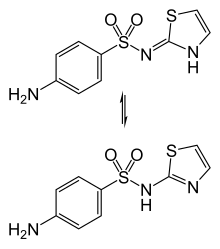
 Imino (top) and amino (bottom) tautomers | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.701 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H9N3O2S2 |
| Molar mass | 255.31 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 202 to 202.5 °C (395.6 to 396.5 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Sulfathiazole is an organosulfur compound used as a short-acting sulfa drug.[1] Formerly, it was a common oral and topical antimicrobial, until less toxic alternatives were discovered.[2]
Sulfathiazole exists in various forms (polymorphs). The imine tautomer is dominant in solid samples.[3]