
In organic chemistry, an allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula −CH2−HC=CH2. It consists of a methylene bridge (−CH2−) attached to a vinyl group (−CH=CH2).[1][2] The name is derived from the scientific name for garlic, Allium sativum. In 1844, Theodor Wertheim isolated an allyl derivative from garlic oil and named it "Schwefelallyl".[3][4] The term allyl applies to many compounds related to H2C=CH−CH2, some of which are of practical or of everyday importance, for example, allyl chloride.
Allylation is any chemical reaction that adds an allyl group to a substrate.[1]
Nomenclature
[edit]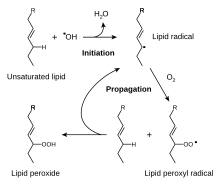
A site adjacent to the unsaturated carbon atom is called the allylic position or allylic site. A group attached at this site is sometimes described as allylic. Thus, CH2=CHCH2OH "has an allylic hydroxyl group". Allylic C−H bonds are about 15% weaker than the C−H bonds in ordinary sp3 carbon centers and are thus more reactive.
Benzylic and allylic are related in terms of structure, bond strength, and reactivity. Other reactions that tend to occur with allylic compounds are allylic oxidations, ene reactions, and the Tsuji–Trost reaction. Benzylic groups are related to allyl groups; both show enhanced reactivity.
Pentadienyl group
[edit]A CH2 group connected to two vinyl groups is said to be doubly allylic. The bond dissociation energy of C−H bonds on a doubly allylic centre is about 10% less than the bond dissociation energy of a C−H bond that is singly allylic. The weakened C−H bonds is reflected in the easy oxidation of compounds containing 1,4-pentadiene (C=C−CH2−C=C) linkages. Some polyunsaturated fatty acids feature this pentadiene group: linoleic acid, α-linolenic acid, and arachidonic acid. They are susceptible to a range of reactions with oxygen (O2), starting with lipid peroxidation. Products include fatty acid hydroperoxides, epoxy-hydroxy polyunsaturated fatty acids, jasmonates, divinylether fatty acids, and leaf aldehydes. Some of these derivatives are signallng molecules, some are used in plant defense (antifeedants), some are precursors to other metabolites that are used by the plant.[5]
One practical consequence of their high reactivity is that polyunsaturated fatty acids have poor shelf life owing to their tendency toward autoxidation, leading, in the case of edibles, to rancidification. Metals accelerate the degradation. These fats tend to polymerize, forming semisolids. This reactivity pattern is fundamental to the film-forming behavior of the "drying oils", which are components of oil paints and varnishes.

Homoallylic
[edit]The term homoallylic refers to the position on a carbon skeleton next to an allylic position. In but-3-enyl chloride CH2=CHCH2CH2Cl, the chloride is homoallylic because it is bonded to the homoallylic site.

Bonding
[edit]The allyl group is widely encountered in organic chemistry.[1] Allylic radicals, anions, and cations are often discussed as intermediates in reactions. All feature three contiguous sp²-hybridized carbon centers and all derive stability from resonance.[6] Each species can be presented by two resonance structures with the charge or unpaired electron distributed at both 1,3 positions.

Resonance structure of the allyl anion. The cation is identical, but carries an opposite-sign charge.[7]
In terms of MO theory, the MO diagram has three molecular orbitals: the first one bonding, the second one non-bonding, and the higher energy orbital is antibonding.[2]

MO diagram for allyl π orbitals. In the radical (shown), the intermediate Ψ2 orbital is singly occupied; in the cation, unoccupied; and in the anion, full.
Reactions and applications
[edit]This heightened reactivity of allylic groups has many practical consequences. The sulfur vulcanization or various rubbers exploits the conversion of allylic CH2 groups into CH−Sx−CH crosslinks. Similarly drying oils such as linseed oil crosslink via oxygenation of allylic (or doubly allylic) sites. This crosslinking underpins the properties of paints and the spoilage of foods by rancidification.
The industrial production of acrylonitrile by ammoxidation of propene exploits the easy oxidation of the allylic C−H centers:
An estimated 800,000 tonnes (1997) of allyl chloride is produced by the chlorination of propylene:
It is the precursor to allyl alcohol and epichlorohydrin.
Allylation
[edit]Allylation is the attachment of an allyl group to a substrate, usually another organic compound. Classically, allylation involves the reaction of a carbanion with allyl chloride. Alternatives include carbonyl allylation with allylmetallic reagents, such as allyltrimethylsilane,[9][10][11] or the iridium-catalyzed Krische allylation.
Allylation can be effected also by conjugate addition: the addition of an allyl group to the beta-position of an enone. The Hosomi-Sakurai reaction is a common method for conjugate allylation.[12]
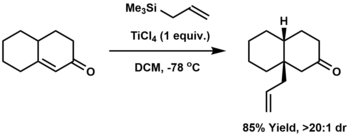
Oxidation
[edit]Allylic C-H bonds are susceptible to oxidation.[13] One commercial application of allylic oxidation is the synthesis of nootkatone, the fragrance of grapefruit, from valencene, a more abundantly available sesquiterpenoid:[14]

In the synthesis of some fine chemicals, selenium dioxide is used to convert alkenes to allylic alcohols:[15]
- R2C=CR'-CHR"2 + [O] → R2C=CR'-C(OH)R"2
where R, R', R" may be alkyl or aryl substituents.
From the industrial perspective, oxidation of benzylic C-H bonds are conducted on a particularly large scale, e.g. production of terephthalic acid, benzoic acid, and cumene hydroperoxide.[16]
Allyl compounds
[edit]Many substituents can be attached to the allyl group to give stable compounds. Commercially important allyl compounds include:
- Crotyl alcohol (CH3CH=CH−CH2OH)
- Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate, central in the biosynthesis of terpenes, a precursor to many natural products, including natural rubber.
- Transition-metal allyl complexes, such as allylpalladium chloride dimer
See also
[edit]- Allylic strain
- Carroll rearrangement
- Allylic palladium complex
- Tsuji–Trost reaction
- Propargylic/Homopropargylic
- Benzylic
- Vinylic
- Acetylenic
- Naloxone
- Allylic rearrangement
References
[edit]- ^ a b c Jerry March, "Advanced Organic Chemistry" 4th Ed. J. Wiley and Sons, 1992: New York. ISBN 0-471-60180-2.
- ^ a b Morrison, Robert Thornton; Boyd, Robert Neilson (1987). Organic Chemistry (4th ed.). Allyn and Bacon.
- ^ Theodor Wertheim (1844). "Untersuchung des Knoblauchöls". Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie. 51 (3): 289–315. doi:10.1002/jlac.18440510302.
- ^ Eric Block (2010). Garlic and Other Alliums: The Lore and the Science. Royal Society of Chemistry. ISBN 978-0-85404-190-9.
- ^ Feussner, Ivo; Wasternack, Claus (2002). "The Lipoxygenase Pathway". Annual Review of Plant Biology. 53: 275–297. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.53.100301.135248. PMID 12221977.
- ^ Organic Chemistry John McMurry 2nd ed. 1988
- ^ Richey, Herman G. (1970). "The properties of alkene carbonium ions and carbanions". In Zabicky, Jacob (ed.). The Chemistry of Alkenes. The Chemistry of Functional Groups. Vol. 2. London: Interscience / William Clowes & Sons. pp. 56–57. ISBN 0471980501. LCCN 64-25218.
- ^ Nogi, Keisuke; Yorimitsu, Hideki (2021). "Carbon–Carbon Bond Cleavage at Allylic Positions: Retro-allylation and Deallylation". Chemical Reviews. 121 (1): 345–364. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c00157. PMID 32396335. S2CID 218617434.
- ^ Yus, Miguel; González-Gómez, José C.; Foubelo, Francisco (2013). "Diastereoselective Allylation of Carbonyl Compounds and Imines: Application to the Synthesis of Natural Products". Chemical Reviews. 113 (7): 5595–5698. doi:10.1021/cr400008h. hdl:10045/38276. PMID 23540914.
- ^ Weaver, Jimmie D.; Recio, Antonio; Grenning, Alexander J.; Tunge, Jon A. (2011). "Transition Metal-Catalyzed Decarboxylative Allylation and Benzylation Reactions". Chemical Reviews. 111 (3): 1846–1913. doi:10.1021/cr1002744. PMC 3116714. PMID 21235271.
- ^ Yus, Miguel; González-Gómez, José C.; Foubelo, Francisco (2011). "Catalytic Enantioselective Allylation of Carbonyl Compounds and Imines". Chemical Reviews. 111 (12): 7774–7854. doi:10.1021/cr1004474. PMID 21923136.
- ^ Sakurai Hideki; Hosomi Akira; Hayashi Josabro (1984). "Conjugate Allylation of α,β-Unsaturated Ketones with Allylsilanes: 4-Phenyl-6-Hepten-2-one". Organic Syntheses. 62: 86. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.062.0086.
- ^ Maison, Wolfgang; Weidmann, Verena (2013). "Allylic Oxidations of Olefins to Enones". Synthesis. 45 (16): 2201–2221. doi:10.1055/s-0033-1338491. S2CID 196767407.
- ^ Horn, Evan J.; Rosen, Brandon R.; Chen, Yong; Tang, Jiaze; Chen, Ke; Eastgate, Martin D.; Baran, Phil S. (2016). "Scalable and sustainable electrochemical allylic C–H oxidation". Nature. 533 (7601): 77–81. Bibcode:2016Natur.533...77H. doi:10.1038/nature17431. PMC 4860034. PMID 27096371.
- ^ Hoekstra, William J.; Fairlamb, Ian J. S.; Giroux, Simon; Chen, Yuzhong (2017). "Selenium(IV) Oxide". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. pp. 1–12. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rs008.pub3. ISBN 978-0-470-84289-8.
- ^ Recupero, Francesco; Punta, Carlo (2007). "Free Radical Functionalization of Organic Compounds Catalyzed by N- Hydroxyphthalimide". Chemical Reviews. 107 (9): 3800–3842. doi:10.1021/cr040170k. PMID 17848093.
| Hydrocarbons (only C and H) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Only carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (only C, H and O) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Only one element, not being carbon, hydrogen, or oxygen (one element, not C, H or O) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Other | |||||||||||||||

