| Timeline of the 1972 Atlantic hurricane season | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Season summary map | |||||
| Season boundaries | |||||
| First system formed | May 23, 1972 | ||||
| Last system dissipated | November 7, 1972 | ||||
| Strongest system | |||||
| Name | Betty (Bravo) | ||||
| Maximum winds | 105 mph (165 km/h) (1-minute sustained) | ||||
| Lowest pressure | 976 mbar (hPa; 28.82 inHg) | ||||
| Longest lasting system | |||||
| Name | Betty (Bravo) | ||||
| Duration | 10 days | ||||
| |||||
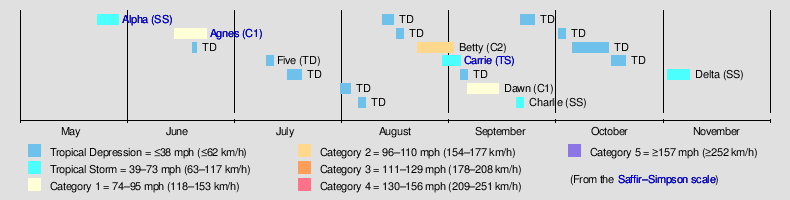
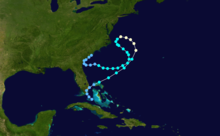
The 1972 Atlantic hurricane season was a cycle of the annual tropical cyclone season in the Atlantic Ocean in the Northern Hemisphere. It was a significantly below average season,[nb 1] having only four fully tropical named storms, the fewest since 1930.[2] It was one of only five Atlantic hurricane seasons since 1944 to have no major hurricanes,[nb 2] the others being 1968, 1986, 1994, and 2013. The season officially began on June 1, 1972 and ended on November 30, 1972. These dates, adopted by convention, historically describe the period in each year when most tropical systems form.[4] However, storm formation is possible at any time of the year, as demonstrated in 1972 by the formation of Subtropical Storm Alpha on May 23. The season's final storm, Subtropical Storm Delta, dissipated on November 7.
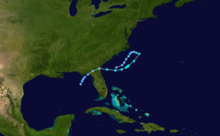
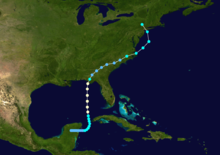
The season produced nineteen tropical or subtropical cyclones, of which seven intensified into tropical or subtropical storms; three became hurricanes, of which only but only one, Betty, had sustained winds greater than minimum hurricane force. Despite its relative inactivity, the 1972 season resulted in one of the worst natural disasters in American history, Hurricane Agnes. Agnes was a weak but large storm that initially made landfall on the Florida Panhandle before moving up the eastern United States. The hurricane killed 122 people and caused $2.1 billion (1972 USD) in damage, mostly due to flooding in Pennsylvania and New York.[2]
This timeline documents tropical cyclone formations, strengthening, weakening, landfalls, extratropical transitions, and dissipations during the season. It includes information that was not released throughout the season, meaning that data from post-storm reviews by the National Hurricane Center, such as a storm that was not initially warned upon, has been included.
By convention, meteorologists use one time zone when issuing forecasts and making observations: Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), and also use the 24-hour clock (where 00:00 = midnight UTC).[5] In this time line, all information is listed by UTC first with the respective local time included in parentheses.