| WikiProject | Requested articles | Assessment | Vital articles | Members | Noticeboard | Recognized content | To do | Portal |
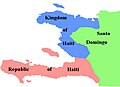
Haiti, officially the Republic of Haiti, is a country on the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and south of The Bahamas. It occupies the western three-eighths of the island, which it shares with the Dominican Republic. Haiti is the third largest country in the Caribbean, and with an estimated population of 11.4 million, is the most populous Caribbean country.0 The capital and largest city is Port-au-Prince. The first century of independence was characterized by political instability, international isolation, crippling debt payments to France, and a costly war with neighboring Dominican Republic. Political volatility and foreign economic influence prompted a U.S. occupation from 1915 to 1934. A series of unstable presidencies gave way to nearly three decades of dictatorship under the Duvalier family (1957–1986), which brought state-sanctioned violence, corruption, and economic stagnation. Following a coup d'état in 2004, the United Nations intervened to stabilize the country. In 2010, Haiti suffered a catastrophic earthquake, followed by a deadly cholera outbreak. With its deteriorating economic situation, the country has experienced a socioeconomic and political crisis marked by riots and protests, widespread hunger, and increased gang activity. As of May 2024, Haiti has no remaining elected government officials and has been described as a failed state. (Full article...) Selected article -
The 2010s Haiti cholera outbreak was the first modern large-scale outbreak of cholera—a disease once considered beaten back largely due to the invention of modern sanitation. The disease was reintroduced to Haiti in October 2010, not long after the disastrous earthquake earlier that year, and since then cholera has spread across the country and become endemic, causing high levels of both morbidity and mortality. Nearly 800,000 Haitians have been infected by cholera, and more than 9,000 have died, according to the United Nations (UN). Cholera transmission in Haiti today is largely a function of eradication efforts including WASH (water, sanitation, and hygiene), education, oral vaccination, and climate variability. Early efforts were made to cover up the source of the epidemic, but thanks largely to the investigations of journalist Jonathan M. Katz and epidemiologist Renaud Piarroux, it is widely believed to be the result of contamination by infected United Nations peacekeepers deployed from Nepal. In terms of total infections, the outbreak has since been surpassed by the war-fueled 2016–2021 Yemen cholera outbreak, although the Haiti outbreak is still one of the most deadly modern outbreaks. After a three-year hiatus, new cholera cases reappeared in October 2022. (Full article...)
Did you know
CategoriesSelected pictureGeneral imagesThe following are images from various Haiti-related articles on Wikipedia.
Related portalsRelated portals and portals of neighbouring countries:
TopicsRecognized content
Featured articlesFeatured listsGood articles
Featured pictures
WikiProjectsGeographical:
History and Society: Things you can doIn the newsOctober 2019: The 2018–19 Haitian protests have challenged Jovenel Moïse's government as more becomes known about the Petrocaribe Affair. Associated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using portals | ||||||||