A state of the United States is one of the 50 constituent entities that shares its sovereignty with the federal government. Americans are citizens of both the federal republic and of the state in which they reside, due to the shared sovereignty between each state and the federal government.[1] Kentucky, Massachusetts, Pennsylvania, and Virginia use the term commonwealth rather than state in their full official names.
States are the primary subdivisions of the United States. They possess all powers not granted to the federal government, nor prohibited to them by the Constitution of the United States. In general, state governments have the power to regulate issues of local concern, such as regulating intrastate commerce, running elections, creating local governments, public school policy, and non-federal road construction and maintenance. Each state has its own constitution grounded in republican principles, and government consisting of executive, legislative, and judicial branches.[2]
All states and their residents are represented in the federal Congress, a bicameral legislature consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives. Each state is represented by two senators, and at least one representative, while the size of a state's House delegation depends on its total population, as determined by the most recent constitutionally mandated decennial census.[3] Additionally, each state is entitled to select a number of electors to vote in the Electoral College, the body that elects the President of the United States and Vice President of the United States, equal to the total of representatives and senators in Congress from that state.[4]
Article IV, Section 3, Clause 1 of the Constitution grants to Congress the authority to admit new states into the Union. Since the establishment of the United States in 1776, the number of states has expanded from the original 13 to 50. Each new state has been admitted on an equal footing with the existing states.[5]
List of U.S. states
[edit]The following table is a list of all 50 states and their respective dates of statehood. The first 13 became states in July 1776 upon agreeing to the United States Declaration of Independence, and each joined the first Union of states between 1777 and 1781, upon ratifying the Articles of Confederation, its first constitution.[6] (A separate table is included below showing AoC ratification dates.) These states are presented in the order in which each ratified the 1787 Constitution and joined the others in the new (and current) federal government. The date of admission listed for each subsequent state is the official date set by Act of Congress.[a]
| State | Date (admitted or ratified) |
Formed from | |
|---|---|---|---|
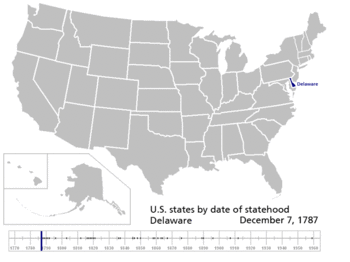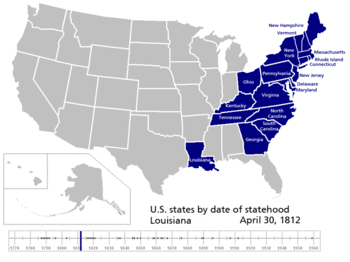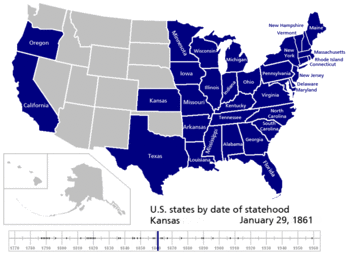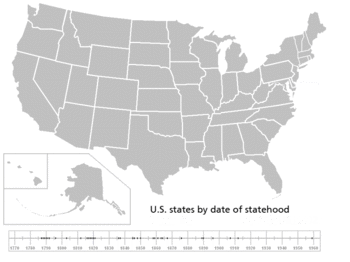
| 1 | December 7, 1787[8] (ratified) |
Colony of Delaware[b] | |
| 2 | December 12, 1787[10] (ratified) |
Proprietary Province of Pennsylvania | |
| 3 | December 18, 1787[11] (ratified) |
Crown Colony of New Jersey | |
| 4 | January 2, 1788[8] (ratified) |
Crown Colony of Georgia | |
| 5 | January 9, 1788[12] (ratified) |
Crown Colony of Connecticut | |
| 6 | February 6, 1788[8] (ratified) |
Crown Colony of Massachusetts Bay | |
| 7 | April 28, 1788[8] (ratified) |
Proprietary Province of Maryland | |
| 8 | May 23, 1788[8] (ratified) |
Crown Colony of South Carolina | |
| 9 | June 21, 1788[8] (ratified) |
Crown Colony of New Hampshire | |
| 10 | June 25, 1788[8] (ratified) |
Crown Colony and Dominion of Virginia | |
| 11 | July 26, 1788[13] (ratified) |
Crown Colony of New York | |
| 12 | November 21, 1789[14] (ratified) |
Crown Colony of North Carolina | |
| 13 | May 29, 1790[8] (ratified) |
Crown Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations | |
| 14 | March 4, 1791[15] (admitted) |
Vermont Republic[c] | |
| 15 | June 1, 1792[16] (admitted) |
Virginia (nine counties in its District of Kentucky[d]) | |
| 16 | June 1, 1796[18] (admitted) |
Southwest Territory | |
| 17 | March 1, 1803[19][e] (admitted) |
Northwest Territory (part) | |
| 18 | April 30, 1812[21] (admitted) |
Territory of Orleans | |
| 19 | December 11, 1816[citation needed] (admitted) |
Indiana Territory | |
| 20 | December 10, 1817[22] (admitted) |
Mississippi Territory | |
| 21 | December 3, 1818[23] (admitted) |
Illinois Territory (part) | |
| 22 | December 14, 1819[24] (admitted) |
Alabama Territory | |
| 23 | March 15, 1820[25] (admitted) |
Massachusetts (District of Maine[f]) | |
| 24 | August 10, 1821[26] (admitted) |
Missouri Territory (part) | |
| 25 | June 15, 1836[27] (admitted) |
Arkansas Territory | |
| 26 | January 26, 1837[28] (admitted) |
Michigan Territory | |
| 27 | March 3, 1845[citation needed] (admitted) |
Florida Territory | |
| 28 | December 29, 1845[29] (admitted) |
Republic of Texas | |
| 29 | December 28, 1846[citation needed] (admitted) |
Iowa Territory (part) | |
| 30 | May 29, 1848[30] (admitted) |
Wisconsin Territory (part) | |
| 31 | September 9, 1850[31] (admitted) |
Unorganized territory / Mexican Cession (part)[g] | |
| 32 | May 11, 1858[32] (admitted) |
Minnesota Territory (part) | |
| 33 | February 14, 1859[citation needed] (admitted) |
Oregon Territory (part) | |
| 34 | January 29, 1861[33] (admitted) |
Kansas Territory (part) | |
| 35 | June 20, 1863[34] (admitted) |
Virginia (50 Trans-Allegheny region counties[h]) | |
| 36 | October 31, 1864[citation needed] (admitted) |
Nevada Territory | |
| 37 | March 1, 1867[citation needed] (admitted) |
Nebraska Territory | |
| 38 | August 1, 1876[37] (admitted) |
Colorado Territory | |
| 39 | November 2, 1889[38][i] (admitted) |
Dakota Territory (part) | |
| 40 | November 2, 1889[38][i] (admitted) |
Dakota Territory (part) | |
| 41 | November 8, 1889[41] (admitted) |
Montana Territory | |
| 42 | November 11, 1889[42] (admitted) |
Washington Territory | |
| 43 | July 3, 1890[citation needed] (admitted) |
Idaho Territory | |
| 44 | July 10, 1890[citation needed] (admitted) |
Wyoming Territory | |
| 45 | January 4, 1896[43] (admitted) |
Utah Territory | |
| 46 | November 16, 1907[44] (admitted) |
Oklahoma Territory and Indian Territory | |
| 47 | January 6, 1912[citation needed] (admitted) |
New Mexico Territory | |
| 48 | February 14, 1912[citation needed] (admitted) |
Arizona Territory | |
| 49 | January 3, 1959[citation needed] (admitted) |
Territory of Alaska | |
| 50 | August 21, 1959[citation needed] (admitted) |
Territory of Hawaii | |
Articles of Confederation ratification dates
[edit]The Second Continental Congress approved the Articles of Confederation for ratification by the individual states on November 15, 1777. The Articles of Confederation came into force on March 1, 1781, after being ratified by all 13 states. On March 4, 1789, the general government under the Articles was replaced with the federal government under the present Constitution.[45]
| State | Date | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | December 16, 1777 | |
| 2 | February 5, 1778 | |
| 3 | February 6, 1778 | |
| 4 | February 9, 1778 | |
| 5 | February 12, 1778 | |
| 6 | February 26, 1778 | |
| 7 | March 4, 1778 | |
| 8 | March 5, 1778 | |
| 9 | March 10, 1778 | |
| 10 | April 5, 1778 | |
| 11 | November 19, 1778 | |
| 12 | February 1, 1779 | |
| 13 | February 2, 1781 | |
See also
[edit]- Territorial evolution of the United States
- Enabling Act of 1802, authorizing residents of the eastern portion of the Northwest Territory to form the state of Ohio
- Missouri Compromise, 1820 federal statute enabling the admission of Missouri (a slave state) and Maine (a free state) into the Union
- Toledo War, 1835–36 boundary dispute between Ohio and the adjoining Michigan Territory, which delayed Michigan's admission to the Union
- Texas annexation, the 1845 incorporation of the Republic of Texas into the United States as a state in the Union
- Compromise of 1850, a package of congressional acts, one of which provided for the admission of California to the Union
- Bleeding Kansas, a series of violent conflicts in Kansas Territory involving anti-slavery and pro-slavery factions in the years preceding Kansas statehood, 1854–61
- Enabling Act of 1889, authorizing residents of Dakota, Montana, and Washington territories to form state governments (Dakota to be divided into two states) and to gain admission to the Union
- Oklahoma Enabling Act, authorizing residents of the Oklahoma and Indian territories to form a state government and to be admitted to the union as a single state, and, authorizing the people of New Mexico and Arizona territories to form a state government and be admitted into the Union, requiring a referendum to determine if both territories should be admitted as a single state
- Alaska Statehood Act, admitting Alaska as a state in the Union as of January 3, 1959
- Hawaii Admission Act, admitting Hawaii as a state in the Union as of August 21, 1959
Notes
[edit]- ^ This list does not account for the secession of 11 states (Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, Florida, Alabama, Mississippi, Tennessee, Arkansas, Louisiana, and Texas) during the Civil War to form the Confederate States of America, nor for the subsequent restoration of those states to the Union, or each state's "readmission to representation in Congress" after the war, as the federal government does not give legal recognition to their having left the Union. Also, the Constitution is silent on the question of whether states have the power to secede from the Union, but the Supreme Court held that a state cannot unilaterally do so in Texas v. White (1869).[7]
- ^ Also known as the "Three Lower Counties Upon Delaware". Delaware became a state on June 15, 1776, when the Delaware Assembly formally adopted a resolution declaring an end to Delaware's status as a colony of Great Britain and establishing the three counties as an independent state under the authority of "the Government of the Counties of New Castle, Kent and Sussex Upon Delaware".[9]
- ^ Between 1749 and 1764 the provincial governor of New Hampshire, Benning Wentworth, issued approximately 135 grants for unoccupied land claimed by New Hampshire west of the Connecticut River (in what is today southern Vermont), territory that was also claimed by New York. The resulting "New Hampshire Grants" dispute led to the rise of the Green Mountain Boys, and the later establishment of the Vermont Republic. New Hampshire's claim upon the land was extinguished in 1764 by royal order of George III, and in 1790 the State of New York ceded its land claim to Vermont for 30,000 dollars.
- ^ The Virginia General Assembly adopted legislation on December 18, 1789, separating its "District of Kentucky" from the rest of the State and approving its statehood.[17]
- ^ The exact date upon which Ohio became a state is unclear. On April 30, 1802, the 7th Congress had passed an act "authorizing the inhabitants of Ohio to form a Constitution and state government, and admission of Ohio into the Union" (Sess. 1, ch. 40, 2 Stat. 173). On February 19, 1803, the same Congress passed an act "providing for the execution of the laws of the United States in the State of Ohio" (Sess. 2, ch. 7, 2 Stat. 201). Neither act, however, set a formal date of statehood. An official statehood date for Ohio was not set until 1953, when the 83rd Congress passed a Joint resolution "for admitting the State of Ohio into the Union", (Pub. L. 83–204, 67 Stat. 407, enacted August 7, 1953) which designated March 1, 1803, as that date.[20]
- ^ The Massachusetts General Court passed enabling legislation on June 19, 1819, separating the "District of Maine" from the rest of the State (an action approved by the voters in Maine on July 19, 1819, by 17,001 to 7,132); then, on February 25, 1820, passed a follow-up measure officially accepting the fact of Maine's imminent statehood.[17]
- ^ Most of the region ceded by Mexico to the United States in 1848, following the Bear Flag Revolt and the Mexican–American War, had been the Mexican Department of Alta California. The Act of Congress establishing California as the 31st state was part of the Compromise of 1850.
- ^ On May 13, 1862, the General Assembly of the Restored Government of Virginia passed an act granting permission for creation of West Virginia.[35] Later, by its ruling in Virginia v. West Virginia (1871), the Supreme Court implicitly affirmed that the breakaway Virginia counties did have the proper consents necessary to become a separate state.[36]
- ^ a b Brought into existence within moments of each other on the same day, North and South Dakota are the nation's only twin-born states. Before signing the statehood papers, President Benjamin Harrison shuffled the papers so that no one would know which became a state first. By custom, North Dakota is commonly recognized as the 39th state and South Dakota as the 40th, as "n" precedes "s" in the alphabet.[39][40]
References
[edit]- ^ Erler, Edward. "Essays on Amendment XIV: Citizenship". The Heritage Foundation.
- ^ "Frequently Asked Questions About the Minnesota Legislature". Minnesota State Legislature.
- ^ Kristin D. Burnett. "Congressional Apportionment (2010 Census Briefs C2010BR-08)" (PDF). U.S. Department of Commerce, Economics and Statistics Administration.
- ^ Elhauge, Einer R. "Essays on Article II: Presidential Electors". The Heritage Foundation.
- ^ "Doctrine of the Equality of States". Justia.com.
- ^ Jensen, Merrill (1959). The Articles of Confederation: An Interpretation of the Social-Constitutional History of the American Revolution, 1774–1781. University of Wisconsin Press. pp. xi, 184. ISBN 978-0-299-00204-6.
- ^ "Texas v. White 74 U.S. 700 (1868)". Justia.com.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Vile, John R. (2005). The Constitutional Convention of 1787: A Comprehensive Encyclopedia of America's Founding (Volume 1: A-M). ABC-CLIO. p. 658. ISBN 1-85109-669-8.
- ^ "Delaware Government". Delaware.gov. Government Information Center, Delaware Department of State.
- ^ "Overview of Pennsylvania History - 1776-1861: Independence to the Civil War". PA.gov. Pennsylvania Historical & Museum Commission.
- ^ "1787 Convention Minutes". NJ.gov. New Jersey Department of State.
- ^ "Today in History: January 9". loc.gov. Library of Congress.
- ^ "Today in History: July 26". loc.gov. Library of Congress.
- ^ "Today in History: November 21". loc.gov. Library of Congress.
- ^ "The 14th State". Vermont History Explorer. Vermont Historical Society. Archived from the original on May 30, 2013.
- ^ "Constitution Square State Historic Site". americanheritage.com. American Heritage Publishing Co. Retrieved April 23, 2019.
- ^ a b "Official Name and Status History of the several States and U.S. Territories". TheGreenPapers.com.
- ^ "State History Timeline". TN.gov. Tennessee Department of State. Archived from the original on April 10, 2016.
- ^ Blue, Frederick J. (Autumn 2002). "The Date of Ohio Statehood". Ohio Academy of History Newsletter. Archived from the original on September 11, 2010.
- ^ Berg-Andersson, Richard E. (January 17, 2007). "Clearing up the Confusion surrounding Ohio's Admission to Statehood". The Green Papers. Retrieved June 15, 2023.
- ^ "About Louisiana: quick facts". louisiana.gov. Archived from the original on March 24, 2013. Retrieved June 15, 2016.
- ^ "Welcome from the Mississippi Bicentennial Celebration Commission". Mississippi Bicentennial Celebration Commission. Retrieved February 16, 2017.
- ^ "Today in History: December 3". loc.gov. Library of Congress.
- ^ "Alabama History Timeline: 1800-1860". alabama.gov. Retrieved June 15, 2016.
- ^ "Today in History: March 15". loc.gov. Library of Congress.
- ^ "Today in History: August 10". loc.gov. Library of Congress.
- ^ "Today in History: June 15". loc.gov. Library of Congress.
- ^ "Today in History: January 26". loc.gov. Library of Congress.
- ^ "Texas enters the Union". This Day In History. A&E Television Networks. March 4, 2010. Retrieved April 23, 2019.
- ^ "Today in History: May 29". loc.gov. Library of Congress.
- ^ "California Admission Day September 9, 1850". CA.gov. California Department of Parks and Recreation.
- ^ "Today in History: May 11". loc.gov. Library of Congress.
- ^ "Today in History: January 29". loc.gov. Library of Congress.
- ^ "Today in History: June 20". loc.gov. Library of Congress.
- ^ "A State of Convenience: The Creation of West Virginia, Chapter Twelve, Reorganized Government of Virginia Approves Separation". Wvculture.org. West Virginia Division of Culture and History.
- ^ "Virginia v. West Virginia 78 U.S. 39 (1870)". Justia.com.
- ^ "Today in History: August 1". loc.gov. Library of Congress.
- ^ a b "Today in History: November 2". loc.gov. Library of Congress.
- ^ MacPherson, James; Burbach, Kevin (November 2, 2014). "At 125 years of Dakotas statehood, rivalry remains". The Bismarck Tribune. AP. Retrieved June 29, 2020.
- ^ Stein, Mark (2008). "How the States Got Their Shapes", Smithsonian Books/Harper Collins, p. 256.
- ^ Wishart, David J. (ed.). "Montana". Encyclopedia of the Great Plains. University of Nebraska–Lincoln. Retrieved February 15, 2017.
- ^ "Today in History: November 11". loc.gov. Library of Congress.
- ^ Thatcher, Linda (2016). "Struggle For Statehood Chronology". historytogo.utah.gov. State of Utah.
- ^ "Today in History: November 16". loc.gov. Library of Congress.
- ^ Rodgers, Paul (2011). United States Constitutional Law: An Introduction. McFarland. p. 109. ISBN 978-0-7864-6017-5.
External links
[edit]- "U.S. States Videos". History.com.
- "Dates of statehood". 50states.com.