-
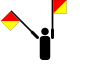
The letter T in German Sign Language
| T | |
|---|---|
| T t | |
 | |
| Usage | |
| Writing system | Latin script |
| Type | Alphabetic and logographic |
| Language of origin | Latin language |
| Sound values | |
| In Unicode | U+0054, U+0074 |
| Alphabetical position | 20 |
| History | |
| Development | |
| Time period | ~−700 to present |
| Descendants | |
| Sisters | |
| Other | |
| Associated graphs | t(x), th, tzsch |
| Writing direction | Left-to-right |
| ISO basic Latin alphabet |
|---|
| AaBbCcDdEeFfGgHhIiJjKkLlMmNnOoPpQqRrSsTtUuVvWwXxYyZz |
T, or t, is the twentieth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is tee (pronounced /ˈtiː/), plural tees.[1]
It is derived from the Semitic Taw 𐤕 of the Phoenician and Paleo-Hebrew script (Aramaic and Hebrew Taw ת/𐡕/![]() , Syriac Taw ܬ, and Arabic ت Tāʼ) via the Greek letter τ (tau). In English, it is most commonly used to represent the voiceless alveolar plosive, a sound it also denotes in the International Phonetic Alphabet. It is the most commonly used consonant and the second-most commonly used letter in English-language texts.[2]
, Syriac Taw ܬ, and Arabic ت Tāʼ) via the Greek letter τ (tau). In English, it is most commonly used to represent the voiceless alveolar plosive, a sound it also denotes in the International Phonetic Alphabet. It is the most commonly used consonant and the second-most commonly used letter in English-language texts.[2]