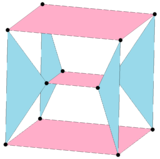
Uniform 3-4 duoprisms 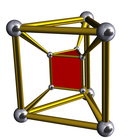 Schlegel diagrams | |
|---|---|
| Type | Prismatic uniform polychoron |
| Schläfli symbol | {3}×{4} |
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagram | |
| Cells | 3 square prisms, 4 triangular prisms |
| Faces | 3+12 squares, 4 triangles |
| Edges | 24 |
| Vertices | 12 |
| Vertex figure |  Digonal disphenoid |
| Symmetry | [3,2,4], order 48 |
| Dual | 3-4 duopyramid |
| Properties | convex, vertex-uniform |
In geometry of 4 dimensions, a 3-4 duoprism, the second smallest p-q duoprism, is a 4-polytope resulting from the Cartesian product of a triangle and a square.
The 3-4 duoprism exists in some of the uniform 5-polytopes in the B5 family.