| C-131 Samaritan R4Y / T-29 | |
|---|---|

| |
| Convair C-131F Samaritan | |
| Role | Military transport |
| Manufacturer | Convair |
| First flight | 22 September 1949 |
| Introduction | 1950 |
| Retired | 1990 |
| Primary users | United States Air Force United States Navy United States Marine Corps United States Coast Guard |
| Number built | 512[1] |
| Developed from | Convair CV-240 |
| Variants | NC-131H TIFS |
The Convair C-131 Samaritan is an American twin-engined military transport produced from 1954 to 1956 by Convair. It is the military version of the Convair CV-240 family of airliners.[2]
This was one of the last radial engined aircraft in US service, along with C-1 Trader.
Design and development
[edit]The design began life in a production requirement by American Airlines for a pressurized airliner to replace the Douglas DC-3. Convair's original design had two engines and 40 seats, and thus it was designated the CV-240. The first CV-240 flew on March 16, 1947, and production aircraft were first delivered to American on February 28, 1948. Seventy-five were delivered to American, with another fifty going to Western Airlines, Continental Airlines, Pan American Airways, KLM, Sabena, Swissair and Trans Australia Airlines.[citation needed]
Operational history
[edit]
The CV-240/340/440 series was used by the United States Air Force (USAF) for medical evacuation and VIP transport and was designated as C-131 Samaritan. The first model Samaritan, the C-131A, was derived from the CV-240 model, and was delivered to the USAF in 1954.[citation needed][contradictory]
The initial trainer model, designated the T-29, was also based on the Convair CV-240 and was used to instruct USAF navigators for all USAF aircraft and United States Navy (USN) Naval Flight Officers (NFOs) selected to fly land-based aircraft. The first deliveries to the USAF were made in 1950 followed by large production quantities until early 1955. The USAF and the USN operated T-29s in separate units at separate locations until 1976. In 1974, the USAF T-29s with the 323d Flying Training Wing (323 FTW) at Mather AFB, California began to be replaced by the Boeing 737-derived T-43. In 1975, the Navy retired all of its T-29s assigned to Training Squadron Twenty-Nine (VT-29) at NAS Corpus Christi, Texas, deactivated VT-29, and merged their advanced navigator training program for land-based NFOs with the Air Force's program at Mather AFB.[3]
A planned bomber training version of the T-29 (designated T-32) was never built.[citation needed]
From 1952, the USN and United States Marine Corps (USMC) took delivery of 36 R4Y-1 transport aircraft similar to the commercial CV-340 and USAF C-131D, configured with 44 passenger seats and powered by a pair of 2,500 hp (1,900 kW) Pratt & Whitney R-2800-52W engines. A single otherwise similar aircraft was acquired with a 24-seat VIP interior and designated R4Y-1Z. In 1957, the USN took delivery of two additional aircraft similar to the commercial CV-440 and designated R4Y-2. With the 1962 redesignation of USN/USMC aircraft, the three types were redesignated as the C-131F, VC-131F, and C-131G respectively.[4] A number of R4Y-1 (C-131F) aircraft were converted to R4Y-1Z (VC-131F) or R4Y-2 (C-131G) standards after delivery, and several C-131F and C-131G aircraft were ultimately sold as military surplus and converted to civil use.[5][6]
Nearly all of the C-131s left the active USAF inventory in the late 1970s, but the U.S. Coast Guard (USCG) operated the aircraft until 1983, while the Air National Guard (ANG) and USN units operated additional C-131 airframes, primarily as Operational Support Aircraft (OSA) for ANG flying wings and as naval air station "station aircraft" until 1990. The C-131 was primarily replaced by the C-9 Nightingale in regular USAF service, with the ANG replacing their OSA with C-130 Hercules aircraft and the USN with C-12 Hurons.[citation needed]

In 1959, a C-131 was the first aircraft to be used as a reduced-gravity aircraft or 'vomit comet', for astronaut training as part of Project Mercury.[7][8][9]
A Samaritan was the first aircraft used as a flying gunship testbed in mid-1963, in a program known as "Project Tailchaser".[10] A C-131B (AF Ser. No. 53-7820) was given a gunsight for the side window, but instead of guns it had cameras in the cargo area. Eventually the C-131 was ferried to Eglin AFB in Florida and a General Electric SUU-11A/A 7.62 mm Gatling-style Minigun was installed. Live ammunition was used and both over-water and overland tests were successful.[11]
Accidents and incidents
[edit]On 17 December 1960, a USAF C-131D Samaritan crashed at Munich after one engine lost power on takeoff from Munich-Riem Airport. Flying in heavy fog and unable to gain altitude, the aircraft struck the steeple of St. Paul's Church and crashed onto a tram, killing all 20 people on the aircraft and 32 on the tram.[12]
Variants
[edit]


- C-131A
- Transport for USAF based on CV-240, capable of carrying 39 passengers on rearward facing seats, or 20 stretchers and 7 seats; 26 built.[13]
- HC-131A
- Surplus C-131As transferred to the USCG, 22 transferred.
- MC-131A
- C-131A used for medivac duties with 27 stretchers.
- VC-131A
- C-131A used as a staff transport.
- C-131B
- A hybrid CV-240/340 with seats for 48 passengers, 36 built.
- JC-131B
- C-131B converted for missile tracking, six conversions.
- NC-131B
- One C-131B used for permanent testing.
- VC-131B
- C-131B when used as a staff transport.
- YC-131C
- Two CV-340s modified with Alison 501D-13 turboprop engines.
- C-131D
- Military version of the Model 340 with seats for 44 passengers, 33 built.
- VC-131D
- C-131D when used as a staff transport.
- C-131E
- Electronic countermeasures (ECM) training version for Strategic Air Command (SAC), later designated TC-131E, 15 built and one conversion from C-131D, two transferred to United States Navy as R4Y-2.
- TC-131E
- C-131E redesignated.
- C-131F
- R4Y-1 redesignated.
- RC-131F
- Conversions for photo-mapping and survey, six conversions.
- VC-131F
- R4Y-1Z redesignated.
- C-131G
- R4Y-2 redesignated.
- EC-131G
- One C-131G modified as an electronics trainer.
- RC-131G
- One C-131G modified for airways checking duties.
- VC-131G
- C-131G when used as a staff transport.
- C-131H
- Conversions to CV-580 turboprop standard.
- NC-131H
- One conversion with an extended nose incorporating a separate cockpit as a Total In-Flight Simulator. This aircraft was transferred to the National Museum of the United States Air Force at Wright-Patterson AFB, Ohio on November 7, 2008[14]
- R4Y-1
- USN/USMC version of CV-340 with 44 passenger seats, redesignated C-131F in 1962, 36 built.[4][5]
- R4Y-1Z
- USN/USMC 24-seat VIP staff transport, redesignated VC-131F in 1962, one built and conversions from R4Y-1.[4][5]
- R4Y-2
- USN/USMC version of CV-440, redesignated C-131G in 1962, two built and conversions from R4Y-1; an additional 13 canceled, of which six were completed as CV-440 airliners.[4][5][6]
- R4Y-2Q
- Proposed ECM version of the R4Y-2, five canceled.[6]
- R4Y-2S
- Proposed anti-submarine warfare version of R4Y-2, 14 canceled.[6]
- XT-29
- Prototype military trainer version of the Model 240 for the United States Air Force, two built.
- T-29A
- Initial production version for navigator training, unpressurized cabin for 14 students, 46 built.
- VT-29A
- T-29As converted for staff transport.
- T-29B
- Pressurized version with room for 10 navigator and four radio operator students, 105 built.
- NT-29B
- One T-29B used for permanent testing.
- VT-29B
- T-29B converted for staff transport with seating for 29 or 32 passengers.
- T-29C
- T-29B with 2,500 hp (1,900 kW) Pratt & Whitney R-2800-29W engines, 119 built.
- AT-29C
- T-29C modified for airways checking duties, redesignated ET-29C in 1962.
- ET-29C
- AT-29C redesignated.
- VT-29C
- T-29C converted to staff transport.
- T-29D
- Bombardier training version of the T-29C with room for six students, 93 built.
- ET-29D
- Airways checking conversion of the T-29D.
- VT-29D
- Staff transport conversion of the T-29D.
- XT-29E
- Proposed turboprop version of T-29B, none built.
- YT-32
- Proposed bomber training version with transparent nose, none built.
Operators
[edit] Paraguay
Paraguay
- Paraguayan Air Force operated one former USAF Convair C-131D[15]
 United States
United States
- United States Air Force operated T-29 and C-131 aircraft.
- United States Navy operated R4Y/C-131 and T-29 aircraft.
- United States Coast Guard operated R4Y/C-131 aircraft.
- NASA
Surviving aircraft
[edit]
- HC-131A
- 52-5794 – On display at the Pueblo Weisbrod Aircraft Museum in Pueblo, Colorado.[16][17]
- C-131A
- 55-4757 – On display at the Minnesota Air National Guard Museum in Minneapolis, Minnesota.[18]
- C-131B
- 53-7811 – Last registered to Tatonduk Outfitters Limited in Fairbanks, Alaska. This aircraft was previously on display at the Kelly Field Heritage Museum, Lackland AFB, Texas.[19]
- 53-7819 – Airworthy with Airborne Resources Inc in Midlothian, Texas.[20][21]
- 53-7821 – On display at the Air Force Armament Museum, Eglin AFB, Florida.[22]
- C-131D
- 54-2806 – On display at the Jimmy Doolittle Air & Space Museum, Travis AFB, California.[23]
- 54-2808 – On display at the March Field Air Museum, March ARB (former March AFB), Riverside, California.[24]
- 54-2810 – Stored at Burlington Air National Guard Base in Burlington, Vermont.[25]
- 54-2822 – On display at the Aerospace Museum of California, former McClellan AFB, California.[26]
- 55-0292 – On display at the South Dakota Air and Space Museum, Ellsworth AFB, South Dakota.[27]
- 55-0293 – On display at the Selfridge Military Air Museum, Selfridge Air National Guard Base, Michigan.[28][29]
- 55-0294 – On display at The Leonardo in Salt Lake City, Utah.[30][failed verification]
- 55-0295 – On display at the Air Mobility Command Museum, Dover AFB, Delaware.[31]
- 55-0300 – On display at the Hill Aerospace Museum, Hill AFB, Utah.[32]
- 55-0301 – Cockpit only with unknown owner in Kenosha, Wisconsin. This airframe was previously on display at the National Museum of the United States Air Force, but was scrapped before 2009.[33][34]
- C-131F
- 140996 – Airworthy with Gulf & Caribbean Cargo of Waterford, Michigan.[35][36]
- 141008 – Airworthy with Conquest Air Inc of Miami Lakes, Florida.[37][38]
- 141013 – On display at the Yanks Air Museum in Chino, California.[39]
- 141015 – On display at the National Museum of Naval Aviation, NAS Pensacola, Florida.[40]
- 141017 – On display at the Pima Air & Space Museum in Tucson, Arizona.[41]
- 141025 – In storage at the Pima Air & Space Museum in Tucson, Arizona.[42]
- NC-131H
- 53-7793 – On display at the National Museum of the United States Air Force in Dayton, Ohio.[43][44]
- T-29A
- 49-1934 – On display at Sheppard AFB, Texas.[45]
- 50-0190 – On display at the Strategic Air and Space Museum in Ashland, Nebraska.[46]
- T-29B
- 51-7906 – On display at the Pima Air & Space Museum in Tucson, Arizona.[47]
- T-29C
- 53-3489 – On display at the 12th Flying Training Wing area, Randolph AFB, Texas.[48] (previously displayed at former Mather AFB, California; disassembled and relocated following BRAC closure of Mather AFB)
- 52-1175 – On display at the Linear Air Park at Dyess Air Force Base in Abilene, Texas.[49]
Specifications (C-131B)
[edit]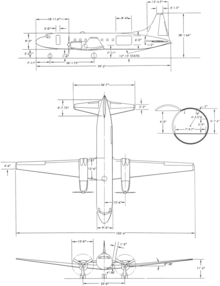
Data from United States Military Aircraft since 1909[50]
General characteristics
- Crew: four
- Capacity: 48 passengers
- Length: 79 ft 2 in (24.14 m)
- Wingspan: 105 ft 4 in (32.11 m)
- Height: 28 ft 2 in (8.59 m)
- Wing area: 920 sq ft (85.5 m2)
- Empty weight: 29,248 lb (13,294 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 47,000 lb (21,363 kg)
- Powerplant: 2 × Pratt & Whitney R-2800-99 "Double Wasp" 18 cylinder air cooled radial engines, 2,500 hp (1,865 kW) each
Performance
- Maximum speed: 293 mph (472 km/h, 255 kn)
- Cruise speed: 254 mph (409 km/h, 221 kn)
- Range: 450 mi (725 km, 391 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 24,500 ft (7,470 m)
- Rate of climb: 1,410 ft/min (7.2 m/s)
See also
[edit]Related development
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
Related lists
- List of military aircraft of the United States
- List of United States Navy aircraft designations (pre-1962)
References
[edit]- Notes
- ^ "T-29 / C-131". www.uswarplanes.net. Archived from the original on 24 July 2017. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^ Gradidge 1997, p. 20–21.
- ^ CAMPUS Magazine, The Navy Education and Training Monthly, Vol. VIII, No. 8, August 1979, pp. 16-19
- ^ a b c d Swanborough, Gordon; Bowers, Peter M. (1976). United States Navy Aircraft since 1911 (2nd ed.). Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. p. 422. ISBN 0-87021-968-5.
- ^ a b c d Baugher, Joe (22 January 2021). "US Navy and US Marine Corps BuNos, Third Series (140053 to 145061)". joebaugher.com. Retrieved 25 January 2021.
- ^ a b c d Baugher, Joe (22 January 2021). "US Navy and US Marine Corps BuNos, Third Series (145062 to 150138)". joebaugher.com. Retrieved 25 January 2021.
- ^ "Mercury Astronauts in Weightless Flight on C-131 Aircraft". 2006-08-02. Archived from the original on 2015-02-14. Retrieved 2016-05-14.
- ^ "Mercury Astronauts in Weightless Flight on C-131 Aircraft". NASA on the Commons. 1959. Archived from the original on 2016-11-08.
- ^ How The Vomit Comet Works – Convair C-131 on YouTube
- ^ "Project Tailchaser". Archived 2011-12-04 at the Wayback Machine globalsecurity.org. Retrieved: 21 July 2011.
- ^ Jack S. Ballard Development and Employment of Fixed-Wing Gunships 1962–1972 Archived 2011-07-11 at the Wayback Machine. Office of Air Force History. 1982
- ^ Accident description for ASN Aircraft accident Convair C-131D (CV-340) 55-0291 München at the Aviation Safety Network
- ^ Wegg 1990, p. 190.
- ^ "Old plane retired." Dayton Daily News. Retrieved: 21 July 2011.
- ^ Andrade 1982, p. 176
- ^ "Actual Aircraft on Display in Pueblo". Pueblo Weisbrod Aircraft Museum. Archived from the original on 25 December 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
- ^ "Airframe Dossier – Convair CV-240/340/440/580/600/640 / C-131 / R4Y / T-29, s/n 5794 USCG, c/n 53-14, c/r N3999P". Aerial Visuals. AerialVisuals.ca. Archived from the original on 6 October 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
- ^ "Convair C-131H Samaritan." Archived 2016-03-04 at the Wayback Machine Minnesota Air National Guard Museum. Retrieved: 30 July 2015.
- ^ "Airframe Dossier – Convair C-131B Samaritan, s/n 53-7811 USAF, c/n 340-263, c/r N2034L". Aerial Visuals. AerialVisuals.ca. Archived from the original on 6 October 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
- ^ "Airframe Dossier - Convair C-131B Samaritan, s/n 53-7819 USAF, c/n 340-271, c/r N131CR". Aerial Visuals. Retrieved 15 September 2021.
- ^ "FAA Registry [N131CR]". Federal Aviation Administration. U.S. Department of Transportation. Retrieved 15 September 2021.
- ^ "Airframe Dossier – Convair C-131B Samaritan, s/n 53-7821 USAF, c/n 340-273". Aerial Visuals. AerialVisuals.ca. Archived from the original on 6 October 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
- ^ Veronico, Nick. "Outdoor Exhibits – C-131D "Samaritan"". Travis Air Force Base Heritage Center. Travis Heritage Center. Archived from the original on 5 June 2015. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
- ^ "C-131D Samaritan". March Field Air Museum. March Field Air Museum. Archived from the original on 31 May 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
- ^ "Airframe Dossier – Convair CV-240/340/440/580/600/640 / C-131 / R4Y / T-29, s/n 54-2810 USAF, c/n 340-207". Aerial Visuals. AerialVisuals.ca. Archived from the original on 14 October 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
- ^ "Convair VC-131D Samaritan". Aerospace Museum of California. Aerospace Museum of California. Archived from the original on 17 April 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
- ^ "Airframe Dossier – Convair C-131D-CO Samaritan, s/n 55-0292 USAF, c/n 340-315, c/r N8435H". Aerial Visuals. AerialVisuals.ca. Archived from the original on 2016-03-25.
- ^ "C-131D Samaritan". Selfridge Military Air Museum. Selfridge Military Air Museum. Archived from the original on 18 August 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
- ^ "Airframe Dossier – Convair C-131D Samaritan, s/n 55-0293 USAF, c/n 440-316, c/r N8436H". Aerial Visuals. AerialVisuals.ca. Archived from the original on 6 October 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
- ^ "C-131D Samaritan". The Leonardo Museum. The Leonardo Museum. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 12 December 2016.
- ^ "C-131D Samaritan". Air Mobility Command Museum. AMC Museum Foundation, Inc. Archived from the original on 30 April 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
- ^ "C-131D "Samaritan"". Hill Air Force Base. 27 September 2007. Archived from the original on 11 September 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
- ^ "Airframe Dossier – Convair C-131D-CO Samaritan, s/n 55-0301 USAF, c/n 440-329, c/r N8443H". Aerial Visuals. AerialVisuals.ca. Archived from the original on 6 October 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
- ^ "Vintage Transports, photos by Friends & Guests". RuudLeeuw.com. Archived from the original on 14 June 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
- ^ "Airframe Dossier - Convair C-131F Samaritan, s/n 140996 USN, c/n 340-279, c/r N351FL". Aerial Visuals. Retrieved 15 September 2021.
- ^ "FAA Registry". Federal Aviation Administration. U.S. Department of Transportation. Retrieved 15 September 2021.
- ^ "Airframe Dossier - Convair C-131F Samaritan, s/n 141008 USN, c/n 340-291, c/r N345GS". Aerial Visuals. Retrieved 15 September 2021.
- ^ "FAA Registry [N345GS]". Federal Aviation Administration. U.S. Department of Transportation. Retrieved 15 September 2021.
- ^ "Convair C-131F Samaritan". Yanks Air Museum. 2017-01-28. Retrieved 2019-12-26.
- ^ "C-131 Samaritan". National Naval Aviation Museum. Naval Aviation Museum Foundation. Archived from the original on 30 August 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
- ^ "Samaritan". Pima Air & Space Museum. PimaAir.org. Archived from the original on 6 October 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
- ^ "Airframe Dossier – Convair C-131F Samaritan, s/n 141025 USN, c/n 340-308, c/r VH-EAQ". Aerial Visuals. AerialVisuals.ca. Archived from the original on 6 October 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
- ^ "Convair NC-131H Total In-Flight Simulator (TIFS)". National Museum of the US Air Force. 9 October 2015. Archived from the original on 11 September 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
- ^ "Airframe Dossier – Convair NC-131H Samaritan, s/n 53-7793 USAF, c/n 340-245, c/r N793VS". Aerial Visuals. AerialVisuals.ca. Archived from the original on 6 October 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
- ^ "Airframe Dossier – Convair GT-29A Samaritan, s/n 49-1934 USAF, c/n 240-201". Aerial Visuals. AerialVisuals.ca. Archived from the original on 25 March 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
- ^ "T-29A "Flying Classroom"". Strategic Air Command & Aerospace Museum. Strategic Air Command & Aerospace Museum. Archived from the original on 1 August 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
- ^ "Flying Classroom". Pima Air & Space Museum. PimaAir.org. Archived from the original on 6 October 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
- ^ "Airframe Dossier – Convair T-29C Samaritan, s/n 53-3489 USAF, c/n 240–443". Aerial Visuals. AerialVisuals.ca. Archived from the original on 6 October 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
- ^ "Airframe Dossier - Convair T-29C Samaritan, s/n 52-1175 USAF, c/n 240-414". Aerial Visuals. Retrieved 15 September 2021.
- ^ Swanborough and Bowers 1969, p. 150.
- Bibliography
- Andrade, John. Militair 1982. London: Aviation Press Limited, 1982. ISBN 0 907898 01 7.
- Frawley, Gerald. "Convair CV-540, 580, 600, 640 & CV5800", The International Directory of Civil Aircraft 1997/98. Fyshwick ACT: Aerospace Publications, 1997. ISBN 1-875671-26-9.
- Gradidge, Jennifer. The Convairliners Story. Tonbridge, Kent, UK: Air-Britain (Historians) Ltd, 1997. ISBN 0-85130-243-2.
- Swanborough, F. G. and Peter M. Bowers. United States Military Aircraft since 1909. London: Punam, 1963.
- Wegg, John. General Dynamics Aircraft and Their Predecessors. London: Putnam, 1990. ISBN 0-85177-833-X.
External links
[edit]- Convair 240 – National Air and Space Museum
- C-131 Samaritan factsheet – National Museum of the United States Air Force
- C-131D Samaritan – March Field Air Museum
- C-131 Samaritan – GlobalSecurity.org
- C-131 Samaritan – The Aviation Zone
- Gunships – The Aviation Zone
Convair and General Dynamics aircraft | |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer designations | |
| Bombers | |
| Fighters and attack aircraft | |
| Civilian transports | |
| Military transports | |
| Experimental aircraft | |
| General Dynamics | |
United States trainer aircraft designations, Army/Air Force and Tri-Service systems | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Trainer (1925–1948) | |||||
| Basic Combat (1936–1940) | |||||
| Basic Trainer (1930–1948) | |||||
| Primary Trainer (1924–1948) | |||||
| Main sequence (1948–present) |
| ||||
| Alternate sequences |
| ||||
1 Not assigned • 2 Assigned to multiple types | |||||
| T-series (pre–1931) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R-series (1931–1962) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||