In the medieval history of Europe, Bulgaria's status as the Bulgarian Empire (Bulgarian: Българско царство, Balgarsko tsarstvo [ˈbəlɡɐrskʊ ˈt͡sarstvʊ]), wherein it acted as a key regional power (particularly rivaling Byzantium in Southeastern Europe[1]) occurred in two distinct periods: between the seventh and eleventh centuries, and again between the twelfth and fourteenth centuries. The two "Bulgarian Empires" are not treated as separate entities, but rather as one state restored after a short period as a self-governing theme with the Eastern Roman Empire.
First Bulgarian Empire
The First Bulgarian Empire was established as a result of an expansion of Old Great Bulgaria to the territory south of Danube River, and is usually described as having lasted between 632 and 1018, when it was subjugated by the Byzantine Empire and Kievan Rus' despite Samuel's fierce resistance. It gradually reached its cultural and territorial apogee in the 9th century and early 10th century under Boris I and Simeon the Great, when it developed into the cultural and literary centre of Slavic Europe, as well as one of the largest states in Europe.
Second Bulgarian Empire
The medieval Bulgarian state was restored as the Second Bulgarian Empire after a successful uprising of two nobles from Tarnovo, Asen and Peter, in 1185, and existed until it was conquered during the Ottoman invasion of the Balkans in the late 14th century, with the date of its subjugation usually given as 1396 or 1422. Under Ivan Asen II in the first half of the 13th century it gradually recovered much of its former power, though this did not last long due to internal problems and foreign invasions.
Maps
-
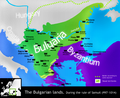
The First Bulgarian Empire's greatest territorial extent during the reign of Tsar Simeon[2]
-
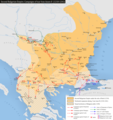
Map of Bulgaria in its largest extension during Samuel's reign
-
The Bulgarian Empire during the reign of Ivan Asen II
-
The Second Bulgarian Empire circa 1340
See also
References
- ^ "War in the Balkans, 1991-2002 - R. Craig Nation - Google Books". Books.google.com. Retrieved 2012-06-28.
- ^ Map of late 9th century eastern central Europe
Further reading
- Zlatarski, Vasil N. (1918). Medieval History of the Bulgarian State (in Bulgarian). Sofia: Science and Arts Publishers, 2nd Edition (Petar Petrov, Ed.), Zahari Stoyanov Publishers, 4th Edition, 2006. ISBN [[Special:BookSources/954-736-628-4 |954-736-628-4 [[Category:Articles with invalid ISBNs]]]].
((cite book)): Check|isbn=value: invalid character (help) - Бакалов, Георги (2003). Електронна издание – История на България (in Bulgarian). София: Труд, Сирма. ISBN 954528613X.
((cite book)): Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Делев, Петър (2006). История и цивилизация за 11. клас (in Bulgarian). Труд, Сирма.
((cite book)): Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Българите и България (in Bulgarian). Министерство на външните работи на България, Труд, Сирма. 2005.
- Fine, Jr., John V.A. (1991). The Early Medieval Balkans. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press. ISBN 978-0-472-08149-3.
| Ancient (Colonies) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Post-classical |
| ||
| Modern |
| ||
| Lists | |||
| Miscellaneous |
| ||
![The First Bulgarian Empire's greatest territorial extent during the reign of Tsar Simeon[2]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/ee/Bulgaria_Simeon_I_%28893-927%29.svg/120px-Bulgaria_Simeon_I_%28893-927%29.svg.png)