
This is a list of the modern equipment in the Georgian Defence Forces.

This is a list of the modern equipment in the Georgian Defence Forces.
| Weapon | Photo | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jericho 941[1] | 
|
Large usage within army.[citation needed] | |
| Glock 17 Glock 19 Gen 4 Glock 21 Glock 18 |

|
Sidearm of the special operations forces. | |
| CZ 75[2] | 
|
||
| SIG Sauer P226[2] | 
|
||
| Heckler & Koch USP[3] | 
|
||
| SPP-1M | 
|
In limited use with special operations forces.[citation needed] |
| Weapon | Photo | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benelli M4[4] | In use with special operation forces. |
| Weapon | Photo | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heckler & Koch MP5 Heckler & Koch MP5SD Heckler & Koch MP5K[5] |

|
In use with special operations forces. |
| Weapon | Photo | Origins | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| AKS-74U[6] | 
|
Used by various units as a personal defense weapon. | |
| M4A1[7] M4A1 SOPMOD[8] M4A2[6] M4A3[6] |

|
Main service weapon of the Georgian military.[9][10] |
| Weapon | Photo | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| AKM AKMS[11] |

|
Former service rifle. Some used by Territorial Defence Forces. | |
| PM md. 63/65[12] | 
|
Issued mainly for exercises in Romania. | |
| AIMS-74[13] | 
|
||
| AK-74[6] AKS-74[11] |
 |
Former main service rifle. Standard issue rifle of Reserve and Territorial Defence Forces. | |
| AR-M1[6][14] | 3500 5.45 AR-M1 rifles imported | ||
| AMD-65[15][16] | 
|
1186 rifles were delivered in 2008 | |
| AS Val[17] | Limited number in service with special operations forces. |
| Weapon | Photo | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Designated marksman rifles | |||
| IMI Galatz[18] | 
|
Standard issue designated marksman rifle | |
| VSS Vintorez | 
|
In use with special operations forces. | |
| SVD | 
|
Former standard issue designated marksman rifle, used by the Territorial Defense Forces. | |
| Bolt action | |||
| Desert Tech SRS | 
|
Medium-long range sniper rifle | |
| M24 Sniper Weapon System[6] | 
|
Medium-long range sniper rifle | |
| Sako TRG-22/42[19] | Long range sniper rifle | ||
| Brügger & Thomet APR[2] | 
|
Medium-long range sniper rifle | |
| Weapon | Photo | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bolt action | |||
| Barrett M95 | 
|
Used by special operations forces.[20] | |
| McMillan Tac-50[21] | Issued mainly to special operations forces.[22] | ||
| Zastava M93 Black Arrow | 
|
In service with the land forces.[23] | |
| Semi-automatic | |||
| Barrett M82[24] | 
|
Used by special operations forces. | |
| Weapon | Photo | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light machine guns | |||
| M249[25] | 
|
Standard issue squad automatic weapon.[26] 600 SAWs received in 2020.[27] | |
| IMI Negev[28] | 
|
Standard issue squad automatic weapon. | |
| RPK[6] | 
|
Former standard issue squad automatic weapon. Currently standard issue of Georgian Reserve and Territorial Defence Forces. | |
| General-purpose machine guns | |||
| M240[29] | 
|
New standard issue general-purpose machine gun, gradually replacing the PK machine gun.[30] | |
| PK machine gun PKM[11] |

|
Standard issue general-purpose machine gun, phasing out. | |
| Heavy machine guns | |||
| M2HB[31] | 
|
Acquired in 2021 from the United States.[32] | |
| DShK/DShKM[6] | 
|
Standard issue heavy machine gun, mounted on T-55 tanks, Otokar Cobra and some on Humvees. | |
| NSV machine gun[6] | 
|
Standard issue heavy machine gun, used on T-72 tanks and Didgori-1 APC. Some also used in ground support and Anti-air roles. | |
| Rotary machine guns | |||
| M134 Minigun[33][34][6] | 
|
Support role, air and ground vehicles[35] | |
| Weapon | Photo | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Belt-fed automatic grenade launchers | |||
| AGS-17 | 
|
||
| MK 19 | 
|
Acquired in 2021 from the United States.[32] | |
| Weapon | Photo | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 
|
Fragmentation grenade | |
| RGD-5 | 
|
Fragmentation grenade | |
| RGN | 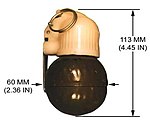
|
Offensive grenade | |
| RGO | 
|
Defensive grenade | |
| M84 | 
|
Stun grenade | |
| AN M18 | 
|
Smoke grenade |
| Weapon | Photo | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| MON-50[36] | 
|
Directional anti-personnel mine. | |
| POMZ-2 | Stake mounted anti-personnel fragmentation mine. | ||
| M18 Claymore mine | 
|
Directional anti-personnel mine. |
| Weapon | Photo | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD-7[37] | 
|
Off-route mine | |
| TM-62 series of mines[6] | 
|
Anti-tank blast mine | |
| TM-57 mine | 
|
Anti-tank blast mine |
| Weapon | Photo | Origin | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reusable grenade launcher | ||||
| RPG-7G[38] | 
|
Based on RPG-7. Lighter, life expectancy increased to 1000 rounds, Compatible with all types of RPG-7 rounds. | ||
| RPG-7 | 
|
Standard issue anti-tank grenade launcher | ||
| Single-shot grenade launcher | ||||
| C90[39] | 
|
Acquired in 2023 | ||
| PDM-1[40][41] | 
|
Domestically produced RPG-26 variant | ||
| RPG-26[6] | 
|
|||
| RPG-22[6] | 
|
|||
| RPG-18[6] | 
|
|||
| M80 Zolja | 
|
|||
| AT4 | 
|
Used in training exercises and by special operations forces | ||
| Recoilless gun | ||||
| SPG-9 recoilless rifle | 
|
|||
| Flamethrower | ||||
| RPO-A Shmel[42] | 
|
|||
| Weapon | Photo | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| MANPATS | |||
| 9K111 Fagot[43] | 
|
Designated AT-4 Spigot by NATO | |
| 9M113 Konkurs[43] | 
|
Designated AT-5 Spandrel by NATO. | |
| 9K115 Metis[43] | 
|
Designated AT-7 Spriggan by NATO. | |
| Skif[44][45][46] | 
|
||
| FGM-148 Javelin | 
|
72 CLUs, 10 basic skills trainers and 410 missiles delivered in 2018–2019 from the United States.[47][48] Contracts were signed in 2020 for the production and delivery of missiles to Georgia in the future.[49] The sale of further 46 CLU's and 82 missiles was approved by the US in 2021.[50] | |
| Vehicle-launched anti-tank guided missiles | |||
| 9K114 Shturm | 
|
Used on Mi-24 gunships. 758 missiles delivered in 2006 from Kazakhstan[48] | |
| Kombat | 
|
Used by T-72 tanks, several hundred missiles in service[48] | |
| Vehicle | Photo | Origin | Versions | Number | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 120MM | |||||
| M75 | 
|
120 mm | 35[43] | Delivers 12 rounds per minute within a firing radius of max 6,4 km. Crew 5 | |
| 2B11 | 
|
120 mm | 14[43] | Delivers 15 rounds per minute within a firing radius of max 7,18 km. Crew 5 | |
| GM-120[51] | 
|
120 mm | 250 | Delivers 15 rounds per minute within a firing radius of min 480 m to max 7,1 km. Crew 5 | |
| Soltam K6 | 
|
120 mm | 135[43] | Delivers 16 rounds per minute within a firing radius of max 7,24 km. Crew 4 | |
| 82MM | |||||
| GM-82[52] | 
|
82 mm | N/A | Firing radius of min 400 m to max 3,05 km. Crew 4 | |
| 2B14 Podnos | 
|
82 mm | N/A | Firing radius of 4 km. Crew 4 | |
| M69 Mortar | 
|
82 mm | 25 | Firing radius of 4 km. Crew 4 | |
| Infantry mortars | |||||
| GNM-60 "Mkudro"[53] | 
|
60 mm | N/A | Noise reduced close fire support mortar for concealed operations. Delivers 30 rounds per minute within a firing radius of 500 m. Crew: 1 | |
| M224 Handheld | 
|
60 mm | N/A | Delivers 20-30 rounds per minute within a firing radius of 1.3 km. Crew: 1-3 | |
| M57 mortar | 
|
60 mm | 50[54] | Delivers 25-30 rounds per minute within a firing radius of 2.5 km. Crew: 3 | |
| GM-60 GM-60LB[55] |

|
60 mm | N/A | GM-60: Delivers 15 rounds per minute within a firing radius of 3 km. Crew: 3 GM-60LB: Delivers 15 rounds per minute within a firing radius of 4.05 km. Crew: 3 | |
| Hirtenberger M6C-210[31] | 
|
60 mm | N/A | Delivers 15-30 rounds per minute within a firing radius of 3 km. Crew: 3 | |
| Vehicle | Image | Origin | Role | Number | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main battle tanks | |||||
| T-72SIM1 T-72B T-72AVT |

|
Main battle tank | 155[57] (before 2008)
≈145 Unknown amount in storage estimated 45-65 [43] |
5 bought from Bulgaria, 55 from Czechia, 5 from Russia, 90 from Ukraine. [58] Upgraded T-72 Sim-1 variants in service which was upgraded in Georgia with the assistance of Israel. Has upgraded armor, GPS navigation systems, thermal vision, target acquisition system, and tactical combat map with friend-or-foe recognition system. | |
| T-55AM2 | 
|
Main battle tank | 120[57] | 120 T-55AM-2's, and some T-54 were delivered from Czechia between 2000 and 2001. Most are in storage And museums.[59] | |
| Infantry fighting vehicles | |||||
| BMP-1 BMP-1U |

|
Infantry fighting vehicle | BMP-1- 57
BMP-1U - 65 [57] |
14 BMP-1U captured by Russia in 2008.Slowly fading[citation needed] | |
| BMP-2 | 
|
Infantry fighting vehicle | 109[57] | Purchased from Ukraine in 2004-2005. Upgraded with NATO standard communication equipment.[citation needed] | |
| Armoured personnel carriers | |||||
| BTR-80 | 
|
Armoured personnel carrier | 95[57] | ||
| BTR-70 | 
|
Armoured personnel carrier | 70
35 in storage [57] |
Including upgraded BTR-70Di's Equipped with "Zaslon" active protection system and new Euro II 276 hp diesel engine from Iveco.[citation needed] | |
| MT-LB | 
|
Armoured tracked vehicle | 88[43] | Including medical evacuation and variants with mounted ZU-23-2 anti-air artillery Many turned into ground artillery.[citation needed] | |
| Wolf Armoured Vehicle | 
|
Armoured personnel carrier | 21[57] | Armed with PK machine gun or grenade launcher, used mainly by military police and some regular units.[citation needed] | |
| Nurol Ejder[43] | 
|
Armoured personnel carrier | 173[57] | Armed with a remote controlled automatic grenade launcher system or a remote MG. 30 more in storage. 60 on order[citation needed] | |
| MRAP | |||||
| Cougar HE | 
|
MRAP | 10[43] | 10 delivered as aid in 2014 from the United States.Plans to purchase 20 more in 2024 [48] | |
| MaxxPro[60] | 
|
MRAP | 25 | Delivered as aid from the United States.Plans to purchase 30 more from United states in 2024 pla[48] | |
| BMC Vuran | 
|
MRAP | 46 on order.[61] | ||
| Infantry mobility and scout vehicles | |||||
| Didgori-1 | 
|
Infantry mobility vehicle | ? | More on order.[62] | |
| Didgori-2[42][63] |    
|
Infantry mobility vehicle | 90 | At least 90 Didgoris of various modification acquired in 2020-2023. Around 50 being produced for 2024.[62]
Variants: | |
| BRDM-2 | 
|
Scout car | 57 | All existing BRDM-2s have been upgraded by STC DELTA. Upgrade includes remote weapon platform, 23×152mm 2A14 auto canon. Additional windshields or hatches have been added as well as two side doors in replacement for the rear door. The bottom side armor has been V-shaped for better protection against mines. Improved frontal armor and smoke grenade dischargers on each side. Periscopes were replaced by digital displays connected to multiple multi-imaging devices for driver and gunner.[citation needed] | |
| Otokar Cobra | 
|
Infantry mobility vehicle | ~400 | Included with two variants. First one armed with a coaxial machine gun and other with an automatic grenade launcher. Reinforcable with additional weapon platforms, such as anti tank systems.[citation needed] | |
| Humvee[64] | 
|
Light utility vehicle | ~800+ | Bought from the United States, used by regular units and military police.around 100 in storage[citation needed] | |
| Military engineering vehicles | |||||
| IMR-2[6] | 
|
Heavy combat engineering vehicle | N/A | ||
| MT-55 | 
|
Armoured vehicle-launched bridge | N/A | ||
| MTU-20[6] | 
|
Armoured vehicle-launched bridge | N/A | ||
| TMM-3 | 
|
Truck-launched bridge | N/A | ||
| UR-77 | 
|
Demining vehicle | N/A | ||
| BTS-5[6] | 
|
Armoured recovery vehicle | N/A | ||
| GMZ-2 | 
|
Combat engineering vehicle | N/A | ||
| BAT-2[6] | 
|
Combat engineering vehicle | N/A | ||
| PMZ-2[6] | 
|
Trencher | N/A | ||
| Vehicle | Image | Origin | Role | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Logistic and transport trucks | ||||
| MAZ-537 | 
|
Heavy military truck | Used for transporting heavy equipment. | |
| Kamaz | 
|
Military truck | Used for various roles. | |
| Ural-375 | 
|
Military truck | Used for supplies transport, also used as launch platform for BM-21 Grad. | |
| Tatra 813 | 
|
Military truck | Used as platform for RM-70 multiple launch rocket system and SpGH DANA. | |
| Unimog | 
|
Military truck | Used in limited numbers.[citation needed] | |
| MAN TG-range | 
|
Military truck | Over 300 MAN TG-range and Iveco Trakker purchased in 2021.[65] | |
| Mercedes-Benz Actros | 
|
Military truck | Used as launch platform for LAR-160 multiple launch rocket system.[citation needed] | |
| Rheinmetall MAN Military Vehicles | 
|
Military truck | Used by engineering brigade.[citation needed] | |
| Iveco Trakker | 
|
Military truck | Over 300 MAN TG-range and Iveco Trakker purchased in 2021.[65] | |
| Roman | 
|
Military truck | Used as launch platform for SPYDER surface-to-air missile.[citation needed] | |
| KrAZ-6322 | 
|
Military truck | Used in troop and supplies transport role, also used as basis for RS-122 multiple launch rocket system. Main logistic truck of the Georgian Army.[citation needed] | |
| M35A2/A3 | Military truck | Used for troop transport. | ||
| Light truck and vehicles | ||||
| Iveco Daily | 
|
Light van | Mobile refrigerator.[66] | |
| Toyota Corolla | 
|
Light car | Used by military police.[citation needed] | |
| Toyota Hilux | 
|
Pickup truck | Many vehicles in service, used for various roles.[67] | |
| Toyota Land Cruiser | 
|
Pickup truck | Used in logistical roles, some configured as mobile command posts.[67] | |
| Mitsubishi L200 | 
|
Pickup truck | Used by Military Police | |
| Renault Duster | 
|
Light car | Used by Military Police | |
| Hyundai Starex | 
|
Light van | ||
| Land Rover Defender | 
|
Light military truck | Used for various roles. | |
| Ford Transit | 
|
Light commercial van | Mainly used for medical purposes.[68] | |
| Ford Ranger | 
|
Pickup truck | 160 Ford Rangers acquired in 2020 as part of ongoing modernization programs.[69] | |
| Polaris Industries XP 1000 S | All-terrain vehicle | Granted by Germany in 2023[70] | ||
| Engineering vehicles | ||||
| Liebherr LTM 1030-2.1 | 
|
Mobile crane | Granted by Germany in 2023[71] | |
| Unmanned ground vehicles | ||||
| AeroVironment tEODor UGV | 
|
Ordnance disposal robot | Granted by Germany in 2023[72] | |
| AeroVironment telemax EVO | 
|
Ordnance disposal robot | Granted by Germany in 2023[73] | |
| Vehicle | Photo | Origin | Versions | Number | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multiple rocket launcher systems | |||||
| BM-21 Grad | 
|
122 mm | 52 | Range: 20 km | |
| RM-70 | 
|
122 mm | 48[43] | Range: 20 km | |
| LAR-160[44] | 
|
160 mm | 23[43] | Range: 45 km[74] | |
| RS-122 | 
|
122 mm | 10+ | Range: 45 km[75] | |
| Self-propelled artillery | |||||
| 2S1 Gvozdika | 
|
122 mm | 35[43] | ||
| 2S3 Akatsiya | 
|
152 mm | 63[43] | ||
| 2S7 Pion | 
|
203 mm | 6[76] | ||
| 2S19 Msta | 
|
152 mm | 1 | ||
| 152 mm SpGH DANA | 
|
152 mm | 54[57] | ||
| Towed artillery guns | |||||
| 85 mm anti-tank gun D-48[43] | 
|
85 mm | 55[77] | ||
| 122 mm howitzer 2A18 (D-30) | 
|
122 mm | 74[43] | ||
| 152 mm towed gun-howitzer M1955 (D-20) | 
|
152 mm | 22[57] | ||
| 152 mm Msta-B | 
|
152 mm | ~89 [43] | ||
| 152 mm Giatsint-B | 
|
152 mm | 3[43] | ||
| Anti-tank guns | |||||
| MT-12 | 
|
100 mm | 47[43] | ||
| Vehicle | Photo | Origin | Number | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZU-23-2 | 
|
300 | Mostly mounted on MT-LB chassis.[citation needed] | |
| 57 mm AZP S-60 | 
|
20[78] | ||
| Self-propelled anti-aircraft weapon | ||||
| ZSU-23-4[43] | 
|
20 | 5 acquired from the Soviet Union and 15 from Ukraine.[citation needed] | |
| Weapon | Photo | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strela-2M[43] | Designated "SA-7 Grail" by NATO.[citation needed] | ||
| 9K34 Strela-3[43] | Designated "SA-14 Gremlin" by NATO.[citation needed] | ||
| 9K38 Igla[43] | 
|
Designated "SA-16 Gimlet" by NATO.[citation needed] | |
| Grom[43] | 
|
30 launchers and 100+ missiles delivered in 2007.[6][79] | |
| FIM-92 Stinger[43] | 
|
| Vehicle | Photo | Origin | Number | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High to medium air defense | ||||
| Buk-M1[43] | 
|
1 Battery [80] | Medium range (35–50 km) 196 9M38 missiles delivered in 2007–2008 from Ukraine.[48] | |
| Multirole | ||||
| SPYDER[43] | 
|
4 Batteries | Short/medium range (15–35+km) 675 Python-5 missiles delivered in 2008 from Israel.[48] | |
| Short range air defense | ||||
| Osa-AKM | 
|
19[81] | Short range (15 km) Six +eight systems + 48 missiles delivered from Ukraine in 2006–2008.[48] | |
| Mistral ATLAS[82] | 
|
6 | [83] | |
| Vehicle | Photo | Origin | Number | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electronic warfare support measures | ||||
| P-18 radar | 
|
N/A | Very high frequency radar. | |
| 1L117 | 
|
N/A | ||
| Ground Master 403 | 
|
1[84] | High-altitude, long range air defence sensor. | |
| Ground Master 200 | 
|
2[84] | Medium range multi-mission tactical radar. | |
| 36D6-M | 
|
2[79] | Long range radar. | |
| Kolchuga passive sensor | 
|
4[79] | Electronic support measures. | |
| ST-68U(19zh6) | 
|
1[79] | ||
| Vehicle | Photo | Origin | Number | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Combat aircraft | ||||
| Su-25KM "Scorpion" SU-25UB "Frogfoot" |

|
12[85] | Half of a full squadron was restored and painted green.[citation needed] | |
| Trainer / Fighter aircraft | ||||
| L-39[86] | 
|
8[85] | Some in airworthy condition, others being restored[87][88] | |
| Transport aircraft | ||||
| Antonov An-2[89] | 
|
6[90] | Some restored to airworthy condition and painted green.[citation needed] | |
| Antonov An-28[91] | 
|
2[85] | ||
| Tupolev Tu-134[86] | 
|
1[90] | Configured as VIP transport.[90] | |
| Yakovlev Yak-40 | 
|
2[90] | ||
| Attack helicopters | ||||
| Mil Mi-35P "Hind" Mi-24V "Hind-E"/Mi-24P "Hind-F"[80] |

|
9[85] | Being restored to airworthy condition.[92] | |
| Utility helicopters | ||||
| Mi-8MT 'Hip-C' Mil Mi-17 |

|
15[85] | Being restored to airworthy condition. 4 more in storage. Some modernized with jammers and additional sensors.[citation needed] | |
| Mi-14PS "Haze-C" | 
|
2[85] | ||
| Bell UH-1H Iroquois | 
|
12[85] | Some airworthy and painted green.[citation needed] | |
| Unmanned aerial vehicles | ||||
| SWAN III | 
|
N/A | Experimental Project | |
| Elbit Hermes 450[43] | 
|
28 | some lost to Russia Air Defence forces in 2008 | |
| WB Electronics Warmate[93] | 
|
N/A | Loitering munition. Joint Georgian-Polish production started in 2023 and will produce hundreds of drones per year.[94] | |
| WB Electronics FlyEye[95] | 
|
N/A | Reconnaissance drone. Joint Georgian-Polish production started in 2023 and will produce hundreds of drones per year.[96] | |
| Aerostar[48] | 
|
42 | ||
| Elbit Skylark[79] | 
|
~ 35 | ||
| Atlantic I[97][98] | N/A | |||
| Alpha 800 VTOL[99][100] | N/A | |||
| DJI M300 RTK series[101] | 
|
N/A | Deployed as reconnaissance drone and loitering munition. | |
| DJI Mavic 3[102] | 
|
N/A | Deployed as reconnaissance drone and loitering munition. | |
| DJI Mavic 2[103][104] | 
|
N/A | Deployed as reconnaissance drone and loitering munition. | |
| Weapon | Photo | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bombs[48][105] | |||
| FAB-250M | Low-Drag General Purpose (LDGP) bomb (550 lb) | ||
| FAB-500M | 
|
Low-Drag General Purpose (LDGP) bomb (1100 lb) | |
| KAB-500L | 
|
Laser guided bomb | |
| Mark 82 bomb GBU-54 |
Low-Drag General Purpose (LDGP) bomb (500 lb) GPS/INS guided bomb | ||
| Mark 83 bomb GBU-32 |
Low-Drag General Purpose (LDGP) bomb (1000 lb) GPS/INS guided bomb | ||
| Mark 84 bomb GBU-31 |
Low-Drag General Purpose (LDGP) bomb (2000 lb) GPS/INS guided bomb | ||
| Air-to air-missiles[48][105] | |||
| R-60M AA-8 Aphid | 
|
Short-range air-to-air missile | |
| R-73M AA-11 Archer | 
|
Short-range air-to-air missile | |
| Air-to-surface missiles[105] | |||
| Kh-25M Kh-25MT Kh-25MP |

|
Laser guided air-to-surface missile TV guided air-to-surface missile Anti-radiation air-to-surface missile | |
| Kh-29L Kh-29T |

|
Laser guided air-to-surface missile TV guided air-to-surface missile | |
| Rockets[105] | |||
| S-5M | 
|
57 mm rocket | |
| S-8 | 
|
80 mm rocket | |
| S-13 | 
|
122 mm rocket | |
| S-24 | 
|
240 mm rocket | |
| S-25 | 
|
340 mm rocket | |
| Machine guns and autocannons | |||
| Afanasev A-12.7 | Mounted on Mil Mi-24 and Mil Mi-8 helicopters.[citation needed] | ||
| YakB-12.7 machine gun | 
|
Mounted on Mil Mi-24.[citation needed] | |
| Gryazev-Shipunov GSh-30-2 | 
|
Mounted on Mi-24P and Sukhoi Su-25.[citation needed] | |
| M134 Minigun | Used on Bell UH-1 Iroquois and Mil 8 helicopters. UH64[citation needed] | ||
| Name | Photo | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| MultiCam[6] | 
|
Standard issue camouflage, produced domestically. Slightly altered variant. | |
| MARPAT[6] | 
|
Former standard issue camouflage, limited use by now. | |
| U.S. Woodland[6] | 
|
Used partially for recruits and by special operations groups. | |
| Universal Camouflage Pattern | 
|
Mainly used by special operations forces. | |
| Desert Camouflage Uniform | 
|
Used by Georgian contingents in Iraq and Afghanistan. Limited use by special operations forces. | |
| Flecktarn | 
|
Was used by Georgian forces in Kosovo. |
| Name | Photo | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ballistic Helmet DH MK-I | 
|
Standard issue ballistic helmet of the Defense Forces. Provides protection in accordance to NIJ 01.01.04 IIIA (Level IIIA).[106] | |
| Tactical Ballistic Helmet DH MK-II | 
|
Standard issue ballistic helmet of the Defense Forces. Provides protection in accordance to NIJ 01.01.04 IIIA (Level IIIA).[107] | |
| Tactical Ballistic Helmet DH MK-III | 
|
FAST type ballistic helmet issued mainly to special operations forces and reconnaissance units. Provides protection in accordance to NIJ 01.01.04 IIIA (Level IIIA).[108] | |
| Modular Tactical Vest MK-I |  
|
Standard issue body armor of the military. The vest itself can provide protection against small arms fire in accordance to Type IIIA NIJ-Std 0101.06 (Level IIIA) without plates.[109] In the process of being replaced by the MK-V vest and MK-VII series tactical plate carriers. | |
| Modular Tactical Vest Mk-II | 
|
Armored tactical plate carrier used by peacekeeping forces primarily. The carrier itself can protect against small arms fire in accordance to Type IIIA NIJ-Std 0101.06 (Level IIIA) without plates.[110] | |
| Modular Tactical Vest MK-V | 
|
General purpose bullet resistant modular body armor. The vest itself can protect against small arms fire in accordance to Type IIIA NIJ-Std 0101.06 (Level IIIA) without plates.[111] | |
| Modular Plate Carrier Mk-VII mod I | 
|
Armored tactical slab-carry armor used by regular and special operations forces. The carrier itself can protect against small arms fire in accordance to Type IIIA NIJ-Std 0101.06 (Level IIIA) without plates.[112] | |
| Personnel Armor System for Ground Troops[6] | 
|
Former standard issue helmets and vests used in the early 2000s. Helmets were initialy mostly provided by foreign countries. Subsequently a domestic variant was introduced. Eventually the PASGT was replaced by DELTA DH MK-I and DH MK-II ballistic helmets as well as MK-I and MK-II series vests. Some are still in use. | |
| Advanced Combat Helmet | 
|
Formerly used by ground troops and peacekeepers, replaced by DELTA DH MK-I and DH MK-II ballistic helmets. | |
| Interceptor Multi-Threat Body Armor System[6] |  
|
Were issued mainly for peacekeeping operations in Iraq and Afghanistan and also used by engineer troops. Replaced by DELTA MK-I and MK-II series vests. | |
| Eagle Industries Multi Mission Armor Carrier | 
|
Modular plate carrier used by special operations forces.[113][114][115] | |
| NBC suit | 
|
Used for CBRN threats. |