
Ancient Rome had a variety of ships that played crucial roles in its military, trade, and transportation activities.[1] Rome was preceded in the use of the sea by other ancient, seafaring civilizations of the Mediterranean. The galley was a long, narrow, highly maneuverable ship powered by oarsmen, sometimes stacked in multiple levels such as biremes or triremes, and many of which also had sails. Initial efforts of the Romans to construct a war fleet were based on copies of Carthaginian warships. In the Punic wars in the mid-third century BCE, the Romans were at first outclassed by Carthage at sea, but by 256 BCE had drawn even and fought the wars to a stalemate. In 55 BCE Julius Caesar used warships and transport ships to invade Britain. Numerous types of transport ships were used to carry foodstuffs or other trade goods around the Mediterranean, many of which did double duty and were pressed into service as warships or troop transports in time of war.
Introduction
[edit]Terminology
[edit]Roman ships are named in different ways, often in compound expressions with the word navis. These are found in many ancient Roman texts, and named in different ways, such as by the appearance of the ship: for example, navis tecta (covered ship); or by its function, for example: navis mercatoria (commerce ship), or navis praedatoria (plunder ship). Others, like navis frumentaria (grain), navis lapidaria (stones), and navis vivaria (live fish), are about the cargo. The Althiburos mosaic in Tunisia lists many types of ships.[2]
The expression naves longae (lit. "long ships") is the plural of the noun phrase navis longa ("long ship"), following the rules for pluralization of feminine, third declension nouns in Latin, and inflectional agreement of the adjective longus to match.
Scope
[edit]In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilization from the founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BCE to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century CE. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), Roman Republic (509–27 BCE), and Roman Empire (27 BCE–476 CE) until the fall of the western empire.[3]
History
[edit]Punic wars
[edit]The First Punic War between Rome and Carthage began in 264 BC with the Romans landing on Sicily.[4] The Romans had the stronger army, while Carthage had overwhelming maritime superiority.[5] By 260 BC the war had reached a stalemate, as the Carthaginians focused on defending their well-fortified Sicilian towns and cities; these were mostly on the coast and so could be supplied and reinforced without the Romans being able to use their superior army to interdict.[6][7] The focus of the war shifted to the sea, where the Romans had little experience; on the few occasions they had previously felt the need for a naval presence they had usually relied on small squadrons provided by their Latin or Greek allies. Warships of the time were specialised vessels known as galleys and which relied on oars for maneuverability.[5][8][9] The Romans set out to construct a war fleet and used a shipwrecked Carthaginian quinquereme as a blueprint for their own.[10] As novice shipwrights, the Romans built copies that were heavier than the Carthaginian vessels, and so slower and less maneuverable.[11]
There were repeated naval clashes during the rest of the war, including the 256 BC battle of Ecnomus, possibly the largest naval battle in history by the number of combatants involved.[12][13][14] In 241 BC the Romans destroyed the Carthaginian fleet at the Battle of the Aegates Islands,[15][16] forcing the cut-off Carthaginian troops on Sicily to negotiate for peace and ending the war.[17][18] The Romans and Carthaginians now had rough equivalence in terms of naval strength in the western Mediterranean.[19]
Invasions of Britain
[edit]Julius Caesar employed warships and transport ships in order to carry out his invasion of Britain in 55 BCE. He gathered a fleet consisting of eighty transport ships, sufficient to carry two legions (Legio VII and Legio X), and an unknown number of warships under a quaestor, at an unnamed port in the territory of the Morini, almost certainly Portus Itius (Saint-Omer). Another eighteen transports of cavalry were to sail from a different port, probably Ambleteuse.[20] These ships may have been triremes or biremes, or may have been adapted from Venetic designs Caesar had seen previously, or may even have been requisitioned from the Veneti and other coastal tribes.[21]
Battle of Actium
[edit]The Battle of Actium in 31 BC between the forces of Augustus and Mark Antony marked the peak of the Roman fleet arm. After Augustus' victory at Actium, most of the Roman fleet was dismantled and burned. The Roman civil wars were fought mostly by land forces, and from the 160s until the 4th century AD, no major fleet actions were recorded. During this time, most of the galley crews were disbanded or employed for entertainment purposes in mock battles or in handling the sail-like sun-screens in the larger Roman arenas. What fleets remained were treated as auxiliaries of the land forces, and galley crewmen themselves called themselves milites, "soldiers", rather than nautae, "sailors".[22]

The Roman galley fleets were turned into provincial patrol forces that were smaller and relied largely on liburnians, compact biremes with 25 pairs of oars. These were named after an Illyrian tribe known by Romans for their sea roving practices, and these smaller craft were based on, or inspired by, their vessels of choice. The liburnians and other small galleys patrolled the rivers of continental Europe and reached as far as the Baltic, where they were used to fight local uprisings and assist in checking foreign invasions. The Romans maintained numerous bases around the empire: along the rivers of Central Europe, chains of forts along the northern European coasts and the British Isles, Mesopotamia, and North Africa, including Trabzon, Vienna, Belgrade, Dover, Seleucia, and Alexandria. Few actual galley battles in the provinces are found in records. One action in 70 AD at the unspecified location of the "Island of the Batavians" during the Batavian Rebellion was recorded, and included a trireme as the Roman flagship. The last provincial fleet, the classis Britannica, was reduced by the late 200s, though there was a minor upswing under the rule of Constantine (272–337). His rule also saw the last major naval battle of the unified Roman Empire (before the permanent split into Western and Eastern [later "Byzantine"] Empires), the Battle of the Hellespont of 324. Some time after the Battle of the Hellespont, the classical trireme fell out of use, and its design was forgotten.[23]
Types
[edit]
The generic Roman term for an oar-driven galley warship was "long ship" (Latin: navis longa, Greek: naus makra), as opposed to the sail-driven navis oneraria (from onus, oneris: burden), a merchant vessel, or the minor craft (navigia minora) like the scapha.[24]
Merchant vessels
[edit]The city of Rome was heavily reliant on the delivery by ship of the large amounts of grain it consumed. Rome imported about 150,000 tons of Egyptian grain each year over the first three centuries AD. Not only were insufficient amounts available in the agricultural areas around the city, but it was cheaper to transport it substantial distances by sea than short distances by land. It has been estimated that it cost less for a sailing ship of the Roman Empire to carry grain the length of the Mediterranean than to move the same amount 15 miles by road.[25][a]
Merchant ships, such as naves onerariae, had always been pressed into service for military purposes such as for transporting troops to North Africa in the Second Punic war.[27] In 204 BCE, Scipio Africanus ordered the impressment of merchantmen for the invasion of Africa, four hundred ships according to Livy.[28](29.26.3)[b]
Actuaria
[edit]
An actuaria (short form of navis actuaria, "ship that moves"; plural naves actuariae) was a type of merchant galley used primarily for trade and transport throughout the Roman Empire. The actuaria was equipped with sails as well as oars. It was more expensive to operate than merchant sailing ships, and was used where speed and reliability were a priority. It could carry both passengers and wares such as honey, cheese, meat, and even live animals intended for gladiator combat.[29]
Variants of the actuaria were used as troop transports, for example in the invasion of Britain. In 47 BCE, Publius Vatinius equipped actuariae at Brindisi with temporary rams to support Julius Caesar's forces in Illyricum, on the other side of the Adriatic, though these were only suitable to combat smaller enemy vessels.[29] Actuariae were also employed along the major rivers by Germanicus in his campaigns against the Germanic tribes around 16 AD.[30]
Navis oneraria
[edit]Roman naves onerariae could have up to three square-rigged masts. They depended on the wind and could not leave port on oar power alone, where the more maneuverable galleys could. If winds were not favorable, warping or towing were alternatives.[31] There is some evidence from Claudian in De Bello Gildonico that naves onerariae were in use until late antiquity.[32]
Images of two naves onerariae were pictured in an ancient mosaic floor discovered in Lod, Israel in 1996. Despite damage to the floor, students of maritime history have been able to glean a great deal of information from the images. The ships are of the navis oneraria type, a Roman merchant ship typically displacing 80–150 tons, used to carry such commodities as garum and grain from Egypt to Rome.[33]
Transportation
[edit]Corbita
[edit]Corbitae were grain ships going back to the Greeks in the 5th c BCE, with loads of around 150 tons. In the first century BCE, they could haul 1300 tons of grain and liquids; the latter in large amphorae. The hulls of the Roman corbitae were little changed from the Greek design, and were large, with high sides. Steering was provided via twin steering oars which were very adequate to the task, and not inferior to medieval rudders from later centuries. The oars could be boxed in to the hull with reinforced planking for protection.[34][35]
Obelisk ship
[edit]Pliny the Elder described how an obelisk was loaded onto a ship.
For this purpose, a canal was dug from the river Nile to the spot where the obelisk lay; and two broad vessels, laden with blocks of similar stone a foot square, the cargo of each amounting to double the size, and consequently double the weight, of the obelisk, were brought beneath it; the extremities of the obelisk remaining supported by the opposite sides of the canal. The blocks of stone were then removed, and the vessels, being thus gradually lightened, received their burden.[36]
Warships
[edit]Bireme
[edit]
Biremes were typically about 80 feet (24 m) long with a maximum beam width of around 10 feet (3 m).[citation needed] These ships were frequently used by the Romans, as during the second of Caesar's invasions of Britain. The bireme eventually evolved into the trireme. A unit commandant (who was given a tent on the open deck) directed a group of marines. The bireme was also recorded in ancient history on the 8th and early 7th-century BC Assyrian reliefs, where they were used to carry out an amphibious attack on the coast of Elam and the lagoons of the Persian Gulf during the reign of Sennacherib.[37]
Liburna
[edit]A liburna was a type of small galley used for raiding and patrols. Originally utilized by the Liburnians, a pirate tribe from Dalmatia, it later became a staple of the Roman navy.[38]
Originally, the liburna was similar to the ancient Greek penteconter.[39] It had one bench with 25 oars on each side, while in the late Roman Republic, it was equipped with two banks of oars (a bireme), remaining faster, lighter, and more agile than triremes.[39] The liburna design was adopted by the Romans and became a key part of the Roman navy in the second half of the 1st century BCE. Liburnae played a key role in the Battle of Actium in Greece (31 BCE), which saw the establishment of Augustus as the undisputed ruler of the Roman world.[citation needed]
The architecture of the liburna differed from that of the battle triremes, quadriremes and quinqueremes.[39][40] It was 109 ft (33 m) long and 5 m (16 ft) wide with a 1 m (3 ft 3 in) draft. Two rows of oarsmen pulled 18 oars per side. The ship could make up to fourteen knots under sail and more than seven knots under oar power.[41]
After adopting the liburna, the Romans made adaptations to add rams and protection from missiles, in order to improve the ships' use as navy ships. The benefits gained more than made up for the slight loss of speed.[42]
The Romans made use of the liburna particularly within the provinces of the empire, where the ships formed the majority of the fleet,[43][44][45] while it was included in smaller numbers in fleets in Ravenna and Misenum, where a large number of the Illyrians were serving.[citation needed]
Gradually, liburna became a generic term for various types of Roman ships, including cargo vessels in late antiquity. Tacitus and Suetonius used it interchangeably with "battleship." Inscriptions listed it last among classes of battleships: hexeres, penteres, quadrieres, trieres, liburna.[46][c]
Navis lusoria
[edit]
A navis lusoria[d] is a type of a small military vessel of the late Roman Empire that served as a troop transport. It was powered by about thirty soldier-oarsmen and an auxiliary sail. Nimble, graceful, and of shallow draft, such a vessel was used on northern rivers close to the Limes Germanicus, the Germanic borderlands, and thus saw service on the Rhine and the Danube. Roman historian Ammianus Marcellinus mentioned the navis lusoria in his writings,[47][48] but not much was learned about them until the discovery of such boats at Mainz, Germany in 1981–82.[49]
Olaf Höckmann claimed that the Mainz boats are probably lusoriae, and have some architectural similarity with earlier liburnae. The type A Mainz ships 1 and 7 appear to be identical in form to the ships Ammianus Marcellinus described in his reports on 4th century Rhine battle vessels, and which he always referred to as naves lusioriae.[50] Höckmann finds that ships 1, 4, 7, and 9 are likely lusoriae.[50]
Quinqueremes
[edit]Quinqueremes, meaning "five-oared" and indicating that there were five oarsmen per bank of oars, were the first warships the Romans built[51] and provided the workhorse of the Roman fleet throughout the Punic Wars.[52] So ubiquitous was this type of ship that the historian Polybius uses it as a shorthand for "warship" in general.[53] Hexaremes (six oarsmen per bank), quadriremes (four oarsmen per bank) and triremes (three oarsmen per bank) are occasionally mentioned in the sources.[53] A quinquereme carried a crew of 300: 280 oarsmen and 20 deck crew and officers.[54] It would also normally carry a complement of 40 marines – usually soldiers assigned to the ship[55] – if battle was thought to be imminent this would be increased to as many as 120.[56][57]
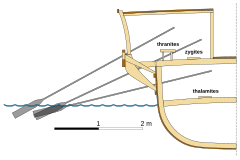
The quinquereme was a galley, c. 45 metres (150 ft) long, c. 5 metres (16 ft) wide at water level, with its deck standing c. 3 metres (10 ft) above the sea, and displacing around 100 tonnes (110 short tons; 100 long tons). Galley expert John Coates suggested that they could maintain 7 kn (8.1 mph; 13 km/h) for extended periods.[58][page needed] The modern replica galley Olympias has achieved speeds of 8.5 kn (9.8 mph; 15.7 km/h) and cruised at 4 knots (4.6 mph; 7.4 km/h) for hours on end.[51] Average speeds of 5–6 knots (5.8–6.9 mph; 9.3–11.1 km/h) were recorded on contemporary voyages of up to a week.[59]
The generally accepted theory regarding the arrangement of oarsmen in quinqueremes is that there would be sets – or files – of three oars, one above the other, with two oarsmen on each of the two uppermost oars and one on the lower, for a total of five oarsmen per file. This would be repeated down the side of a galley for a total of 28 files on each side; thus 28 × 3 × 2 or 168 oars in total.[60]
Getting the oarsmen to row as a unit, let alone to execute more complex battle maneuvers, required long and arduous training.[61] At least half of the oarsmen would need to have had some experience if the ship was to be handled effectively.[62] As a result, the Romans were initially at a disadvantage against the more experienced Carthaginians. To counter this, the Romans introduced the corvus, a bridge 1.2 metres (4 feet) wide and 11 metres (36 feet) long, with a heavy spike on the underside of the free end, which was designed to pierce and anchor into an enemy ship's deck.[56] This allowed Roman legionaries acting as marines to board enemy ships and capture them, rather than employing the previously traditional tactic of ramming.[63]
All warships were equipped with rams. See details at § Ramming.
Trireme
[edit]A trireme was a type of galley with three tiers of oars that was used by the ancient maritime civilizations of the Mediterranean Sea, especially the Phoenicians, ancient Greeks and Romans.[64][65]
Others
[edit]- camarae: a flat-hulled, double ended, low freeboard ship from the eastern Black Sea (1st century CE) with 25 to 30 men; could be rowed in either direction[66]
- cybaea – used in Sicily first century BC[66]
- lembus – a small, fast, and maneuverable, light Illyrian warship, capable of carrying 50 men in addition to the rowers. It was the galley used by Illyrian pirates[67]
- moneres – single-row oared vessels[35]
- phaseli – sailing passenger ferries first centuries BCE and CE[66]
- vectoria - passenger ferry second century CE[66]
- Roman penteconter – the name of the Greek penteconter was not romanized for the Roman version of this ship.[35]
Naval tactics
[edit]Major tactics of naval vessels in combat included physically ramming the enemy boats, brushing alongside with oars retracted to break their oars, or attempting to board them and engage in hand-to-hand combat.
Boarding
[edit]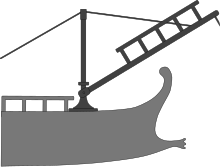
Despite the attempts to counter increasingly heavy ships, ramming tactics were superseded in the last centuries BC by the Macedonians and Romans who were primarily land-based powers. Hand-to-hand fighting with large complements of heavy infantry supported by ship-borne catapults dominated the fighting style during the Roman era, a move that was accompanied by the conversion to heavier ships with larger rowing complements and more men per oar. Though effectively lowering mobility, it meant that less skill was required from individual oarsmen. Fleets thereby became less dependent on rowers with a lifetime of experience at the oar.[68]
The Romans baffled the ramming tactics of the Carthaginians by the invention of the corvus, or crow, a plank with a spike for hooking onto enemy ships which grappled the prow of the rammer, and provided a gangway for boarders.[69] The Romans did continue their boarding tactics in the naval battles of the Punic Wars, but are also reported as ramming the Carthaginian vessels after the abandonment of the corvus. An older and alternative way for boarding was the use of grappling hooks and planks, also a more flexible system than the corvus. Agrippa introduced a weapon with a function similar to the corvus, the harpax.[69]
Ramming
[edit]In antiquity, the naval ram was a weapon that dominated Mediterranean naval warfare for nearly five hundred years. The use and devastating force of the ram is evidenced in the ancient sources, but the former weapon was not discovered by archaeologists until the 1980s.[70]
All warships were equipped with rams, a triple set of 60-centimetre-wide (2 ft) bronze blades weighing up to 270 kilograms (600 lb) positioned at the waterline. In the century prior to the Punic Wars, boarding had become increasingly common and ramming had declined, as the larger and heavier vessels adopted in this period lacked the speed and manoeuvrability necessary to ram, while their sturdier construction reduced the ram's effect even in case of a successful attack. The Roman adaptation of the corvus was a continuation of this trend and compensated for their initial disadvantage in ship-manoeuvring skills. The added weight in the prow compromised both the ship's manoeuvrability and its seaworthiness, and in rough sea conditions the corvus became useless.[63][71][72] In 255 BC the Romans lost 384 ships from a fleet of 464 warships off the south-east corner of Sicily, more than 100,000 men were lost.[73][74][75] It is possible that the presence of the corvus made the Roman ships unusually unseaworthy; there is no record of them being used after this disaster.[76][77]
Ramming was done by smashing into the rear or side of an enemy ship, punching a hole in the planking. This did not actually sink an ancient galley unless it was heavily laden with cargo and stores. With a normal load, it was buoyant enough to float even with a breached hull.[78] War galleys gradually began to develop heavier hulls with reinforcing beams at the waterline, where a ram would most likely hit. Besides ramming, breaking enemy oars was also a way to impede mobility and make it easier to drive home a successful ramming attack.[79]
Success in ramming depended so much on a combination of skill and good fortune that it played a somewhat subordinate part in most ancient sea fights.[69]
No later than the 7th century AD, ramming tactics had completely disappeared along with the knowledge of the original trireme and its high speed and mobility. The ram was replaced by a long spur in the bow that was designed to break oars and to act as a boarding platform for storming enemy ships. The only remaining examples of ramming tactics was passing references to attempts to collide with ships in order to roll it over on its side.[80]
Dozens of bronze Carthaginian and Roman rams from the period have been found;[81] see § Punic War rams below.
Shipbuilding
[edit]
When the Romans first engaged with the Carthaginians, they knew nothing about shipbuilding, and their early war-vessels were merely copies of those used by the Carthaginians, which were of the same general type as the Greek galleys. The first Roman fleet appears to have consisted of quinqueremes.[82]
During the First Punic War, the admiralty of the Roman Republic conceived new and progressive ways of fleet construction, development and composition in order to successfully engage the Carthaginian navy. Victories at the Battle of Mylae, the Battle of Cape Ecnomus, the Battle of Cape Hermaeum and the Battle of the Aegates encouraged the Romans to pursue naval-based warfare and strategies in order to push the center of combat to the Carthaginian heartland in North Africa.[85][86]
Capacity
[edit]Large numbers of ships could be constructed in a short time: 600 hundred oared transport ships were built in one winter for Caesar's planned invasion of Britain.[27]
Wrecks and relics
[edit]Alkedo
[edit]
Arles Rhône 3
[edit]
Blackfriars I
[edit]
Discovered by Peter Marsden on 6 September[citation needed] 1962, the first Blackfriars ship became the earliest known indigenous seagoing sailing ship to be found in northern Europe, dating back to the 2nd century AD. The wreck is dated to a period of great Roman expansion and construction. Found between Blackfriars Bridge and Blackfriars Railway Bridge during the construction of a new riverside wall, the Blackfriars I has been variously interpreted as a native Brythonic shipbuilding style or a traditional Roman style.[95]
Black Sea
[edit]Ancient shipwrecks found in the Black Sea date to Antiquity. In 1976, Willard Bascom suggested that the deep, anoxic waters of the Black Sea might have preserved ships from antiquity because typical wood-devouring organisms could not survive there. At a depth of 150m, the Black Sea contains insufficient oxygen to support most familiar biological life forms.[96]
Caligula's Giant Ship
[edit]De Meern
[edit]From 1997 to 2008, a set of six vessels, consisting of varying states of preservation were discovered in the town of De Meern, Utrecht, Netherlands. Some were utilized as landfill like The De Meern 6, discovered in 2008, but the De Meern 1, first discovered in 1997, and excavated in 2003, was determined to be run aground. The latter was in a good state of preservation with a cabin, and a toolbox. They likely served as transport of the Roman military supply chain in proximity to the Castellums of Laurium and Nigrum Pullum. The De Meern 1 on display at the Museum Hoge Woerd.[98][99][100]
Madrague de Giens
[edit]
Mainz
[edit]In November 1981, during excavation in the course of a construction of a Hilton Hotel at Mainz, wooden remains were found and identified as parts of an old ship. Before construction resumed three months later, the site yielded remnants of five ships that were dated to the 4th century using dendrochronology. The wrecks were measured, taken apart and, in 1992, brought to the Museum of Ancient Seafaring (German: Museum für Antike Schifffahrt) of the Romano-Germanic Central Museum (Römisch-Germanisches Zentralmuseum) for further preservation and study.[49]
Scientifically the wrecks were termed "Mainz 1" through "Mainz 5" and generally referred to as the "Mainzer Römerschiffe" (the Mainz Roman ships). They were identified as military vessels that belonged to the Roman flotilla in Germania, the Classis Germanica. The vessels could be classified into two types, namely small troop transports (Mainz 1, 2, 4, 5) termed navis lusoria and a patrol vessel (Mainz 3). The lusoria is narrower than the actuaria, an earlier and wider type of Roman cargo vessel.[citation needed]
Höckmann conjectured that the Mainz boats are probably lusoriae, and have some architectural similarity with earlier liburnae. The type A Mainz ships 1 and 7 appear to be identical in form to the ships Ammianus Marcellinus described in his reports on 4th century Rhine battle vessels, and which he always referred to as naves lusioriae.[50] Höckmann finds that ships 1, 4, 7, and 9 are likely lusoriae.[50]
Marausa
[edit]Nemi
[edit]
Sinop D
[edit]Punic War rams
[edit]Beginning in 2010 bronze warship rams have been found by archaeologists in the sea off the west coast of Sicily, near where the 241 BC battle of the Aegates is believed to have taken place; as of August 2022, twenty four have been identified, as have ten bronze helmets and hundreds of amphorae.[81][109][110][111] All twenty-four rams, seven of the helmets, and six intact amphorae, along with a number of fragments, have since been recovered.[112] Inscriptions allowed four of the rams to be identified as coming from Roman-built ships.[113] It is possible that some of these had been captured by the Carthaginians earlier in the war and were crewed by them when they were sunk.[114] It is believed that the rams were each attached to a sunken warship when they were deposited on the seabed.[115] Based on the dimensions of the recovered rams, the archaeologists who have studied them believe that they all came from triremes, contrary to Polybius's account of all of the warships involved being quinqueremes.[110][116]
Yassi Ada
[edit]Three wrecks near Bodrum, Turkey have been excavated, including a 4th century Roman, and 7th century Byzantine wreck only meters away.[117]
The University Museum of the University of Pennsylvania under its director George Bass excavated a shipwreck site near Yassi Ada in 1967 and 1969. This expedition was funded by the Museum and the National Geographic Society. A few students from the university joined the team, along with an architect and a physician. The main site under excavation was a 4th-century vessel 19 meters in length, lying between 36 and 42 meters below the sea surface 100 meters south of Yassi Ada. Its hull was made of cypress, and the keel of white oak. There is also a 7th-century vessel near the reef, with one end resting over another wrecked vessel. Bass used the mini-sub Asherah to conduct some of the investigation of the site.[118]
Experimental archaeology
[edit]Olympias trireme – 1987
[edit]The Olympias trireme is a reconstruction of an ancient Athenian trireme and an important example of experimental archaeology.
Olympias was constructed from 1985 to 1987 by a shipbuilder in Piraeus. She was built to drawings by the naval architect John F. Coates which he developed through long discussions with the historian J. S. Morrison following the longest correspondence on any subject in The Times in the early 1980s. The work was also advised by the classics teacher Charles Willink and drew on evidence gained from Greek literature, history of art and archaeology above and below water. Finance came from the Hellenic Navy and donors such as Frank Welsh (a banker, writer and trireme enthusiast). Morrison, Coates and Willink founded the Trireme Trust together with Welsh. The Trireme Trust was chaired by professor Boris Rankov. It was wound up c. 2012 and its documents archived at Wolfson College, Cambridge.[citation needed]
Lusoria – 2004
[edit]The Regina is a reconstruction of a lusoria by students of the Department for Ancient History of the University of Regensburg.[119] Launched in 2004, the boat was used to test its abilities in numerous trips along the Naab and Danube. In 2006, the Regina travelled from Regensburg to Budapest covering distances of up to 100 km (54 nmi) per day confirming that the vessel was speedy and demonstrating the great mobility the military could achieve by its use.[citation needed]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- Notes
- ^ The distance by sea from Alexandria (the main Egyptian grain port during the Roman Empire) to Civitavecchia (the modern port for Rome) is 1,142 nautical miles (2,115 km; 1,314 mi).[26]
- ^ Livy: circum oram omnem maritimam misit ut naves onerariae comprensae Lilybaeum omnes contraheren. Livy 29.24.9
- ^ The ship shown on the famous so-called in the Prenestine relief kept in the Vatican Museum, dated to the period of Octavian's civil wars, according to some it also shows a liburna. Over time, "liburna" became a general name for various types of Roman ships, and in later antiquity for cargo ships. Tacitus and Suetonius use this name as a synonym for a warship. Suetonius calls the large, lavishly equipped ships, which Emperor Caligula built for his entertainment, deceres liburnae (Suet., Calig., 37). Inscriptions mention the liburna as the last in a class among ancient warships: hexeres, penteres, quadrieres, trieres, liburna.
Lađa prikazana na poznatom tzv. prenestinskom reljefu koji se čuva u Vatikanskom muzeju, datirana u razdoblje Oktavijanovih građanskih ratova, po nekima također prikazuje liburnu. Eijekom vremena "liburna" postaje opći naziv za različite tipove rimskih brodova, a u kasnijoj antici za teretne brodove. Tacit i Svetonije upotrebljavaju to ime kao sinonim za ratni brod. Velike, raskošno opremljene lađe, što ih je sebi za zabavu sagradio ar Kaligula, Svetonije naziva deceres liburnae (Suet., Calig., 37). Natpisi spominju liburnu kao posljendnji u klasi među antičkim ratnim brodovima: hexeres, penteres, quadrieres, trieres, liburna.[46] - ^ navis lusoria: from Latin 'dancing/playful ship', plural naves lusoriae.
- Citations
- ^ Labate 2017, Conclusion.
- ^ Carlson 2011, p. 397.
- ^ Petit et al. 2023, ancient Rome.
- ^ Lazenby 1996, pp. 48–49.
- ^ a b Miles 2011, p. 179.
- ^ Bagnall 1999, pp. 64–66.
- ^ Goldsworthy 2006, p. 97.
- ^ Bagnall 1999, p. 66.
- ^ Goldsworthy 2006, pp. 91–92, 97.
- ^ Goldsworthy 2006, pp. 97, 99–100.
- ^ Murray 2011, p. 69.
- ^ Goldsworthy 2006, pp. 110–111.
- ^ Lazenby 1996, p. 87.
- ^ Tipps 1985, p. 436.
- ^ Miles 2011, p. 196.
- ^ Bagnall 1999, p. 96.
- ^ Lazenby 1996, p. 157.
- ^ Scullard 2006, p. 565.
- ^ Collins 1998, p. 13.
- ^ Frere 1987, p. 19.
- ^ Gilliver 2003.
- ^ Rankov 1995, pp. 78–80.
- ^ Rankov 1995, pp. 80–85.
- ^ Saddington 2007, pp. 202–203.
- ^ Casson 1995, p. 297.
- ^ "Alexandria - Civitavecchia distance is 1142 NM - SeaRoutes". m.classic.searoutes.com. Retrieved 16 June 2022.
- ^ a b Charles 2005, p. 297.
- ^ Charles 2005, p. 289.
- ^ a b Casson 1991, pp. 119–123.
- ^ Viereck 1975, p. 86.
- ^ Charles 2005, p. 292.
- ^ Charles 2005, pp. 291–292.
- ^ Friedman 2004, pp. 164–168.
- ^ Denny 2009, p. 21.
- ^ a b c Bocquelet 2022.
- ^ a b c Pliny & Bostock 1855, 36.14.
- ^ Casson 1995, pp. 57–58.
- ^ Starr 1941, p. 54 et seq..
- ^ a b c Starr 1941, p. 54.
- ^ Zaninović 1988, pp. 46–47.
- ^ Gabriel 2007, pp. 36–43.
- ^ Morrison & Coates 2016, pp. 170, 317.
- ^ Casson 1971, p. 141.
- ^ Morrison & Coates 2016, p. 171.
- ^ Starr 1941, p. 54ff.
- ^ a b Zaninović 1988, p. 47.
- ^ Ammianus & Yonge 1862, 2-§12.
- ^ Bierweiler.
- ^ a b Höckmann 1993.
- ^ a b c d Höckmann 1993, p. 131.
- ^ a b Goldsworthy 2006, p. 98.
- ^ Lazenby 1996, pp. 27–28.
- ^ a b Goldsworthy 2006, p. 104.
- ^ Goldsworthy 2006, p. 100.
- ^ Tipps 1985, p. 435.
- ^ a b Casson 1995b, p. 121.
- ^ Goldsworthy 2006, pp. 102–103.
- ^ Coates 1995, p. 138.
- ^ Casson 1995, p. 283.
- ^ Casson 1995, p. 101.
- ^ Casson 1995b, pp. 278–280.
- ^ de Souza 2008, p. 358.
- ^ a b Miles 2011, p. 178.
- ^ Coates 2000, pp. 127–230.
- ^ Welsh 1988.
- ^ a b c d Pitassi 2011, p. 180.
- ^ Wilkes 1995, pp. 157, 163.
- ^ Morrison, Coates & Rankov 2000, pp. 48–49.
- ^ DeCasien 2019.
- ^ Wallinga 1956, pp. 77–90.
- ^ Goldsworthy 2006, pp. 100–101, 103.
- ^ Goldsworthy 2006, p. 115.
- ^ Tipps 1985, p. 438.
- ^ Miles 2011, p. 189.
- ^ Scullard 2006, p. 557.
- ^ Lazenby 1996, pp. 112, 117.
- ^ Casson 1991, p. 139.
- ^ Coates 1995, p. 133.
- ^ Hocker 1995, pp. 86–100.
- ^ a b Tusa & Royal 2012, p. 12.
- ^ Holmes 1906, p. 36.
- ^ Hanson (2006), p. 262
- ^ Fields (2007), p. 9
- ^ Casson 1995, p. 105.
- ^ Tusa & Royal 2012.
- ^ "Alkedo ship". Artsupp. Retrieved 2021-12-11.
- ^ The barge’s long and graceful bow ... nationalgeographic.com
- ^ Built for river commerce in the first century A.D ... nationalgeographic.com
- ^ Inauguration de l’extension du musée départemental Arles antique pour la présentation du chaland antique Arles Rhône 3 Archived 2014-04-16 at the Wayback Machine culture-13.fr (in French language)
- ^ Built for river commerce in the first century A.D ... nationalgeographic.com
- ^ Working in water rarely this clear ... nationalgeographic.com
- ^ La barge gallo-romaine Arles-Rhône 3 N. Despinoy, randomania.fr (in French language)
- ^ The boat’s flat bottom was made of ... nationalgeographic.com
- ^ a b Heritage Gateway 2012.
- ^ Brennan et al. 2011.
- ^ Allaby, Michael; Richard, Garratt (2010). Exploration: New Lands, New Worlds. Infobase Publishing.
- ^ van Holk 2011.
- ^ Hoge Woerd 2018.
- ^ "De Meern 6 | MaSS". mass.cultureelerfgoed.nl. Retrieved 2023-07-18.
- ^ a b c Tchernia, André (November 1987). "The Madrague de Giens Wreck: a Roman freighter yields its secrets". UNESCO Courier: 11.
- ^ Pomey, Patrice (1982). "Le Navire Romain de la Madrague de Giens". Comptes rendus des séances de l'Académie des Inscriptions et Belles-Lettres. 126 (1): 133–154.
- ^ Green, Kevin (1986). The Archaeology of the Roman Economy. Berkeley and Los Angeles: University of California Press. pp. 25–27.
- ^ a b c Pomey, Patrice (2011). "Chapter 1: Defining a Ship: architecture, function, and human space". In Catsambis, Alexis; Ford, Ben; Hamilton, Donny (eds.). The Oxford Handbook of Maritime Archaeology. Oxford University Press. p. 40.
- ^ Muckelroy, Keith (1978). Maritime Archaeology. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 64–75.
- ^ Whitewright, Julian (March 2011). "The Potential Performance of Ancient Mediterranean Sailing Rigs: THE POTENTIAL PERFORMANCE OF ANCIENT MEDITERRANEAN SAILING RIGS". International Journal of Nautical Archaeology. 40 (1): 2–17. doi:10.1111/j.1095-9270.2010.00276.x.
- ^ Croff, Katherine; Martinez, Catalina. "Aegean and Black Sea Expedition 2007". Ocean Explorer. NOAA.
- ^ Curry 2012, p. 37.
- ^ Prag 2013.
- ^ a b Murray 2019.
- ^ "Battle of the Egadi Islands Project". RPM Nautical Foundation.
- ^ Tusa & Royal 2012, pp. 12, 26, 31–32.
- ^ Tusa & Royal 2012, p. 18.
- ^ Tusa & Royal 2012, p. 45.
- ^ Tusa & Royal 2012, p. 39.
- ^ Tusa & Royal 2012, pp. 39–42.
- ^ Bass & van Doorninck 1971, p. 27.
- ^ Bass & van Doorninck 1971, pp. 27–29.
- ^ Dietz, R. F. (2004). "Alte Geschichte auf neuen Wegen" [Old history in new ways]. Regensburger Universitätszeitung [Regensburg University Newspaper] (in German). University of Regensburg. p. 1. Archived from the original on 2006-05-22. Retrieved August 13, 2010.
Works cited
[edit]- Ammianus Marcellinus (1862) [c. 390]. "2". Res Gestae [Roman History]. Vol. Book XVIII. Translated by Yonge, C.D. London: Bohn. § 12. Retrieved 29 July 2023.
- Bagnall, Nigel (1999). The Punic Wars: Rome, Carthage and the Struggle for the Mediterranean. London: Pimlico. ISBN 978-0-7126-6608-4.
- Bass, George F.; van Doorninck, Frederick H. (1971). "A Fourth-Century Shipwreck at Yassi Ada". American Journal of Archaeology. 75 (1): 27–37. doi:10.2307/503679. JSTOR 503679. S2CID 191403303.
- Bierweiler, Jan. "Hintergrund – Was sind die Besonderheiten der naves lusoriae?" [Background – What are the special features of the naves lusoriae?] (in German). Universität Regensberg, Der Verein Römerschiff. Archived from the original on 3 March 2016.
- Bocquelet, David (2022-10-24) [2017-10-13]. "Roman Ships – From SPQR to the Imperium". Naval Encyclopedia. Retrieved 12 July 2023.
- Brennan, Michael L.; Ballard, Robert D.; Croff Bell, Katherine L.; Piechota, Dennis (2011). "Archaeological oceanography and environmental characterization of shipwrecks in the Black Sea". In Buynevich, Ilya V.; Yanko-Hombach, Valentina; Gilbert, Allan S.; Martin, Ronald E. (eds.). Geology and Geoarchaeology of the Black Sea Region: Beyond the Flood Hypothesis. Special Papers. Vol. 473. Geological Society of America. doi:10.1130/2011.2473(11). ISBN 978-0-8137-2473-7. ISSN 0072-1077.
- Casson, Lionel (1971). Ships and Seamanship in the Ancient World. Princeton University Press. ISBN 9780691035369. OCLC 141594.
- Casson, Lionel (December 1, 1995) [1971]. Ships and Seamanship in the Ancient World. Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-5130-8. OCLC 32549371.
- Casson, Lionel (1991). The Ancient Mariners: Seafarers and Sea Fighters of the Mediterranean in Ancient Times (2nd ed.). Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-01477-7. OCLC 1153575745.
- Catsambis, Alexis; Ford, Ben; Hamilton, Donny L., eds. (2011). The Oxford Handbook of Maritime Archaeology. OUP. ISBN 978-0-19-537517-6. OCLC 639940479.
- Carlson, Deborah N. "17. The Seafarers and Shipwrecks of Ancient Greece and Rome". In Catsambis, Ford & Hamilton (2011), pp. 379–405.
- Delgado, James P. "Ships on Land". In Catsambis, Ford & Hamilton (2011), pp. 182–191.
- Charles, Michael (2005). "Transporting the Troops in Late Antiquity: Naves Onerariae, Claudian and the Gildonic War". Classical Journal. 100 (3). Johns Hopkins University Press: 275–299. ISSN 0009-8353. JSTOR 4133022.
- Coates, John F. (2000). The Athenian Trireme (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press.
- Collins, Roger (1998). Spain: An Oxford Archaeological Guide. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-285300-4.
- Curry, Andrew (2012). "The Weapon That Changed History". Archaeology. 65 (1): 32–37. JSTOR 41780760.
- DeCasien, Stephen (2019). "Naval Ram Collection". The Nautical Archaeology Digital Library. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- Denny, Mark (2009). Float Your Boat!: The Evolution and Science of Sailing. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 9780801890093. OCLC 214066711.
- Frere, Sheppard Sunderland (1987). Britannia: A History of Roman Britain (3rd ed.). Routledge & Kegan Paul. ISBN 978-0-7102-1215-3.
- Friedman, Zazara (2004). "The Ships Depicted in the Lod Mosaic Reconsidered". International Journal of Nautical Archaeology. 33 (1). Portsmouth: The Nautical Archaeology Trust Ltd: 164–168. doi:10.1111/j.1095-9270.2004.0015b.x. S2CID 162519294.
- Gabriel, Richard A. (2007). "The Roman Navy: Masters of the Mediterranean". Military History. 29 (9): 36–43.
- Gilliver, Catherine (2003). Caesar's Gallic wars, 58–50 BC. New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-203-49484-4. OCLC 57577646.
- Goldsworthy, Adrian (2006). The Fall of Carthage: The Punic Wars 265–146 BC. London: Phoenix. ISBN 978-0-304-36642-2. OCLC 162111692.
- "Blackfriars Ship I". Heritage Gateway. 2012.
- Holmes, Sir George Charles Vincent (1906). Ancient and Modern Ships. Victoria and Albert Museum science handbook. H. M. Stationery Office. OCLC 5268420.
- This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Hannay, David McDowall (1911). "Navy". In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 19 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
- "Ship and limes". Museum Hoge Woerd. 12 November 2018. Retrieved 2023-07-18.
- Höckmann, Olaf (May 1993). "Late Roman Rhine vessels from Mainz, Germany". International Journal of Nautical Archaeology. 22 (2). Wiley: 125–135. Bibcode:1993IJNAr..22..125H. doi:10.1111/j.1095-9270.1993.tb00401.x. ISSN 1095-9270. Archived from the original on 2013-01-05.
- Labate, Victor (6 March 2017). "Roman Shipbuilding & Navigation". World History Encyclopedia. World History Publishing. Retrieved 12 July 2023.
- Lazenby, John Francis (1996). The First Punic War: A Military History. Stanford, California: Stanford University Press. ISBN 0-8047-2673-6.
- Miles, Richard (2011). Carthage Must be Destroyed. London: Penguin. ISBN 978-0-14-101809-6.
- Morrison, John S.; Coates, John F. (2016). Greek and Roman Oared Warships 399–30 B.C. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9781785704017. OCLC 8183635058.
- Morrison, John S.; Coates, John F.; Rankov, N. B. (2000) [1986]. The Athenian trireme : the history and reconstruction of an ancient Greek warship (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-56419-0. OCLC 42683057.
- Morrison, John S; Gardiner, Robert, eds. (1995). The Age of the Galley: Mediterranean Oared Vessels Since Pre-Classical Times. London: Conway Maritime. ISBN 0-85177-554-3. OCLC 32117584.
- Casson, Lionel (1995b). "Merchant Galleys". In Morrison & Gardiner (1995), pp. 117–126.
- Coates, John F. "The Naval Architecture and Oar Systems of Ancient Galleys". In Morrison & Gardiner (1995), pp. 127–141.
- Dotson, John E. "Economics and Logistics of Galley Warfare". In Morrison & Gardiner (1995), pp. 218–223.
- Hocker, Frederick M. "Late Roman, Byzantine, and Islamic Galleys and Fleets". In Morrison & Gardiner (1995), pp. 86–100.
- Morrison, John S. "Hellenistic Oared Warships 399-31 BC". In Morrison & Gardiner (1995), pp. 66–77.
- Pryor, John H. "From Dromōn to Galea: Mediterranean Bireme Galleys AD 500–1300". In Morrison & Gardiner (1995), pp. 101–116.
- Rankov, Boris. "Fleets of the Early Roman Empire, 31 BC–AD 324". In Morrison & Gardiner (1995), pp. 78–85.
- Wachsmann, Shelley. "Paddled and Oared Ships Before the Iron Age". In Morrison & Gardiner (1995), pp. 10–25.
- Murray, William M. (2011). The Age of Titans: The Rise and Fall of the Great Hellenistic Navies. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-993240-5. OCLC 900200567.
- Murray, William M. (2019). "The Ship Classes of the Egadi Rams and Polybius' Account of the First Punic War". Society for Classical Studies.
- Petit, Paul; Hornblower, Simon; Ferguson, John; et al. (9 November 2023). "ancient Rome". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 29 November 2023.
- Pitassi, Michael (2011). Roman Warships. Woodbridge, Suffolk: Boydell Press. ISBN 9781843836100. OCLC 646110784.
- Pliny the Elder (1855) [77 CE]. "14. Obelisks". The Natural History. Vol. 7, Book 36. Translated by Bostock, John; Riley, H.T. London: Taylor and Francis. OCLC 1377782773.
- Prag, Jonathan (2013). "Rare Bronze Rams Excavated from Site of the Final Battle of the First Punic War". University of Oxford media site. University of Oxford. Archived from the original on 2013-10-01. Retrieved 2014-08-03.
- Saddington, D.B. (2007). "Classes. The Evolution of the Roman Imperial Fleets". In Erdkamp, Paul (ed.). A Companion to the Roman Army. Blackwell companions to the ancient world. Malden, Mass.: Blackwell Publishing. pp. 201–217. ISBN 978-1-4051-2153-8. OCLC 65197913.
- Scullard, H.H. (2006) [1989]. "Carthage and Rome". In Walbank, F. W.; Astin, A. E.; Frederiksen, M. W. & Ogilvie, R. M. (eds.). Cambridge Ancient History: Volume 7, Part 2, 2nd Edition. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 486–569. ISBN 978-0-521-23446-7.
- de Souza, Philip (2008). "Naval Forces". In Sabin, Philip; van Wees, Hans & Whitby, Michael (eds.). The Cambridge History of Greek and Roman Warfare, Volume 1: Greece, the Hellenistic World and the Rise of Rome. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 357–367. ISBN 978-0-521-85779-6.
- Starr, Chester G. (1941). The Roman Imperial Navy 31 B.C. – A.D. 324. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
- Tipps, G.K. (1985). "The Battle of Ecnomus". Historia: Zeitschrift für Alte Geschichte. 34 (4): 432–465. JSTOR 4435938.
- Tusa, Sebastiano; Royal, Jeffrey (2012). "The landscape of the naval battle at the Egadi Islands (241 B.C.)" (PDF). Journal of Roman Archaeology (in Italian and English). 25. Cambridge University Press: 7–48. doi:10.1017/S1047759400001124. ISSN 1047-7594. S2CID 159518193. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 August 2020.
- van Holk, André (2011). "2 - Recent Research on Roman Shipfinds from the Netherlands". In Boetto, Giulia; Pomey, Patrice; Tchernia, André (eds.). Batellerie gallo-romaine:Pratiques régionales et influences maritimes méditerranéennes [Gallo-Roman inland navigation:Regional practices and Mediterranean maritime influences]. Bibliothèque d'archéologie méditerranéenne et africaine, 9 (New (online) ed.). Aix-en-Provence: Publications du Centre Camille Jullian, Éditions Érrance. doi:10.4000/books.pccj.967. ISBN 9782957155781.
- Viereck, Hans D. L (1975). Die römische Flotte: Classis Romana [The Roman Fleet: Classis Romana] (in German). Herford, Germany: Koehler. ISBN 378220106X. OCLC 2318792.
- Wallinga, Herman (1956). The Boarding-bridge of the Romans: Its Construction and its Function in the Naval Tactics of the First Punic War. Groningen: J.B. Wolters. OCLC 458845955.
- Welsh, Frank (1988). Building the Trireme. London: Constable and Company Limited. ISBN 9780094668805.
- Wilkes, John J. (1 December 1995) [1988]. The Illyrians (The Peoples of Europe). Oxford: Blackwell. ISBN 9780631198079. OCLC 36173200.
- Zaninović, M. (1988). "Liburnia Militaris". Opusc. Archeol. 13: 43–67.
Further reading
[edit]- Blaschke, Jayme (23 June 2008). "Tide and time: Re-dating Caesar's invasion of Britain". Texas State University. Archived from the original on 1 August 2013.
- Chatterton, Edward Keble (2010) [1909:Sidgwick & Jackson]. The history of sailing ships the story of their development from the earliest times until the 19th century. Historische Schiffahrt, 150. Bremen: Salzwasser. p. 107. ISBN 9783861953081. OCLC 845685916.
- D'Amato, Raffaele (2015). Republican Roman Warships 509–27 BC. New Vanguard, vol. 225. Illustrated by Giuseppe Rava. Bloomsbury. ISBN 9781472808295.
- Dreyer, Boris (March 2011). "Principles and Progress in the Shipbuilding Part of the EU Interreg DTP Project 'Living Danube Limes.'". Építés - Építészettudomány [Architectonics and Architecture]. 49 (1–2). AK Journals: 171–208. doi:10.1556/096.2021.00008. S2CID 233899291 – via TWL/EBSCOhost.
- Günther, Sven; Ruffing, Kai; Stoll, Oliver (2007). Pragmata: Beiträge zur Wirtschaftsgeschichte der Antike im Gedenken an Harald Winkel [Pragmata: Contributions to the Economic History of Antiquity in Memory of Harald Winkel]. Philippika, 17 (in German). Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz. ISBN 9783447055369. OCLC 153885180.
- Ermatinger, James William (11 August 2015). The World of Ancient Rome: A Daily Life Encyclopedia. Santa Barbara: Greenwood. p. 725. ISBN 9781440829079. OCLC 1440829071.
- Emil Luebeck: "Actuariae". In: Realencyclopädie der classischen Altertumswissenschaft (RE). Volume I, 1, Stuttgart 1893, p. 331.
- Meijer, Fik A History of Seafaring in the Classical World
- Pitassi, Michael The Roman Navy: Ships, Men and Warfare 350 BC–AD 475
- Starr, Chester (1991) [1965]. A History of the Ancient World. New York, New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-506628-9.
- Steinby, Christa Rome versus Carthage
- Torr, Cecil Ancient Ships
External links
[edit] Media related to Ancient Roman ships at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Ancient Roman ships at Wikimedia Commons- Roman ships and navigation in ancient Rome


