9) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 39.6 (4.2) |
40.7 (4.8) |
44.1 (6.7) |
48.2 (9.0) |
54.5 (12.5) |
59.1 (15.1) |
64.2 (17.9) |
64.2 (17.9) |
59.1 (15.1) |
50.3 (10.2) |
43.2 (6.2) |
38.9 (3.8) |
50.5 (10.3) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 33.2 (0.7) |
32.3 (0.2) |
34.5 (1.4) |
37.5 (3.1) |
43.0 (6.1) |
47.4 (8.6) |
50.7 (10.4) |
50.5 (10.3) |
46.2 (7.9) |
40.5 (4.7) |
35.8 (2.1) |
32.8 (0.4) |
40.4 (4.7) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 18.8 (−7.3) |
19.0 (−7.2) |
23.9 (−4.5) |
27.5 (−2.5) |
32.3 (0.2) |
38.4 (3.6) |
42.7 (5.9) |
41.9 (5.5) |
35.9 (2.2) |
27.9 (−2.3) |
21.6 (−5.8) |
18.4 (−7.6) |
12.6 (−10.8) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −8 (−22) |
−1 (−18) |
9 (−13) |
23 (−5) |
25 (−4) |
30 (−1) |
35 (2) |
33 (1) |
25 (−4) |
14 (−10) |
−1 (−18) |
−7 (−22) |
−8 (−22) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 7.80 (198) |
5.09 (129) |
5.68 (144) |
3.67 (93) |
2.26 (57) |
1.46 (37) |
0.53 (13) |
0.96 (24) |
2.04 (52) |
5.07 (129) |
8.21 (209) |
7.85 (199) |
50.62 (1,286) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 2.0 (5.1) |
0.6 (1.5) |
0.1 (0.25) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
1.2 (3.0) |
3.9 (9.9) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 20.3 | 16.4 | 18.8 | 16.3 | 11.4 | 8.5 | 4.0 | 4.8 | 8.1 | 15.1 | 19.5 | 20.2 | 163.4 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 2.2 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 87.5 | 84.5 | 80.0 | 75.6 | 72.9 | 72.4 | 70.8 | 72.1 | 77.6 | 85.1 | 88.4 | 89.1 | 79.7 |
| Average dew point °F (°C) | 34.5 (1.4) |
36.0 (2.2) |
36.9 (2.7) |
39.2 (4.0) |
43.9 (6.6) |
48.9 (9.4) |
52.0 (11.1) |
52.7 (11.5) |
49.6 (9.8) |
44.8 (7.1) |
39.6 (4.2) |
35.4 (1.9) |
42.8 (6.0) |
| Source 1: NOAA (dew points and relative humidity 1961–1990)[20][21] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: National Weather Service[22] | |||||||||||||

North Pacific Oak Woodland is one of the principal plant associations of the Puget Trough, where many of the soils are well drained mesic.[23]
|
Further information: Puget Sound § Flora and fauna |
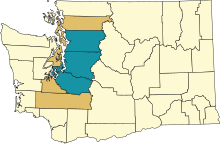
Counties of the Puget Sound region:
In addition, the San Juan Islands (all of San Juan County plus a few islands belonging to Whatcom County) are often considered part of the greater Puget Sound area.[citation needed]
Prominent islands:
Urban centers:
Satellite cities:
Other principal cities:
Military bases: