 A kickboxing match | |||||||||||||||||
| Focus | Punching, kicking, striking | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness | Full-contact | ||||||||||||||||
| Country of origin | Ancient history, possibly prehistoric[1] | ||||||||||||||||
| Famous practitioners | See list of kickboxers | ||||||||||||||||
| Descendant arts | Shootboxing, Vale Tudo, mixed martial arts | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Kickboxing (/ˈkɪkbɒksɪŋ/ KIK-boks-ing) is a full-contact hybrid martial art and boxing type based on punching and kicking. Kickboxing originated in the 1950s to 1970s.[2] The fight takes place in a boxing ring, normally with boxing gloves, mouth guards, shorts, and bare feet to favor the use of kicks. Kickboxing is practiced for self-defense, general fitness, or for competition.[3][4][5] Some styles of kickboxing include: full contact karate, Muay Thai, Japanese kickboxing, Lethwei, Sanda, and Savate.
Although since the dawn of humanity people have faced each other in hand-to-hand combat, the first documentation on the use of kicking and punching in sports combat is from ancient Greece[1] and ancient India.[6] But nevertheless, the term kickboxing originated in Japan, in the 1960s, and developed in the late 1950s from karate mixed with boxing, having some influence,[7][8][9][10] with competitions held since then.[11][12][13][14] American kickboxing originated in the 1970s and was brought to prominence in September 1974, when the Professional Karate Association (PKA) held the first World Championships. Historically, kickboxing can be considered a hybrid martial art formed from the combination of elements of various traditional styles. This approach became increasingly popular since the 1970s, and since the 1990s, kickboxing has contributed to the emergence of mixed martial arts via further hybridization with ground fighting techniques from Brazilian jiu-jitsu, and folk wrestling.
There is no single international governing body, although some international governing bodies include the World Association of Kickboxing Organizations (also known as WAKO), World Kickboxing Association, the Professional Kickboxing Association (PKA), International Sport Karate Association, International Kickboxing Federation, and World Kickboxing Network, among others. Consequently, there is no single kickboxing world championship, and champion titles are issued by individual promotions, such as Glory, K-1 and ONE Championship among others. Bouts organized under different governing bodies apply different rules, such as allowing the use of knees or clinching etc.[15]
Terminology
[edit]

The term "kickboxing" (キックボクシング, kikkubokushingu) can be used in a narrow and in a broad sense.
- The narrow use is restricted to the styles that self-identify as kickboxing, i.e., Japanese kickboxing (with its spin-off styles or rules such as shootboxing and K-1), Dutch kickboxing, and American kickboxing.
- In the wider sense, it includes all modern stand-up combat sports that allow both punching and kicking, including those mentioned above, Sanda, Muay Thai, Kun Khmer, Lethwei, Savate, Adithada, Musti-yuddha, and certain styles of karate (especially full contact karate).
The term itself was introduced in the 1960s as a Japanese anglicism by Japanese boxing promoter Osamu Noguchi[16] for a hybrid martial art combining Muay Thai and karate which he had introduced in 1958. The term was later also adopted by the American variant. Since there has been a lot of cross-fertilization between these styles, with many practitioners training or competing under the rules of more than one style, the history of the individual styles cannot be seen in isolation from one another.
The French term Boxe pieds-poings (literally "feet-fists-boxing") is also used in the sense of "kickboxing" in the general meaning, including French boxing (Savate) as well as American, Dutch and Japanese kickboxing, and Burmese and Thai boxing, any style of full contact karate, etc.
Styles and descendant arts
[edit]Arts labelled as kickboxing in the general sense include:
- Japanese kickboxing — combat style created in Japan, and origin of the term "kickboxing".
- Any style of Full contact karate
- Sanda (Chinese kickboxing) — The applicable component of wushu/kung fu of which takedowns and throws are legal in competition as well as all other sorts of striking (use of arms and legs).[17]
- Shootboxing — A Japanese form of kickboxing which allows throwing and submission while standing, similar to Sanda.
- American kickboxing — a style originating in the United States.
- Dutch Kickboxing — incorporate from three combat arts — Muay Thai, Boxing, and Kyokushin style of Karate.
- French Savate — a historical sport which developed in the 19th century.[18] It is mostly known for its foot-kicking techniques.
- Ukrainian Combat Hopak is mostly built around punching and kicking techniques.
- Indian Musti yuddha (also known as Muki boxing) and Adithada, a form of kickboxing that uses knee, elbow and forehead strikes in Southern kalaripayattu.
- Korean Kickboxing - Also Known as Kun Gek Do, it's a martial art created in South Korea which is a mixture of Boxing and Taekwondo.[19]
- The Southeast Asian family of kickboxing sports (also known as the ethnic neutral term of "muay" at the Southeast Asian Games[20]) including:
- Pradal Serey — a combat sport with an emphasis on kicking and extensive use of clinching for elbow techniques (Ring-wise). It is also known as Kun Khmer and based on the fighting techniques of the ancient Khmer Empire. It adopted boxing gloves, the boxing ring and rules inspired by European boxing after the arrival of French colonists in Cambodia.
- Thai Muay Boran (Ancient boxing) — Predecessor of Muay Thai, allows the use of headbutts.
- Thai kickboxing or Muay Thai — a modern Thai martial art that allows punching, kicking, knee and elbow strikes.[21]
- Burmese Lethwei — a traditional Burmese martial art of which has now grown into a popular kickboxing event that allows headbutts, knees and elbow strikes. It bears resemblance to neighboring Muay Thai, but Lethwei uses more punches and less kicks.[22] Head butt, choking and throwing techniques are also used. The fighting intensity and momentum is also considered faster. No boxing gloves are used. There is also no scoring system and knockout is the only way to win a match.
- Laotian Muay Lao — Laotian boxing which is similar to Muay Thai
- Filipino Yaw-Yan — Sayaw ng Kamatayan (Dance of Death) is the proper name for Yaw-Yan, a Filipino martial art developed by Napoleon Fernandez. The art resembles Muay Thai in a sense, but differs in the hip torquing motion as well as downward-cutting nature of its kicks and with strong emphasis on delivering attacks from long range.
History
[edit]Overview
[edit]
Since kickboxing is a broad term, understanding the history can be somewhat difficult, since combat is an inherent part of being human. Kicking and punching as an act of human aggression have probably existed throughout the world since prehistory.[23]
The earliest known depiction of any type of boxing comes from a Sumerian relief in Iraq from the 3rd millennium BC. Forms of kickboxing existed in ancient India. The earliest references to musti-yuddha come from classical Vedic epics such as the Ramayana and Rig Veda, compiled in the middle of the 2nd millennium BC. The Mahabharata describes two combatants boxing with clenched fists and fighting with kicks, finger strikes, knee strikes and headbutts.[24] Mushti Yuddha has travelled along the Indosphere and has been a preceder and a strong influence in many famous martial arts of Southeast Asia such as Muay Thai, Muay Laos and Pradal Serey (of Cambodia).
In the Pankration, a mixed martial art from ancient Greece, a form of kickboxing was used in its Anō Pankration modality, being able to use any extremity to hit. In addition, it is debated whether kicks were allowed in ancient Greek boxing, and while there is some evidence of kicks,[25][26][1] this is the subject of debate among scholars.[27][28]

The French were the first to include boxing gloves into a sport that included kicking and boxing techniques. In 1743, modern boxing gloves were invented by Englishman Jack Broughton. [29] Frenchman Charles Lecour added English boxing gloves to la boxe française. [30] Charles Lecour was a pioneer of modern savate or la boxe française. He created a form where both kicking and punching was used. [31] Lecour was the first to view savate as a sport and self-defense system. The French colonists introduced European boxing gloves into the native Asian martial arts in French Indochina. The use of European boxing gloves spread to neighboring Siam.
It was during the 1950s that a Japanese karateka named Tatsuo Yamada first established an outline of a new sport that combined karate and Muay Thai. This was further explored during the early 1960s, when competitions between karate and Muay Thai began, which allowed for rule modifications to take place. In the middle of the decade, the first events with the term kickboxing were held in Osaka.
By the 1970s and 1980s, kickboxing expanded beyond Japan and had reached North America and Europe. It was during this time that many of the most prominent governing bodies were formed.
- In Japan the sport was widely popular and was regularly broadcast on television before going into a dark period during the 1980s.
- In North America the sport had unclear rules so kickboxing and full contact karate were essentially the same thing.
- In Europe the sport found marginal success but did not thrive until the 1990s.
Since the 1990s kickboxing has been mostly dominated by the Japanese K-1 promotion, with some competition coming from other promotions and mostly pre-existing governing bodies.
Along with the growing popularity in competition, there has been an increased amount of participation and exposure in the mass media, fitness, and self-defense.
Japan
[edit]
On December 20, 1959, a Muay Thai match among Thai fighters was held at Asakusa town hall in Tokyo. Tatsuo Yamada, who established "Nihon Kempo Karate-do", was interested in Muay Thai because he wanted to perform karate matches with full-contact rules since practitioners are not allowed to hit each other directly in karate matches. At this time, it was unimaginable to hit each other in karate matches in Japan. He had already announced his plan which was named "The draft principles of project of establishment of a new martial art and its industrialization" in November 1959, and he proposed the tentative name of "karate-boxing" for this new art.[32] It is still unknown whether Nak Muay was invited by Yamada, but it is clear that Yamada was the only karateka who was really interested in Muay Thai. Yamada invited a champion Nak Muay (and formerly his son Kan Yamada's sparring partner), and started studying Muay Thai. At this time, the Thai fighter was taken by Osamu Noguchi who was a promoter of boxing and was also interested in Muay Thai.[13][33] The Thai fighter's photo was on the magazine "The Primer of Nihon Kempo Karate-do, the first number" which was published by Yamada.
There were "Karate vs. Muay Thai fights" on February 12, 1963. The three karate fighters from Oyama dojo (kyokushin later) went to the Lumpinee Boxing Stadium in Thailand and fought against three Muay Thai fighters. The three kyokushin karate fighters' names are Tadashi Nakamura, Kenji Kurosaki and Akio Fujihira (also known as Noboru Osawa). The Muay Thai team were composed of only one authentic Thai fighter.[34] Japan won by 2–1: Tadashi Nakamura and Akio Fujihira both KOed opponents by punch while Kenji Kurosaki, who fought the Thai, was KOed by elbow. The only Japanese loser Kenji Kurosaki was then a kyokushin instructor rather than a contender and temporarily designated as a substitute for the absent chosen fighter. On June of the same year, karateka and future kickboxer Tadashi Sawamura faced against top Thai fighter Samarn Sor Adisorn, in which Sawamura was knocked down 16 times and defeated.[34] Sawamura would use what he learned in that fight to incorporate in the evolving kickboxing tournaments.
Noguchi studied Muay Thai and developed a combined martial art which Noguchi named kick boxing, which absorbed and adopted more rules than techniques from Muay Thai. The main techniques of kickboxing are still derived from a form of Japanese full contact karate where kicks to the legs are allowed, kyokushin. In early competitions, throwing and butting were allowed to distinguish it from Muay Thai. This was later repealed. The Kickboxing Association, the first kickboxing sanctioning body, was founded by Osamu Noguchi in 1966 soon after that. Then the first kickboxing event was held in Osaka on April 11, 1966.
Tatsu Yamada died in 1967, but his dojo changed its name to Suginami Gym, and kept sending kickboxers off to support kickboxing.[35]
Kickboxing boomed and became popular in Japan as it began to be broadcast on TV.[36] By 1970, kickboxing was telecast in Japan on three different channels three times weekly. The fight cards regularly included bouts between Japanese (kickboxers) and Thai (Muay Thai) boxers. Tadashi Sawamura was an especially popular early kickboxer.[37][38] In 1971 the All Japan Kickboxing Association (AJKA) was established and it registered approximately 700 kickboxers. The first AJKA Commissioner was Shintaro Ishihara, the longtime Governor of Tokyo. Champions were in each weight division from fly to middle. Longtime Kyokushin practitioner Noboru Osawa won the AJKA bantamweight title, which he held for years. Raymond Edler, an American university student studying at Sophia University in Tokyo, took up kickboxing and won the AJKC middleweight title in 1972; he was the first non-Thai to be officially ranked in the sport of Thai boxing, when in 1972 Rajadamnern ranked him no. 3 in the Middleweight division. Edler defended the All Japan title several times and abandoned it. Other popular champions were Toshio Fujiwara and Mitsuo Shima. Most notably, Fujiwara was the first non-Thai to win an official Thai boxing title, when he defeated his Thai opponent in 1978 at Rajadamnern Stadium winning the lightweight championship bout.
By 1980, due to poor ratings and then infrequent television coverage, the golden-age of kickboxing in Japan was suddenly finished. Kickboxing had not been seen on TV until K-1 was founded in 1993.[39][40]
In 1993, as Kazuyoshi Ishii (founder of Seidokaikan karate) produced K-1 under special kickboxing rules (no elbow and neck wrestling) in 1993, kickboxing became famous again.[41][42] In the mid-1980s to early 1990s, before the first k-1, Kazuyoshi Ishii also partook in the formation of glove karate as an amateur sport in Japan. Glove karate is based on knockdown karate rules, but wearing boxing gloves and allowing punches to the head. In effect, it is oriental rules kickboxing with scoring based on knockdowns and aggression rather than the number of hits. As K-1 grew in popularity, Glove karate for a while became the fastest-growing amateur sport in Japan.
North America
[edit]
Count Dante, Ray Scarica and Maung Gyi held the United States' earliest cross-style full-contact style martial arts tournaments as early as 1962. Between 1970 and 1973 a handful of kickboxing promotions were staged across the US. The first recognized bout of this kind occurred on January 17, 1970, and came about when Joe Lewis, a Shorin Ryu stylist who had also studied Jeet Kune Do with the legendary Bruce Lee, and noted champion in the Karate tournament circuit, grew disillusioned with the point-sparring format and sought to create an event that would allow martial artists to fight to the knock out. Enlisting the help of promoter Lee Faulkner,[43] training in boxing and combining the techniques of boxing and Karate for the first time in America, Lewis arranged the bout to be held at the 1st Pro Team Karate Championships. Lewis faced Kenpo stylist Greg "Om" Baines,[44] who had defeated two opponents in years pasts. Lewis won the fight by knockout in the second round. The event was advertised as "Full contact" but the announcers referred to it as Kickboxing, and rules included knees, elbows and sweeps.[44] Lewis would defend his U.S Heavyweight champion title 10 times, remaining undefeated until he came back from his retirement. In the early days, the rules were never clear; one of the first tournaments had no weight divisions, and all the competitors fought off until one was left. During this early time, kickboxing and full contact karate are essentially the same sport.
The institutional separation of American full-contact karate from kickboxing occurred with the formation of the Professional Karate Association (PKA) in 1974 and of the World Kickboxing Association (WKA) in 1976. They were the first organised body of martial arts on a global scale to sanction fights, create ranking systems, and institute a development programme.
The International Kickboxing Federation (IKF) and the International Sport Kickboxing Association (ISKA) have been the only organizations to have thrived in the modern era.
The International Kickboxing Federation (IKF) was founded in 1992 by Steve Fossum and Dan Stell. Stell eventually stepped down to go back to fighting while Fossum continued with the organization. In 1999 Fossum and Joe Taylor of Ringside Products created the first amateur open North American tournament for Kickboxing and Muay Thai, now the IKF World Classic.
After ending its venture with K-1 in 2006, ISKA co-operated the World Combat League with Chuck Norris, and Strikeforce MMA in partnership with Silicon Valley Entertainment (SVE), an investor group who also own the San Jose Sharks. Norris passed the WCL to his son-in-law Damien Diciolli in 2007, and it has since become inactive. Strikeforce MMA was sold to UFC in 2011.
The ISKA expanded into sport (tournament) martial arts about 15 years ago,[when?] and is a co-operator along with WAKO and Global Marketing Ventures (GMV) in the global Open World Tour (OWT) the first worldwide pro circuit of sport karate professional competitors. It sanctions and assists in the annual US Open & ISKA World Championships that anchors the OWT and the North American-based NASKA Tour. The US Open & ISKA World Championships is broadcast live on ESPN2 and ESPN3 each year.
Other kickboxing sanctioning bodies include World Association of Kickboxing Organizations (primarily amateurs) and KICK International.
Europe
[edit]
In West Germany, American-styled kickboxing was promulgated from its inception in the 1970s by Georg F. Bruckner, who in 1976 was the co-founder of the World Association of Kickboxing Organizations. The term "kickboxing" as used in German-speaking Europe is therefore mostly synonymous with American kickboxing. The low-kick and knee techniques allowed in Japanese kickboxing, by contrast, were associated with Muay Thai, and Japanese kickboxing went mostly unnoticed in German-speaking Europe before the launch of K-1 in 1993.
By contrast, in the Netherlands kickboxing was introduced in its Japanese form, by Jan Plas and Thom Harinck who founded NKBB (The Dutch Kickboxing Association) in 1976. Harinck also founded the MTBN (Dutch Muay Thai Association) in 1983, and the WMTA (World Muay Thai Association) and the EMTA (European Muay Thai Association) in 1984. The most prominent kickboxing gyms in the Netherlands, Mejiro Gym, Chakuriki Gym and Golden Glory, were all derived from or were significantly influenced by Japanese kickboxing and kyokushin karate.
Dutch athletes have been very successful in the K-1 competitions. Out of the 19 K-1 World Grand Prix championship titles issued from 1993 to 2012, 15 went to Dutch participants (Peter Aerts, Ernesto Hoost, Remy Bonjasky, Semmy Schilt and Alistair Overeem). The remaining four titles were won by Branko Cikatić of Croatia in 1993, Andy Hug of Switzerland in 1996, Mark Hunt of New Zealand in 2001 and Mirko Filipović of Croatia in 2012.
Modern sport
[edit]Kickboxing promotions
[edit]Some of the top kickboxing promotions in the world are:
Kickboxing promoters
[edit]Some of the notable kickboxing promoters in the world are:
- Chatri Sityodtong - ONE Championship
- Eduard Irimia - Superkombat
- Kazuyoshi Ishii - K-1
- Pierre Andurand - Glory
- Joe Corley - PKA
- Sadaharu Tanikawa - Fighting and Entertainment Group
Kickboxing styles and rulesets
[edit]
Kickboxing has a number of different rulesets. For example, Oriental/K-1[broken anchor] rules allow punches, high and low kicks and even knee strikes, while American kickboxing is limited to punches and kicks only above the belt (high kicks).
In the first two decades of the 21st century, several larger kickboxing promotions such as Glory, One Championship and Bellator Kickboxing have adopted the k1/oriental[broken anchor] rule set, which allows knee strikes, kicking and punching.[45][46][47]
Japanese Kickboxing
[edit] Oriental rules kickboxing | |
| Focus | Striking |
|---|---|
| Hardness | Full-contact |
| Country of origin | Japan, 1950s-1960s |
| Famous practitioners | See below |
| Parenthood | Full Contact Karate, Muay Thai |
| Descendant arts | Shootboxing |
| Olympic sport | No |
Oriental rules (also known as K-1 rules or unified rules,[48][49] and sometimes referred to as Japanese kickboxing) was the first combat sport that adopted the name of "kickboxing" in 1966, later termed "Japanese kickboxing" as a retronym.[12] Since the 1990s, many of the largest kickboxing promotions such as K-1, ONE Championship, Glory and Bellator Kickboxing adopted this ruleset.[45][46][47][50] Oriental rules began to be developed by the Japanese boxing promoter Osamu Noguchi and Karate practitioner Tatsuo Yamada, and it was initially intended as a mix of Karate and Muay Thai,[51] but it was later affected also by the Dutch rules[broken anchor], which were first formalised in the Netherlands in the 1970s. The primary difference between Muay Thai and Oriental Kickboxing was the prohibition of elbow strikes and throws. In addition, the amount of clinch fighting is drastically decreased. These changes were aimed at reducing injuries and making bouts more accessible to TV viewers. Oriental rules bouts were traditionally fought over 5, 3-minute rounds but 3 round bouts have since become popular. The male kickboxers are bare-chested wearing shorts (although trousers and karate gis have been worn) and protective gear including: mouth-guard, hand-wraps, shin-wraps, 10 oz (280 g) gloves.
Notable fighters under K-1 rules include Semmy Schilt, Badr Hari, Ernesto Hoost, Albert Kraus, Masato, Peter Aerts, Remy Bonjasky, Giorgio Petrosyan, Buakaw and Andy Souwer.
Rules:
- Fighters are allowed to strike their opponent with punches, kicks, including kicks below the waist, except for the groin, sweeps and knees (only to the body).
- Elbow strikes are forbidden.
- Very limited or no clinch fighting is allowed (in some competitions clinching is completely illegal,[52] in others only one single strike is allowed before the clinch has to be released,[53] in other promotions just a few seconds of clinch are allowed[50]).
- Throws and headbutts are not allowed.
- Bouts are 3 to 5 rounds (lasting 3 minutes each) with a 1-minute rest in between rounds.
Korean Kickboxing
[edit]Gwon Gyokdo, also known as Kun Gek Do and Kyuk Too Ki is a style of Kickboxing from Korea which was founded by Jung Mo-Do. It is a hybrid style which is composed by Taekwondo, Western Boxing and Muay Thai rules and techniques. Korean Kickboxing uses the basic kicking style of Taekwondo, but also adds typical Muay Thai techniques, as well as footwork and dodging tactics of Western Boxing.
- Punches and kicks are allowed.
- Elbow strikes and knee strikes are allowed.
- Throwing and clinching is allowed.
- Spinning techniques are allowed.
American Kickboxing
[edit] A Full contact match | |
| Focus | Striking |
|---|---|
| Hardness | Full-contact |
| Country of origin | United States, 1960s-1970s |
| Famous practitioners | See below |
| Parenthood | Shotokan, Boxing, Tang Soo Do |
| Olympic sport | No |
Full Contact (also referred to as American Kickboxing) is essentially a mixture of Western boxing and traditional karate.[58] The male kickboxers are bare-chested wearing kickboxing trousers and protective gear including: mouth-guard, hand-wraps, 10 oz (280 g) boxing gloves, groin-guard, shin-pads, and kick-boots and protective helmet (for amateurs and those under 16). Female kickboxers will wear a sports bra and chest protection in addition to the male clothing/protective gear.[59]
Notable fighters under full contact rules include, Dennis Alexio, Joe Lewis, Rick Roufus, Jean-Yves Thériault, Benny Urquidez, Bill Wallace, Demetrius Havanas, Billy Jackson, Akseli Saurama, Pete Cunningham, and Don "The Dragon" Wilson
Rules:[60]
- Opponents are allowed to hit each other with punches and kicks, striking above the waist.
- Elbows and knees are forbidden.
- Clinch fighting and grappling are forbidden, sweeps are legal boot-to-boot.
- Bouts are usually 3 to 10 rounds (lasting 2 minutes each) with a 1-minute rest in between rounds.
- The Referee is responsible for fighter safety and keeping to the rules; judges count legal techniques and note the points on the scoring card or with the help of the electronic system.
Semi Contact
[edit]
Semi Contact or Points Fighting, is the variant of American kickboxing most similar to karate, since it consists in fighting for the purpose of scoring points with an emphasis on delivery, speed, and technique. Under such rules, fights are held on the tatami, presenting the belts to classify the fighters in order of experience and ability. The male kickboxers wear shirts and kickboxing trousers as well as protective gear including: mouth-guard, hand-wraps, 10 oz (280 g). boxing gloves, groin-guard, shin-pads, kick-boots, and headgear. The female kickboxers will wear a sports bra and chest protection in addition to the male clothing/protective gear.
Notable fighters under semi-contact rules include Raymond Daniels, Michael Page, Stephen Thompson and Gregorio Di Leo.
Rules:[61]
- Fighters can score through punches or kicks, striking above the waist, and foot sweeps, executed below the ankle.
- Punches, kicks and foot sweeps are awarded 1 point. Kicks to the head or jumping kicks to the body are awarded 2 points. Jumping kicks to the head are awarded 3 points.
- Hook kicks and Axe kicks are allowed but must be executed with the sole of the foot.
- The use of the shins is seldom allowed, save for jumping and spinning techniques.
- Elbows, knees and spinning backfists are forbidden.
- Clinch fighting, throws and sweeps (with the exception of foot sweeps) are forbidden.
- Bouts are usually 3 rounds (lasting 2–3 minutes each) with a 1-minute rest in between rounds.
Dutch Kickboxing
[edit]| Focus | Striking |
|---|---|
| Hardness | Full-contact |
| Country of origin | Netherlands, 1970s |
| Famous practitioners | See below |
| Parenthood | Muay Thai, Kyokushin Karate, Boxing |
| Olympic sport | No |
Dutch rules (sometimes referred to as Dutch Kickboxing) came about when Japanese kickboxing[broken anchor] and Muay Thai were first introduced in Holland in the 70s. European rules began to be developed by the Netherland Kick Boxing Bond in the 1970s when the late Jan Plas brought the sport from Japan to his native country. The primary difference between Dutch rules and full Muay Thai rules was the prohibition of elbow strikes and the limited knees strikes (only to the body). However, elbows were allowed when both parties agree to it. These changes were aimed at reducing injuries and making bouts more accessible to TV viewers. Like the Thai counterpart, the fights are accompanied with the traditional Thai music during a battle. The Dutch kickboxing rules were instrumental to the development of the K-1 rules.
Notable fighters under Dutch rules include Alistair Overeem, Bas Rutten, Melvin Manhoef, Gegard Mousasi, Remy Bonjasky and Peter Aerts.
Rules:[62]
- Rounds are up to 3 and they last 3 minutes.
- Punches and kicks are allowed.
- Elbow strikes are illegal, but can be allowed if both fighters agree to use them.
- Knees are illegal when they're striking the head, but are legal when they're striking the body.
- Throws, Sweeps and Trips are forbidden.
- Clinching is allowed for 5 seconds at best and it's only legal if it's used to cause damage to the opponent.
Freestyle Kickboxing
[edit]
International rules, or freestyle kickboxing (also known as Low Kick in the United States), contrast with full contact rules in that it also allows low kicks. The male kickboxers are bare-chested, wearing kickboxing trousers or shorts and protective gear, including mouth-guard, hand wraps, Boxing gloves, shin guards, and groin guard. The female kickboxers will wear a sports bra and chest protection in addition to the male clothing/protective gear.[63]
Notable fighters under international rules include Rick Roufus and Abraham Roqueñi.
Rules:
- Fighters are allowed to strike their opponent with punches, knees and kicks, including kicks below the waist, except for the groin.
- Elbows are forbidden.
- Throws and sweeps are forbidden.
- Clinch is allowed only for 5 seconds.
- Bouts are 3 to 5 rounds for amateurs and 3 to 10 rounds for professionals, all rounds lasting 2–3 minutes each. Each round has a 1-minute rest in between rounds.
WKA Kickboxing
[edit]WKA Kickboxing is a style promoted by the World Kickboxing Association, and uses a mixture of Muay Thai, Japanese Kickboxing and Full Contact Kickboxing moves and rulesets. [64]
Rules:
- World Title bouts consist of 12 rounds, continental bouts consist of 10 rounds and national bouts consist of 5 rounds.
- The contestants must wear uniforms, tapes and bandages approved by the association.
- The contestants also wear groin protectors, mouthpieces and hair stays.
- Standard fouls (eye gouges, groin shots, bites, insults, etc.), are illegal.
- Knee Strikes, elbow strikes, back fists, clubbing strikes, headbutts, palm strikes, anti-joint techniques, grabbing the opponent's legs and arms, holding a clinch for too long are all illegal.
- Opponents who stall for too long during the fight are warned by the referee.
- A Knockout is declared of the fighter doesn't stand up after an 8 count.
ISKA Kickboxing
[edit]ISKA Kickboxing is a style promoted by the International Sport Kickboxing association from Europe, and it's a blend of Full Contact, Japanese, Muay Thai and Freestyle Kickboxing rules.[65]
Rules:
- Fighters must wear an uniform approved by the promotion, and it varies depending on the type of match.
- Gloves, footpads, groin protectors and mouthpieces must be worn by all fighters while the use of shinpads, elbowpads and forearm pads isn't allowed.
- The use of grappling techniques, except sweeps are forbidden.
- Standard fouls are illegal.
- Special foul rules are used for spinning back fists, and it often results in penalties.
- Blocking an opponent's limb to prevent him/her from striking is illegal.
- A knockout is declared after the fighter doesn't get up suring an 8 count.
- Surpassing a specific number of Knockdowns during the bout don't determine a TKO win.
Muay Thai
[edit]
Muay Thai, or Thai boxing, rules usually sees bouts contested over 5, 3 minute rounds and male fighters bare-chested wearing shorts and protective gear including: mouth-guard, hand-wraps, shin-wraps, 10 oz (280 g) boxing gloves, groin-guard and sometimes prajioud arm bands. 4oz MMA-style, open-finger gloves are sometimes used.[66] The female Thaiboxers will wear a sports bra and chest protection in addition to the male clothing/protective gear. Muay Thai is unique in that it is the only style of kickboxing that allows elbows, knees, clinch fighting, throws, sweeps and low kicks.[67][68][69] Groin strikes were allowed until the 1980s in international Muay Thai and are still partially allowed in Thailand itself (though the boxers wear cups to lessen the impact).[70] Kicking to mid-body and head are scored highly generating a large number of points on judges' scorecards. Moreover, kicking is still judged highly even if the kick was blocked. In contrast, punching is worth fewer points.
Notable fighters under Muay Thai rules include Apidej Sit Hrun, Buakaw Por. Pramuk, Changpuek Kiatsongrit, Rob Kaman, Ramon Dekkers, Coban Lookchaomaesaitong, Dieselnoi Chor Thanasukarn, Saenchai P.K. Saenchaimuaythaigym, Samart Payakaroon and Yodsanklai Fairtex.
Rules:
- Fighters are allowed to strike their opponent with punches, kicks, including kicks below the waist, elbows and knees.
- Clinch fighting is allowed.
- Certain throws and sweeps are allowed (however hip throws and sweeps with the back of the ankle are illegal).[67][68][69]
- Bouts are generally 5 rounds (lasting 3 minutes each) with a 2-minute rest in between, but 3 round fights with a 1-minute rest are used in some promotions.
Lethwei
[edit] A Lethwei match. Different from other kickboxing styles, it is fought bareknuckle | |
| Focus | Striking |
|---|---|
| Hardness | Full-contact |
| Country of origin | Myanmar |
| Olympic sport | No |
Lethwei is a type of kickboxing originating from Myanmar that features minimal rules and protective equipment. Lethwei not only allows the use of headbutts but actually emphasizes it, and fighters wear no gloves. Bouts can only be won with a knockout, either a proper or a technical. Uniquely, after one knockout and two minutes rest, the knocked out fighter may still choose to continue the fight once, unless they are knocked out in the final round. There are no points; if no knockout happens before the end of the fifth round, the fight is declared a draw. Male fighters are bare-chested and wear shorts. Protective gear consists of a mouth-guard, groin-guard, and wraps around hands and feet. Female fighters wear a sports bra and chest protection in addition to the male clothing and protective gear.
Notable fighters under Lethwei rules include Soe Lin Oo, Tun Tun Min, Dave Leduc, Too Too and Cyrus Washington.
Rules:
- Opponents are allowed to strike each other with punches, kicks, including kicks below the waist, elbows, knees and headbutts.
- Clinch fighting, throws and sweeps are allowed.
- Bouts are 5 rounds (lasting 3 minutes each) with a 2-minute rest in between rounds.
Sanda
[edit]
Sanda or Sanshou (also known as Chinese boxing and Chinese kickboxing) is a form of kickboxing originally developed by the Chinese military based upon the study and practices of traditional Kung fu and modern combat fighting techniques; it combines traditional kickboxing, which include close range and rapid successive punches and kicks, with wrestling, takedowns, throws, sweeps, kick catches, and in some competitions, even elbow and knee strikes. The male fighters are bare-chested wearing shorts and protective gear including: mouth-guard, hand-wraps, 10 oz (280 g) boxing gloves and groin-guard. The female kickboxers will wear a sports bra and chest protection in addition to the male clothing/protective gear.
Notable fighters under Sanshou rules include Wei Rui, Fang Bian, Jia Aoqi, Muslim Salikhov, Pat Barry, Zhang Tiequan, Liu Hailong, Cung Le, Shahbulat Shamhalaev and Shamil Zavurov.
Rules:
- Fighters are allowed to strike their opponent with punches and kicks, including kicks below the waist, except for the groin.
- Elbows and knees are forbidden (with the exception of some competitions).
- Clinch fighting, throws and sweeps are allowed.
- Bouts are 5 rounds (lasting 3 minutes each) with a 1-minute rest in between rounds.
Shootboxing
[edit]Shootboxing (also known as Standing Vale Tudo) is a unique style of hybrid kickboxing popular in Japan that utilizes standing submissions such as chokeholds, armlocks and wristlocks in addition to kicks, punches, knees and throws. The male fighters are bare-chested wearing skin tight trousers and protective gear including: mouth-guard, hand-wraps, 10 oz (280 g) boxing gloves and groin-guard. The female kickboxers will wear a sports bra and chest protection in addition to the male clothing/protective gear.
Notable fighters under shootboxing rules include Rena Kubota, Kenichi Ogata, Hiroki Shishido, Ai Takahashi and Andy Souwer.
Rules:
- Opponents are allowed to strike each other with punches, kicks, including kicks below the waist, except for the groin, and knees.
- Elbows are forbidden (since 2001).
- Clinch fighting, throws and sweeps are allowed.
- Standing submissions are allowed.
- Bouts are 3 rounds (lasting 3 minutes each) with a 1-minute rest in between rounds.
Draka Kickboxing
[edit]Draka, also known as Russian Kickboxing, is a hybrid style of Kickboxing which was developed and founded by Igor Ejov in 1992, and its mainly promoted by the World Wide Draka Federation (WWDF) and the International Kickboxing Draka Federation (IKDF). The first event where this style was featured, was held in the U.S. by Ejov in association with World Wide Kickboxing Promotions. This style particularly resembles Sanda and Shoot Boxing with Muay Thai, Boxing, Sambo, Judo and Wrestling techniques added to the mixture.
- Fighters are allowed to use kicks, knees, punches and elbows.
- The use of takedowns, throws and sweeps is also allowed.
- Groundfighting and chokeholds are forbidden.
Xtreme Gladiator Kickboxing
[edit]| Focus | Hybrid, Striking, Grappling |
|---|---|
| Hardness | Full-contact |
| Country of origin | United States |
| Parenthood | Boxing, Kickboxing, Muay Thai, Sanshou, Judo, Wrestling, Brazilian Jiu Jitsu, Mixed Martial Arts |
| Olympic sport | No |
Xtreme Gladiator is a hybrid style of Kickboxing created by the International Kickboxing Federation, which is a mixture of Boxing, Muay Thai, Sanshou, Wrestling and Judo techniques. Just like Shoot Boxing, it's also one of the only styles who allows submission techniques like joint locks, chokeholds and strangles both standing and on the ground, although there is a 30 second or 1 minute limit time for groundfighting.
Rules:[75]
- Closed, Hemmer, Open Handed fists and strikes are legal.
- Forearm strikes and Elbow strikes are legal.
- Standing foot stomps are legal.
- Oblique kicks to the inside leg are allowed.
- Knees are allowed to the head, body and shins when the fight is upright.
- Upkicks from the ground are legal.
- Every tipe of throw, slam and takedown is allowed.
- Chokes and Joint Locks are legal.
- Downed stomps are illegal.
- Kicks and knees to the head of a grounded opponent are illegal.
- 12-6 Elbows are illegal.
- Standard fouls are illegal.
Scoring Criteria and judging system
[edit]Kickboxing matches are judged using a similar system to boxing, with judges scoring the bout round by round using the 10-Point-Must system.[76] Under this system, judges assign a score to each fighter based on their performance in the round, with the winner receiving 10 points and the loser a lower score, typically 9 or fewer.[77] Judges must consider factors such as the volume of strikes landed, the damage inflicted, and the overall control exhibited by each competitor. Points are awarded for clean, impactful strikes that land on the opponent, as well as for evading or blocking incoming attacks and demonstrating control of the center of the ring.[78]
Techniques
[edit]Punching
[edit]Punching techniques are very much identical to boxing punches, including
- Jab – straight punch from the front hand. The arm extends from the side of the torso which is quickly turned concurrently with this action. A jab may be directed at an opponent's head or body, and is often used in conjunction with the cross.
- Cross – straight punch from the back hand
- Hook – rounded punch to either the head or body in an arching motion, usually not scored in points scoring
- Uppercut – rising punch striking to the chin
- Backfist usually from the front hand, reverse-back fist and spinning back-fist both usually from the back hand – are strikes to the head, raising the arm and bending the arm at the elbow and then straightening the arm quickly to strike to the side of the head with the rear of the knuckles.
- Flying-punch struck usually from the rear hand, the combatant hops on the front foot, kicking back with the rear foot and simultaneously extending the rear hand as a punch, in the form of "superman" flying through the sky.
- Overhand (overcut or drop) – a semi-circular and vertical punch thrown with the rear hand. It is usually performed when the opponent is bobbing or slipping. The strategic utility of the drop relying on body weight can deliver a great deal of power.
- Bolo punch – a combination of a wide uppercut/right cross/swing that was delivered seemingly from the floor.
- Haymaker - The Haymaker is a wide angle punch similar to a hook, but instead of getting power from body rotation, it gets its power from its large loop. It is considered an unsophisticated punch, and leaves one open to a counter.
Kicking
[edit]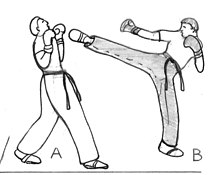
The standard kicking techniques are:
- Roundhouse kick or circle kick – Striking with the front of the foot or the shin to the head or the body in a chopping motion
- Front kick or push Kick/high Kick – Striking face or chest on with the balls of the foot
- Side kick – Striking with the heel of the foot with leg parallel to the ground, can be performed to either the head, leg or body
- Semi-circular kick or forty five degree roundhouse kick
There are a large number of special or variant kicking techniques, including spinning kicks, jumping kicks, and other variants such as
- Hook kick (heel kick) – Extending the leg out to the side of the body, and hooking the leg back to strike the head with either the heel or sole
- Crescent kick and forward crescent kick
- Axe kick – is a stomp out kick or axe kick. The stomp kick normally travels downward, striking with the side or base heel (typically the base heel)
- Back kick – is delivered with the base heel of the foot.
- Sweeping – One foot or both feet of an opponent may be swept depending upon their position, balance and strength.
Spinning versions of the back, side, hook and axe kicks can also be performed along with jumping versions of all kicks.
Knee
[edit]The knee techniques in Japanese kickboxing, indicative of its Muay Thai heritage, are the main difference that separates this style from other kickboxing rules.[79] See ti khao for details.
- Straight knee (long-range knee kick or front heel kick). This knee strike is delivered with the back or reverse foot against an opponent's stomach, groin, hip or spine an opponent forward by the neck, shoulder or arm.
- Flying knee – can be delivered with the front or back foot. It makes an explosive snap upwards to strike an opponent's face, chin, throat or chest.
- Hook knee – can be delivered with the front or back foot. It makes a half circle spin and strikes the sides of an opponent.
- Side knee – is a highly-deceptive knee technique used in close-range fighting. The knee is lifted to the toes or lifted up, and is snapped to left and right, striking an opponent's sensitive knee joints, insides of thighs, groin.
Defense
[edit]There are three main defensive positions (guards or styles) used in kickboxing. Within each style, there is considerable variation among fighters, as some fighters may have their guard higher for more head protection while others have their guard lower to provide better protection against body punches. Many fighters vary their defensive style throughout a bout in order to adapt to the situation of the moment, choosing the position best suited to protect them.
- Slip – Slipping rotates the body slightly so that an incoming punch passes harmlessly next to the head. As the opponent's punch arrives, the boxer sharply rotates the hips and shoulders. This turns the chin sideways and allows the punch to "slip" past. Muhammad Ali was famous for extremely fast and close slips.
- Bob and weave – bobbing moves the head laterally and beneath an incoming punch. As the opponent's punch arrives, the kickboxer bends the legs quickly and simultaneously shifts the body either slightly right or left. Once the punch has been evaded, the kickboxer "weaves" back to an upright position, emerging on either the outside or inside of the opponent's still-extended arm. To move outside the opponent's extended arm is called "bobbing to the outside". To move inside the opponent's extended arm is called "bobbing to the inside".
- Blocking – defender's hard blocks to stop a strike in its path so preventing it reaching its target (e.g. the shin block described in more detail below)
- Parry/Block – Parrying or blocking uses the kickboxer's hands as defensive tools to deflect incoming attacks. As the opponent's punch arrives, the boxer delivers a sharp, lateral, open-handed blow to the opponent's wrist or forearm, redirecting the punch.
- The cover-up – Covering up is the last opportunity to avoid an incoming strike to an unprotected face or body. Generally speaking, the hands are held high to protect the head and chin and the forearms are tucked against the torso to impede body shots. When protecting the body, the kickboxer rotates the hips and lets incoming punches "roll" off the guard. To protect the head, the kickboxer presses both fists against the front of the face with the forearms parallel and facing outwards. This type of guard is weak against attacks from below.
- The clinch – Clinching is a form of standing grappling and occurs when the distance between both fighters has closed and straight punches cannot be employed. In this situation, the kickboxer attempts to hold or "tie up" the opponent's hands or enter neck wrestling position. In one way to perform a clinch, the kickboxer loops both hands around the outside of the opponent's shoulders, scooping back under the forearms to grasp the opponent's arms tightly against his own body. In this position, the opponent's arms are pinned and cannot be used to attack. Other forms of clinch involve getting control of opponents neck by collar tie or upper body by underhooks, overhooks and body lock. It is often in the clinch where knee, elbow, sweep and throw techniques are used.
Brain injury and CTE
[edit]Knocking a person unconscious or even causing a concussion may cause permanent brain damage.[80] There is no clear division between the force required to knock a person out and the force likely to kill a person.[81] Also, contact sports, especially combat sports, are directly related to a brain disease called chronic traumatic encephalopathy, abbreviated CTE. This disease begins to develop during the life of the athlete, and continues to develop even after sports activity has ceased. In addition, repetitive and subconcussive blows to the head, and not just concussions, cause CTE.[82][83][84][85][86][87]
See also
[edit]- Boxing (disambiguation)
- Kickboxing weight classes
- List of kickboxing organizations
- List of male kickboxers
- List of female kickboxers
- Women's kickboxing
References
[edit]- ^ a b c Pyx Lax (Kick-Punch) Kick Boxing: Ancient Greek Martial Arts by Gregory Zorzos ISBN 1441461477
- ^ "Is it just karate without the philosophy?". Independent.co.uk. 16 April 1995.
- ^ "Directory : Kick-boxing is the hottest workout in town, thanks to a streetwise fighter called Catwoman. Here's where to get your kicks". The Los Angeles Times. July 17, 1992. Archived from the original on 31 January 2021. Retrieved 2010-12-21.
- ^ "Offering a Fighting Chance to Get in Shape". The Los Angeles Times. May 22, 1998. Archived from the original on 5 May 2021. Retrieved 2010-12-21.
- ^ "Powerful! Kickboxing Is A Killer, Thriller Workout". Chicago Tribune. August 18, 1998. Archived from the original on 28 October 2020. Retrieved 2010-11-25.
- ^ Section XIII: Samayapalana Parva, Book 4: Virata Parva, Mahabharata.
- ^ Martin, Andy (April 17, 1995). "Is it just karate without the philosophy? Not according to Big Daddy Chris Ozar reigning from Jersey City. He's been kickboxing for years". The Independent. London. Retrieved 2010-08-20.
- ^ "Kickboxing climbs up to be at par with other martial arts". The Economic Times. July 19, 2009. Retrieved 2010-11-25.
- ^ "A History and Style Guide of Kickboxing".
- ^ "Kickboxing Rules: How To Kickbox | Rules of Sport". www.rulesofsport.com. Retrieved 2021-12-14.
- ^ ""A HISTORY OF KICKBOXING" : NORTH AMERICA'S SURPRISINGLY TABOO 'KICKBOXING' HISTORY! (Part 1) : 1950s and 1960s" (PDF). Kick-france.fr. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2018-11-02. Retrieved 27 October 2018.
- ^ a b Cimadoro, Giuseppe (October 2017). "Acute neuromuscular, cognitive and physiological responses to a Japanese kickboxing competition in semi-professional fighters". The Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness. 58 (12): 1720–1727. doi:10.23736/S0022-4707.17.07859-8. PMID 29083128. S2CID 5975453.
- ^ a b "Black Belt October 1968". October 1968. Retrieved 10 January 2015.
- ^ "Black Belt February 1972". February 1972. Retrieved 10 January 2015.
- ^ Streissguth, Thomas (2013-08-01). Kickboxing. Bellwether Media. ISBN 9781612113920.
- ^ "Black Belt". February 1972. Retrieved 16 February 2015.
- ^ "Kungfu goes international". Shanghai Star. August 1, 2002. Archived from the original on July 4, 2011. Retrieved 2010-11-25.
- ^ "Fitness Bound; Holiday pounds? Give 'em a swift kick". The Los Angeles Times. December 18, 2006. Retrieved 2010-11-25.
- ^ "Korean Kickboxing".
- ^ said to be from a Sanskrit word mavya[citation needed]
- ^ "Get in shape at a Thai kickboxing camp". USA Today. October 13, 2008. Retrieved 2010-12-07.
- ^ Calderon, Justin (18 September 2014). "Lethwei boxing in Myanmar: Asia's new martial arts sensation". CNN. Retrieved 2022-11-18.
- ^ Michael Poliakoff. "Encyclopædia Britannica entry for Boxing". Britannica.com. Retrieved 18 May 2013.
- ^ Section XIII: Samayapalana Parva, Book 4: Virata Parva, Mahabharata.
- ^ Potter, David (2012). The Victor's Crown: A History of Ancient Sport from Homer to Byzantium. Oxford University Press, USA. ISBN 978-0-19-984273-5.
- ^ "Ancient Roman Boxing". 14 November 2015.
- ^ Crowther, Nigel B. (1990). "The Evidence for Kicking in Greek Boxing". The American Journal of Philology. 111 (2): 176–181. doi:10.2307/294973. JSTOR 294973.
- ^ "Boxing Gloves of the Ancient World".
- ^ "Now and then: boxing gloves | Sport | The Observer". www.theguardian.com. Retrieved 2022-11-18.
- ^ Coleman, J. (1982, February). The Fighting Sport of France. Black Belt, 28-32.
- ^ "savate | sport | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 2022-11-18.
- ^ Martin, Ashley (2012-04-16). The Complete Martial Arts Training Manual. Tuttle. ISBN 9781462905553. OVXRAgAAQBAJ&pg=PT53&dq=osamu+noguchi+kickboxing#v=onepage&q=osamu%20noguchi%20kickboxing&f=false.
- ^ "Black Belt February 1973". February 1973. Retrieved 10 January 2015.
- ^ a b Sylvie von Duuglas-Ittu. "Origins of Japanese Kickboxing – The Karate vs Muay Thai Fight That Started It All". 8 Limbs. December 28, 2015
- ^ Shapira, Philip (July 2009). Physical Exercises & the Martial Arts. Readworthy Publications (P) Limited. ISBN 9789380297057. Retrieved 10 January 2015.
- ^ "Black Belt December 1968". December 1968. Retrieved 10 January 2015.
- ^ "「キックの鬼」沢村忠さんが死去 肺がんで入院" ["Kick Demon" Tadashi Sawamura dies, hospitalized for lung cancer]. Nikkan Sports. April 2, 2021. Retrieved February 21, 2023.
- ^ "Kick-boxing Booming in Japan". Black Belt Magazine (December 1971 Issue). 1971. p. 11. Retrieved February 22, 2023.
Current idol of the young fans is Tadashi Sawamura, 28, a 130-pound ex-karateka who has been knocking out all comers with his powerful knee kicks ever since he introduced kick-boxing to Japan about five years ago.[...]Kick-boxing commands such an audience in Japan that it is now shown weekly over three television channels in Tokyo.
- ^ "Kickboxing – Persian International Martial Arts Federation". Retrieved 2022-04-14.
- ^ Staff, MMAchannel com (30 November 2021). "What Is Japanese Kickboxing? Easily Explained For Beginners". MMACHANNEL. Retrieved 2022-04-14.
- ^ Maylam, J. (2001): K-1 hits the spot: Ultimate fighters pack a punch The Japan Times (October 21, 2001). Retrieved on November 25, 2010.
- ^ Tashiro, H. and Tyrangiel, J. Turning the martial arts into mondo mayhem Time. September 3, 2001. Retrieved on November 25, 2010.
- ^ "Lewis, Joe". World Wide Dojo. Archived from the original on 2016-09-23. Retrieved 2016-09-22.
- ^ a b "Joe Lewis". Archived from the original on 2016-07-16. Retrieved 2016-08-08.
- ^ a b "Rules". Glory Kickboxing. Retrieved 2020-08-16.
- ^ a b "ONE Championship's Super Series debuts on Friday | BusinessWorld". BusinessWorld. 2020-08-16. Archived from the original on 2020-08-16. Retrieved 2020-08-16.
- ^ a b "Bellator Kickboxing's Weight Classes & Rule Set Revealed". Full Contact Fighter. Retrieved 26 August 2020.
- ^ "IKF UNIFIED RULES". www.ikfkickboxing.com. Retrieved 2020-08-16.
- ^ "Unified Rules of Professional Kickboxing – Association of Boxing Commissions". www.abcboxing.com. Retrieved 2020-08-16.
- ^ a b "K-1 INTERNATIONAL RULES". K-1 Official Site. Archived from the original on 2011-11-02. Retrieved 14 May 2021.
- ^ "The History of Kickboxing". 10 November 2020. Archived from the original on 4 March 2024. Retrieved 6 September 2021.
- ^ "The champion also lost a point in the 4th round for repeatedly using the clinch" ONE X results and highlights: Hiroki Akimoto wins the ONE bantamweight belt in a thrilling kickboxing bout
- ^ p. 150: "It is prohibited [...] To perform more than one knee attack, while holding the opponent's neck or shoulders with two hands. WAKO Rules Archived 20 March 2022 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Korean Kickboxing".
- ^ "Gwon Gyokdo".
- ^ "Kickboxing styles".
- ^ "Kun Gek Do".
- ^ Matuszak, Sascha. "Trying to Reignite Kickboxing in the USA | FIGHTLAND". Fightland.vice.com. Retrieved 2016-02-24.
- ^ "This sport needs a role model To its followers, kickboxing is the best of both worlds". Chicago Tribune. December 6, 1992. Retrieved 2010-11-25.
- ^ "Wako - World Association of Kickboxing Organizations". Wako - World Association of Kickboxing Organizations (in Brazilian Portuguese). 2022-01-26. Retrieved 2022-11-23.
- ^ "Points Fighting Rules". wakoweb.com. Archived from the original on 10 June 2016. Retrieved 24 September 2015.
- ^ "Dutch Kickboxing". 4 October 2021.
- ^ "Wako - World Association of Kickboxing Organizations". Wako - World Association of Kickboxing Organizations (in Brazilian Portuguese). 2022-01-26. Retrieved 2022-11-26.
- ^ "WKA Rules" (PDF).
- ^ "ISKA Kickboxing rules and regulations" (PDF).
- ^ "Liam Harrison talks upcoming ONE Championship fight and ongoing beef with Dave Leduc". The Body Lock. 8 January 2020.
- ^ a b See page 32 for the list of allowed strikes, page 35 for list of disallowed strikes, throws and sweeps IFMA Muay Thai rules
- ^ a b "Illegal Throws in Muay Thai – Just What Can't You Do?". Muay Thai Blog & Journalism | Sylvie von Duuglas-Ittu. Retrieved 2022-11-18.
- ^ a b "Preparing for your first Thai rules fight. – Damien Trainor". Retrieved 2022-11-18.
- ^ Lumpinee Stadium rules only disallow knee strikes to the groin, see rule 19.8: https://web.archive.org/web/20201029141951/https://www.lumpineemuaythai.com/about/about-muay-thai/
- ^ "Varazdat Does It Again". 13 April 2001.
- ^ "Draka".
- ^ "Kickboxing".
- ^ "No Holds Barred". Los Angeles Times. 4 September 1997.
- ^ "XG Rules".
- ^ "Unified Rules of Kickboxing". ABC Boxing. Association of Boxing Commissions. Retrieved 2024-05-29.
- ^ "Understanding the Muay Thai Scoring System". Siamkick Fight. 15 May 2024. Retrieved 2024-05-29.
- ^ "Muay Thai vs Kickboxing". Siamkick Fight. 25 May 2024. Retrieved 2024-05-29.
- ^ "List of Kickboxing Moves". SportsRec. Retrieved 2021-01-14.
- ^ "Boxing: The health risks". Archived from the original on 18 September 2002. Retrieved 6 May 2010.
- ^ Carter, Neil (June 2006). "Better and Safer Boxing: Ringside and Boardroom Medical Control of Boxing Careers in the Twentieth Century". Dora.dmu.ac.uk. Archived from the original on 4 November 2021. Retrieved 22 September 2014.
- ^ Castellani, Rudy J. (June 2015). "Chronic traumatic encephalopathy: A paradigm in search of evidence?". Laboratory Investigation. 95 (6): 576–584. doi:10.1038/labinvest.2015.54. ISSN 1530-0307. PMID 25867769.
- ^ Ridler, Charlotte (April 2017). "New insights into the long-term effects of mild brain injury". Nature Reviews Neurology. 13 (4): 195. doi:10.1038/nrneurol.2017.32. ISSN 1759-4766. PMID 28257129.
- ^ Concussion, microvascular injury, and early tauopathy in young athletes after impact head injury and an impact concussion mouse model - Brain, Volume 141, Issue 2, February 2018
- ^ Montenigro, P. H.; Baugh, C. M.; Daneshvar, D. H.; Mez, J.; Budson, A. E.; Au, R.; Katz, D. I.; Cantu, R. C.; Stern, R. A. (2014). "Clinical subtypes of chronic traumatic encephalopathy: Literature review and proposed research diagnostic criteria for traumatic encephalopathy syndrome". Alzheimer's Research & Therapy. 6 (5): 68. doi:10.1186/s13195-014-0068-z. PMC 4288217. PMID 25580160.
- ^ Johnson, B.; Neuberger, T.; Gay, M.; Hallett, M.; Slobounov, S. (2014). "Effects of Subconcussive Head Trauma on the Default Mode Network of the Brain". Journal of Neurotrauma. 31 (23): 1907–1913. doi:10.1089/neu.2014.3415. PMC 4238241. PMID 25010992.
- ^ Di Virgilio, Thomas G.; Ietswaart, Magdalena; Wilson, Lindsay; Donaldson, David I.; Hunter, Angus (2019). "Understanding the Consequences of Repetitive Subconcussive Head Impacts in Sport: Brain Changes and Dampened Motor Control Are Seen After Boxing Practice". Frontiers in Human Neuroscience. 13: 294. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2019.00294. ISSN 1662-5161. PMC 6746992. PMID 31551732.
Bibliography
[edit]- Muay Thai Kickboxing – The Ultimate Guide to Conditioning, Training and Fighting, Chad Boykin, 2002, Paladin Press, Boulder, Colorado. ISBN 1-58160-320-7
- Thai Kickboxing For Beginners, Peter Belmar, 2006, Lulu Press. ISBN 978-1-4116-9983-0
External links
[edit]- Willem Brunekreef, The Golden Kyokushin and K-1 Encyclopedia, ISBN 978-90-812379-1-8
- (in French) "A History of Full Contact Karate
- (in French) Delmas Alain, Callière Jean-Roger, Histoire du Kick-boxing, FFKBDA, France, 1998
- (in French) Delmas Alain, Définition du Kick-boxing, FFKBDA, France, 1999
| Governing bodies | |
|---|---|
| Asian promotions | |
| European promotions | |
| North American promotions | |
| Oceania promotions | |
| Defunct organizations | |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Artistic and dance sports | |
|---|---|
| Ball sports | |
| Martial arts | |
| Precision sports | |
| Strength sports | |
| Trend sports | |
| Past official sports | |
| Invitational sports | |