List of substituted piperazines
Benzylpiperazines
|
See also: Benzylpiperazine § Chemical derivatives |
-
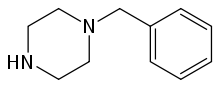
1-Benzylpiperazine (BZP)
-
1-Methyl-4-benzylpiperazine (MBZP)
-
1,4-Dibenzylpiperazine (DBZP)
-
4-Bromo-2,5-dimethoxy-1-benzylpiperazine (2C-B-BZP)
-
Methoxypiperamide (MeOP, MEXP) ((4-methoxyphenyl)(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methanone)
-
Sunifiram (1-benzoyl-4-propanoylpiperazine)
-
3-Methylbenzylpiperazine (3-MeBZP)
-
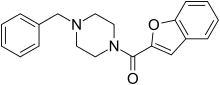
Befuraline
(also produces benzylpiperazine as a metabolite) -
Fipexide
(also produces substituted benzylpiperazine as a metabolite) -
Piberaline
(also produces benzylpiperazine as a metabolite)
Phenylpiperazines
|
See also: Phenylpiperazine |
ortho-Substituted
- 2-Chlorophenylpiperazine (oCPP)
- 2-Methylphenylpiperazine (oMPP)
- 2-Methoxyphenylpiperazine (oMeOPP)
- Vortioxetine
Enpiprazole is known to produce oCPP as a metabolite.
Enciprazine was initially anticipated to produce oMeOPP as a metabolite, but this turned out not to be the case.
meta-Substituted
- 3-Chlorophenylpiperazine (mCPP)
- 3-Methoxyphenylpiperazine (mMeOPP)
- 3-Trifluoromethylphenylpiperazine (TFMPP)
- 1-(3-Chlorophenyl)-4-(2-phenylethyl)piperazine (3C-PEP)
Trazodone, nefazodone, mepiprazole, and others produce mCPP as a metabolite.
para-Substituted
- 4-Chlorophenylpiperazine (pCPP)
- 4-Fluorophenylpiperazine (pFPP)
- 4-Methylphenylpiperazine (pMPP)
- 4-Methoxyphenylpiperazine (MeOPP)
- 4-Nitrophenylpiperazine (pNPP)
- 4-Trifluoromethylphenylpiperazine (pTFMPP)
Multiple substitutions
-
2,3-Dichlorophenylpiperazine (2,3-DCPP)
-
3,4-Dichlorophenylpiperazine (3,4-DCPP)
- 2,3-Methylphenylpiperazine (DMPP)
- 3-Trifluoromethyl-4-chlorophenylpiperazine (TFMCPP)
Others
- 1-Phenylpiperazine (PP)
Other arylpiperazines
- 1-(1-Naphthyl)piperazine (1-NP)
- 1-(2-Pyrimidinyl)piperazine (1-PP)
- ORG-12962 (1-(5-trifluoromethyl-6-chloropyridin-2-yl)piperazine)
- Quipazine (2-piperazin-1-ylquinoline)
Many azapirones such as buspirone, gepirone, and tandospirone produce 1-PP as a metabolite.