 The SpartaDOS X DIR command | |
| Developer(s) | DEC, DR, Intel, Cromemco, MetaComCo, Microsoft, IBM, Datalight, ICD, Inc. |
|---|---|
| Operating system | CP/M, MP/M, ISIS-II, iRMX 86, CDOS, TRIPOS, DOS, MSX-DOS, SISNE plus, 4690 OS, PC-MOS, OS/2, Windows, Singularity, ReactOS, AROS, VMS, RT-11, RSX-11, OS/8 |
| Platform | Cross-platform |
| Type | Command |
| License | CP/M, MP/M: BSD-like MS-DOS: MIT PC-MOS: GPL-3.0-only ReactOS: GPL |
In computing, dir (directory) is a command in various computer operating systems used for computer file and directory listing.[1] It is one of the basic commands to help navigate the file system. The command is usually implemented as an internal command in the command-line interpreter (shell). On some systems, a more graphical representation of the directory structure can be displayed using the tree command.
Implementations
[edit]
The command is available in the command-line interface (CLI) of the operating systems Digital Research CP/M,[2] MP/M,[3] Intel ISIS-II,[4] iRMX 86,[5] Cromemco CDOS,[6] MetaComCo TRIPOS,[7] DOS, IBM/Toshiba 4690 OS,[8] IBM OS/2,[9] Microsoft Windows,[10] Singularity, Datalight ROM-DOS,[11] ReactOS,[12] GNU,[13] AROS[14] and in the DCL command-line interface used on DEC VMS, RT-11 and RSX-11. It is also supplied with OS/8 as a CUSP (Commonly-Used System Program).
The dir command is supported by Tim Paterson's SCP 86-DOS.[15] On MS-DOS, the command is available in versions 1 and later.[16] It is also available in the open source MS-DOS emulator DOSBox. MS-DOS prompts "Abort, Retry, Fail?" after being commanded to list a directory with no diskette in the drive.
The numerical computing environments MATLAB and GNU Octave include a dir
function with similar functionality.[17][18]
Examples
[edit]
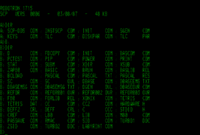

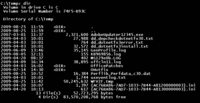
DOS, Windows, ReactOS
[edit]List all files and directories in the current working directory.
C:\Users>dir
List any text files and batch files (filename extension ".txt" or ".bat").
C:\Users>dir *.txt *.bat
Recursively list all files and directories in the specified directory and any subdirectories, in wide format, pausing after each screen of output. The directory name is enclosed in double-quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted is as two separate command-line options because it contains a whitespace character.
C:\Users>dir /s /w /p "C:\Users\johndoe\My Documents"
List any NTFS junction points:
C:\Users>dir /ashVolume in drive C is OS.Volume Serial Number is xxxx-xxxxDirectory of C:\Users12/07/2019 02:30 AM <SYMLINKD> All Users [C:\ProgramData]12/07/2019 02:30 AM <JUNCTION> Default User [C:\Users\Default]12/07/2019 02:12 AM 174 desktop.ini1 File(s) 174 bytes2 Dir(s) 332,659,789,824 bytes free
Unices
[edit]dir is not a Unix command; Unix has the analogous ls command instead. The GNU operating system, however, has a dir command that "is equivalent to ls -C -b; that is, by default files are listed in columns, sorted vertically, and special characters are represented by backslash escape sequences".[19] Actually, for compatibility reasons, ls produces device-dependent output. The dir instruction, unlike ls -Cb, produces device-independent output.
See also
[edit]- Directory (OpenVMS command)
- List of DOS commands
- ls (corresponding command for *nix systems)
References
[edit]- ^ Rügheimer, Hannes; Spanik, Christian (October 22, 1988). AmigaDOS quick reference. Grand Rapids, Mi : Abacus. ISBN 9781557550491 – via Internet Archive.
- ^ "Operating manual" (PDF). cpm.z80.de. Retrieved 2019-10-22.
- ^ Digital Research (1981-09-25). MP/M-86 Operating System - User's Guide (PDF) (1 ed.). Pacific Grove, CA, USA: Digital Research. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-01-04. Retrieved 2017-01-04.
- ^ ISIS II Users Guide
- ^ iRMX 86 INTRODUCTION AND OPERATOR'S REFERENCE MANUAL For Release 6
- ^ CDOS USER'S MANUAL
- ^ "Introduction to Tripos" (PDF). Retrieved 2019-10-22.
- ^ [1][dead link]
- ^ "JaTomes Help - OS/2 Commands". www.jatomes.com. Archived from the original on 2019-04-14. Retrieved 2019-07-20.
- ^ "MS-DOS and Windows command line dir command". www.computerhope.com.
- ^ "Datalight ROM-DOS User's Guide" (PDF). www.datalight.com.
- ^ "GitHub - reactos/reactos: A free Windows-compatible Operating System". October 22, 2019 – via GitHub.
- ^ "GNU Coreutils Manual". Free Software Foundation.
- ^ "AROS Research Operating System". aros.sourceforge.net.
- ^ 86-DOS - Disk Operating System for the 8086 - User's Manual (PDF). Version 0.3 (Preliminary ed.). Seattle, Washington, USA: Seattle Computer Products, Inc. 1980. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2019-07-14. Retrieved 2019-07-14. (59 pages)
- ^ Wolverton, Van (2003). Running MS-DOS Version 6.22 (20th Anniversary Edition), 6th Revised edition. Microsoft Press. ISBN 0-7356-1812-7.
- ^ "List folder contents - MATLAB dir". www.mathworks.com.
- ^ "Function Reference: dir". octave.sourceforge.io.
- ^ dir invocation (GNU coreutils) at www.gnu.org
Further reading
[edit]- Wolverton, Van (1990). MS-DOS Commands: Microsoft Quick Reference, 4th Revised edition. Microsoft Press. ISBN 978-1556152894.
- Kathy Ivens; Brian Proffit (1993). OS/2 Inside & Out. Osborne McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0078818714.
- Frisch, Æleen (2001). Windows 2000 Commands Pocket Reference. O'Reilly. ISBN 978-0-596-00148-3.
External links
[edit]- dir | Microsoft Docs
- Open source DIR implementation that comes with MS-DOS v2.0
- Dir command syntax and examples
| File system navigation | |
|---|---|
| File management | |
| Archiving | |
| Disk management | |
| Processes | |
| Registry | |
| User environment | |
| File contents | |
| Scripting | |
| Networking | |
| Maintenance and care | |
| Boot management | |
| Software development | |
| Miscellaneous | |