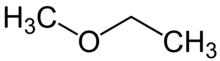
| |

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methoxyethane[1] | |
| Other names
ethyl methyl ether
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.128.000 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H8O | |
| Molar mass | 60.096 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless gas[2] |
| Density | 0.7251 g cm−3 (at 0 °C)[2] |
| Melting point | −113 °C (−171 °F; 160 K) |
| Boiling point | 7.4 °C (45.3 °F; 280.5 K) |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.3420 (at 4 °C)[2] |
| Viscosity | 0.224 cP at 25 °C |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Extremely Flammable (F+), Liquefied gas |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Related Ethers
|
Dimethyl ether Diethyl ether Methoxypropane |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Methoxyethane, also known as ethyl methyl ether, is a colorless gaseous ether with the formula CH3OCH2CH3. Unlike the related dimethyl ether and diethyl ether, which are widely used and studied, this mixed alkyl ether has no current applications. It is a structural isomer of isopropyl alcohol. Its utility as an anesthetic[3] and solvent[4] have been investigated.
