| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
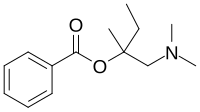
| IUPAC name
[1-(Dimethylamino)-2-methylbutan-2-yl] benzoate
| |
| Other names
Stovaine; Benzoic acid [1-(dimethylaminomethyl)-1-methylpropyl] ester
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.375 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H21NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 235.327 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Amylocaine was the first synthetic local anesthetic. It was synthesized and patented under the name Stovaine by Ernest Fourneau at the Pasteur Institute in 1903.[1] It was used mostly in spinal anesthesia.[2]
