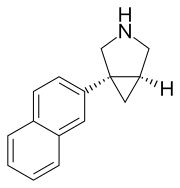
Serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor
Centanafadine [1]
| Site |
IC50 (nM) |
Action |
Ref
|
| SERTTooltip Serotonin transporter |
83 nM |
Blocker |
[1]
|
| NETTooltip Norepinephrine transporter |
6 nM |
Blocker |
[1]
|
| DATTooltip Dopamine transporter |
38 nM |
Blocker |
[1]
|
Centanafadine (INN) (former developmental code name EB-1020) is a serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI) that began its development with Euthymics Bioscience after they acquired DOV Pharmaceutical. It was developed as a treatment for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and inhibits the reuptake of norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin with an IC50 ratio of 1:6:14, respectively.[1][2][3][4] In 2011, Euthymics Bioscience spun off its development of centanafadine to a new company called Neurovance.[5][6] In March 2017, Otsuka Pharmaceutical acquired Neurovance and the rights to centanafadine.[7] As of January 2018, Otsuka's pipeline indicates it is in Phase II and III clinical trials for a number of different applications to medical conditions.[8][9][10]