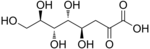
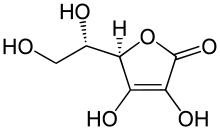
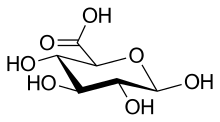
In organic chemistry, a sugar acid or acidic sugar is a monosaccharide with a carboxyl group at one end or both ends of its chain.[1]
Main classes of sugar acids include:
- Aldonic acids, in which the aldehyde group (−CH=O) located at the initial end (position 1) of an aldose is oxidized.
- Ulosonic acids, in which the hydroxymethyl group (−CH2OH) at the initial end of a 2-ketose is oxidized creating an α-ketoacid.
- Uronic acids, in which the −CH2OH group at the terminal end of an aldose or ketose is oxidized.
- Aldaric acids, in which both ends (−CH=O and −CH2OH) of an aldose are oxidized.
 |
 |
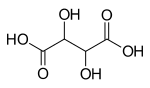 |