 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Consumer Drug Information |
| MedlinePlus | a682022 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth (tablets) |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 3–9 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.514 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
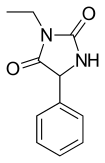
| Formula | C11H12N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 204.229 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Ethotoin (previously marketed as Peganone) is an anticonvulsant drug used in the treatment of epilepsy.[1] It is a hydantoin, similar to phenytoin. It is not available in the United States.
Mechanism of action
[edit]The mechanism of action of ethotoin is similar to that of phenytoin.[citation needed]
Approval history
[edit]- 1957 Peganone was granted Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval to Abbott Laboratories for treatment of grand mal (tonic clonic) and partial complex (psychomotor) seizures.
- 2003 Peganone was acquired from Abbott Laboratories by Ovation Pharmaceuticals (specialty pharmaceutical company who acquire underpromoted branded pharmaceutical products).
- 2018 It was announced by Recordati Rare Diseases Inc. that due to a combination of low product demand and complex manufacturing difficulties, product manufacturing, distribution and sale was being discontinued.
Indications and usage
[edit]Ethotoin is indicated for tonic-clonic and partial complex seizures.[2]
Dosing
[edit]Ethotoin is available in 250 mg tablets.[3][4] It is taken orally in 4 to 6 divided doses per day, preferably after food.
Side effects
[edit]Side effects include ataxia, visual disturbances, rash, and gastrointestinal problems.[citation needed]
Chemistry
[edit]Ethotoin is synthesized by the reaction of benzaldehyde oxynitrile (2) with urea or ammonium bicarbonate, which forms an intermediate urea derivative (3) which on acidic conditions cyclizes to 5-phenylhydantoin (4).[5] Alkylation of this product using ethyl iodide leads to the formation of ethotoin (5).
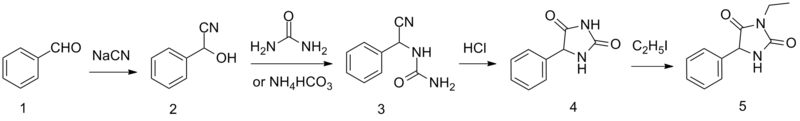
Synthesis of ethotoin
References
[edit]- ^ Schwade ED, Richards RK, Everett GM (May 1956). "Peganone, a new antiepileptic drug". Dis Nerv Syst. 17 (5): 155–8. PMID 13317788.
- ^ Shorvon, S.D.; Fish, David R.; Perucca, Emilio; Dodson, W. Edwin, eds. (2004). The Treatment of Epilepsy. Blackwell Publishing. ISBN 0-632-06046-8.
- ^ "Ethotoin". drugs.com.
- ^ "PEGANONE 250 mg Ethotoin Tablets, USP" (PDF).
- ^ A. Pinner, Chem. Ber., 21, 2324 (1888); W.J. Close, U.S. patent 2,793,157 (1946)
| GABAergics | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Channel modulators | |||||
| Others |
| ||||
| |||||