Samarium(III) perchlorate
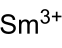   
|
| Identifiers
|
|
|
|
| Properties
|
|
|
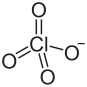
Cl3O12Sm
|
| Molar mass
|
448.70 g·mol−1
|
| Appearance
|
white solid[1]
pale yellow crystals[2]
|
|
|
soluble in water and ethanol[2]
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). |
Chemical compound
Samarium(III) perchlorate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Sm(ClO4)3.
Preparation
Samarium(III) perchlorate can be obtained by the reaction of perchloric acid and samarium(III) oxide.[3] The hydrate precipitated from the solution can be dehydrated with dichlorine hexoxide to obtain the anhydrous form.[1]
Properties
Anhydrous samarium perchlorate forms hexagonal crystals, space group P63/m, unit cell parameters a=9.259 Å, c=5.746 Å, Z=2.[4] It reacts with ammonium thiocyanate and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium thiocyanate ([BMIM]SCN) in absolute ethanol to obtain the ionic liquid [BMIM]4[Sm(NCS)7(H2O)].[5]


