| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
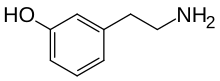
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-(2-Aminoethyl)phenol | |
| Other names
m-Tyramine; 3-Tyramine;
3-Hydroxyphenylethylamine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.197.155 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H11NO | |
| Molar mass | 137.182 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
meta-Tyramine, also known as m-tyramine and 3-tyramine, is an endogenous trace amine neuromodulator and a structural analog of phenethylamine.[1][2][3] It is a positional isomer of para-tyramine, and similarly to it, has effects on the adrenergic and dopaminergic systems.[4][5]
meta-Tyramine is produced in humans via aromatic amino acid decarboxylase-mediated metabolism of meta-tyrosine.[6] meta-Tyramine can be metabolized into dopamine via peripheral or brain CYP2D6 enzymes in humans.[7]