Three-dimensional chess (or 3‑D chess) is any chess variant that replaces the two-dimensional board with a three-dimensional array of cells between which the pieces can move. In practice, this is usually achieved by boards representing different layers being laid out next to each other. Three-dimensional chess has often appeared in science fiction—the Star Trek franchise in particular—contributing to the game's familiarity.
Three-dimensional variants have existed since at least the late 19th century, one of the oldest being Raumschach (German for "Space chess"), invented in 1907 by Ferdinand Maack and considered the classic 3‑D game.[1] Chapter 25 of David Pritchard's The Classified Encyclopedia of Chess Variants discusses some 50 such variations extending chess to three dimensions as well as a handful of higher-dimensional variants. Chapter 11 covers variants using multiple boards normally set side by side which can also be considered to add an extra dimension to chess.[2]
The expression "Three-dimensional chess" is sometimes used as a colloquial metaphor to describe complex, dynamic systems with many competing entities and interests, including politics, diplomacy and warfare. To describe an individual as "playing three-dimensional chess" implies a higher-order understanding and mastery of the system beyond the comprehension of their peers or ordinary observers, who are implied to be "playing" regular chess.[3]
Lionel Kieseritzky (1806–1853) developed Kubikschach (German for "Cube chess") in 1851.[4] He used an 8×8×8 board, labelling the third dimension with Greek letters alpha through theta. This format was later picked up by Maack in 1907 when developing Raumschach. According to David Pritchard, this format is:
the most popular 3‑D board amongst inventors, and at the same time the most mentally indigestible for the players ... Less demanding on spatial vision, and hence more practical, are those games confined to three 8×8 boards and games with boards smaller than 8×8.[5]
Ferdinand Maack (1861–1930) developed Raumschach (German for "Space chess") in 1907. He contended that for chess to be more like modern warfare, attack should be possible not only from a two-dimensional plane but also from above (aerial) and below (underwater). Maack's original formulation was for an 8×8×8 board, but after experimenting with smaller boards eventually settled on 5×5×5 as best. Other obvious differences from standard chess include two additional pawns per player, and a special piece (two per player) named unicorn.
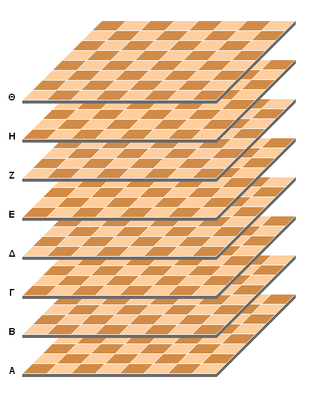
The Raumschach 3‑D board can be thought of as a cube sliced into five equal spaces across each of its three major coordinal planes. This sectioning yields a 5×5×5 (125 cube) gamespace. The cubes (usually represented by squares and often called cells) alternate in color in all three dimensions.

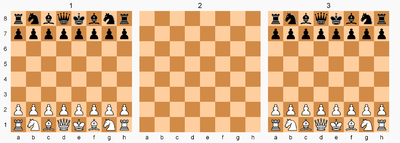
The horizontal levels are denoted by capital letters A through E. Ranks and files of a level are denoted using algebraic notation. White starts on the A and B levels and Black starts on E and D.
| Raumschach starting position.[6] White's pawn on Bd2 can move to cells with a white dot or capture on cells marked "×". Black's unicorn on Dd5 can move to cells with a black dot or capture the white pawn on Aa2. | ||
White moves first. The game objective, as in standard chess, is checkmate. Rooks, bishops, and knights move as they do in chess in any given plane.

Tri-Dimensional Chess, Tri-D Chess, or Three-Dimensional Chess[a] is a chess variant which can be seen in many Star Trek TV episodes and movies, starting with the original series (TOS) and proceeding in updated forms throughout the subsequent movies and spinoff series.[9]
The original Star Trek prop was crafted using boards from 3D Checkers and 3D Tic-Tac-Toe sets available in stores at the time (games also seen in TOS episodes) and adding chess pieces from the futuristic-looking Classic chess set designed by Peter Ganine in 1961.[10] The design retained the 64 squares of a traditional chessboard, but distributed them onto separate platforms in a hierarchy of spatial levels, suggesting to audiences how chess adapted to a future predominated by space travel. Rules for the game were never invented within the series[11] – in fact, the boards are sometimes not even aligned consistently from one scene to the next within a single episode.
The Tri-D chessboard was further realized by its inclusion in the Star Trek Star Fleet Technical Manual by Franz Joseph, who created starting positions for the pieces and short, additional rules.
The complete Standard Rules for the game were originally developed in 1976 by Andrew Bartmess (with encouragement from Joseph) and were subsequently expanded by him into a commercially available booklet.[12] A free summary in English of the Standard Rules is contained on Charles Roth's website, including omissions and ambiguities regarding piece moves across the four Tri‑D gameboard 2×2 attack boards.
A complete set of tournament rules for Tri-Dimensional Chess written by Jens Meder is available on his website. Meder's rules are based on FIDE's rules more than Andrew Bartmess' Standard Rules, with some deviations too. A repository of Tournament Rules games can be found on the website of Michael Klein.
Plans for constructing a Tri‑D chessboard can be found on The Chess Variant Pages, as well as in Bartmess' Tri‑D Chess Rules. Details for building a travel-size board are included on Meder's website.
There is software for playing Tri‑D Chess. Parmen (potentially named after a lead character in the episode "Plato's Stepchildren") is a Windows application written by Doug Keenan and available free on his website. A free Android version of Tri‑D Chess is offered by AwfSoft.