 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Leritine |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Routes of administration | Tablets, injection |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | > 95% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
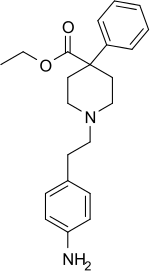
| Formula | C22H28N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 352.478 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 83 °C (181 °F) |
| |
| |
| | |
Anileridine (trade name: Leritine) is a synthetic analgesic drug[2] and is a member of the piperidine class of analgesic agents[3] developed by Merck & Co. in the 1950s.[4] It differs from pethidine (meperidine) in that the N-methyl group of meperidine is replaced by an N-aminophenethyl group, which increases its analgesic activity.
Anileridine is no longer manufactured in the US or Canada.[5] Anileridine is in Schedule II of the Controlled Substances Act 1970 of the United States as ACSCN 9020 with a zero aggregate manufacturing quota as of 2014. The free base conversion ratio for salts includes 0.83 for the dihydrochloride and 0.73 for the phosphate.[6] It is also under international control per UN treaties.