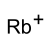 rubidium ion
| |
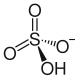 hydrogen sulfate ion
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.036.029 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| RbHSO4 | |
| Molar mass | 182,54 g/mol−1 |
| Appearance | Crystals with no colour[1] |
| Density | 2.89 g·cm−3 |
| Melting point | 214 °C (417 °F; 487 K)[2] |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations
|
rubidium oxide rubidium hydroxide |
Related compounds
|
rubidium sulfate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Rubidium hydrogen sulfate, sometimes referred to as rubidium bisulfate, is the half neutralized rubidium salt of sulfuric acid. It has the formula RbHSO4.


