| Hyperbaric medicine | |
|---|---|
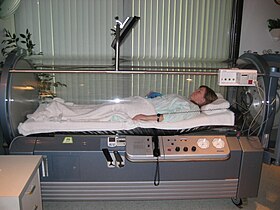 A Sechrist Monoplace hyperbaric oxygen chamber at the Moose Jaw Union Hospital, Saskatchewan, Canada | |
| Specialty | diving medicine, emergency medicine, neurology, infectious diseases |
| ICD-9-CM | 93.95 |
| MeSH | D006931 |
| OPS-301 code | 8-721 |
| MedlinePlus | 002375 |
Hyperbaric medicine is a medical treatment in which an increase in barometric pressure over ambient pressure is employed increasing the partial pressures of all gases present in the compressed air. The immediate effects include reducing the size of gas embolisms and raising the partial pressures of all gases present according to Henry's law. Currently, there are two types of hyperbaric medicine depending on the gases compressed, hyperbaric air and hyperbaric oxygen.
Hyperbaric air (HBA), consists of compressed room air (79% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and minor gases) and is FDA-approved for acute mountain sickness. The hyperbaric air environment is created by placing the patient in a portable hyperbaric air chamber and inflating that chamber up to 7.35 psi gauge (1.5 atmospheres absolute) using a foot-operated or electric air pump. Although the mechanisms of hyperbaric air are poorly understood it is thought that it relieves hypoxemia caused by the decreased partial pressure of oxygen resulting from high altitude by increasing the partial pressure of air (including oxygen and nitrogen) simulating a descent in altitude.[1] [2] [3]
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), the medical use of greater than 99% oxygen at an ambient pressure higher than atmospheric pressure, and therapeutic recompression for decompression illness, intended to reduce the injurious effects of systemic gas bubbles by physically reducing their size and providing improved conditions for elimination of bubbles and excess dissolved gas.
The equipment required for hyperbaric oxygen treatment consists of a Pressure vessel for human occupancy, which may be of rigid or flexible construction, and a means of a controlled atmosphere. Operation is performed to a predetermined schedule by trained personnel who monitor the patient and may adjust the schedule as required. HBOT found early use in the treatment of decompression sickness, and has also shown great effectiveness in treating conditions such as gas gangrene and carbon monoxide poisoning. More recent research has examined the possibility that it may also have value for other conditions such as cerebral palsy and multiple sclerosis, but no significant evidence has been found.
A Pressure vessel for human occupancy (PVHO) is an enclosure that is intended to be occupied by one or more persons at a pressure which differs from ambient by at least 2 pounds per square inch (0.14 bar). All chambers made for hyperbaric medicine fall under the jurisdiction of the Federal Food and Drug Agency (FDA). The FDA requires hyperbaric chambers to comply with the American Society of Mechanical Engineers PVHO Codes[4] and the National Fire Protection Association Standard 99, Health Care Facilities Code. [5]
Hyperbaric medicine poses some inherent hazards that are mitigated by FDA-compliant equipment and trained personnel. Serious injury can occur at pressures as low as 2 psig (13.8 kPa) if a person in the PVHO is rapidly decompressed.[6][7] If oxygen is used in the hyperbaric therapy, this can increase the fire hazard. This is why the FDA requires hyperbaric chambers to meet ASME PVHO and NFPA 99 standards. All chambers that meet FDA standards must have an ASME data plate, and people seeking hyperbaric treatment should check to ensure the equipment and facilities are to proper standards.
Therapeutic recompression is usually also provided in a hyperbaric chamber. It is the definitive treatment for decompression sickness and may also be used to treat arterial gas embolism caused by pulmonary barotrauma of ascent. In emergencies divers may sometimes be treated by in-water recompression (when a chamber is not available) if suitable diving equipment (to reasonably secure the airway) is available.
A number of hyperbaric treatment schedules have been published over the years for both therapeutic recompression and hyperbaric oxygen therapy for other conditions.
Scope
[edit]Hyperbaric medicine includes hyperbaric oxygen treatment, which is the medical use of oxygen at greater than atmospheric pressure to increase the availability of oxygen in the body;[8] and therapeutic recompression, which involves increasing the ambient pressure on a person, usually a diver, to treat decompression sickness or an air embolism by eliminating bubbles that have formed within the body.[citation needed]
Medical uses
[edit]In the United States the Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society, known as UHMS, lists approvals for reimbursement for certain diagnoses in hospitals and clinics. The following indications have approved (for reimbursement) uses of hyperbaric oxygen therapy as defined by the UHMS Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Committee:[9][10]
- Air or gas embolism;[11]
- Carbon monoxide poisoning;[12][13]
- Central retinal artery occlusion;[17]
- Clostridal myositis and myonecrosis (gas gangrene);[18][19][20]
- Crush injury, compartment syndrome, and other acute traumatic ischemias;[21][22]
- Decompression sickness;[23][24][25]
- Enhancement of healing in selected problem wounds;[26][27]
- Diabetically derived illness, such as short-term relief of diabetic foot,[28][29][30] diabetic retinopathy,[31][32] diabetic nephropathy;[33]
- Exceptional blood loss (anemia);[34][35]
- Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss;[36]
- Intracranial abscess;[37][38]
- Mucormycosis, especially rhinocerebral disease in the setting of diabetes mellitus;[39]
- Necrotizing soft tissue infections (necrotizing fasciitis);[40][41]
- Osteomyelitis (refractory);[42][43][44]
- Delayed radiation injury (soft tissue and bony necrosis);[45][46][47]
- Skin grafts and flaps (compromised);[48]
- Thermal burns.[49][50]
There is no reliable evidence to support its use in autism, cancer, diabetes, HIV/AIDS, Alzheimer's disease, asthma, Bell's palsy, cerebral palsy, depression, heart disease, migraines, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, spinal cord injury, sports injuries, or stroke.[51][52][53] Furthermore, there is evidence that potential side effects of hyperbaric medicine pose an unjustified risk in such cases. A Cochrane review published in 2016 reviewed a small set of clinical trials attempting to treat autism spectrum disorders with hyperbaric oxygen therapy. They noted a small sample size and large "confidence intervals" did not provide much evidence. No links between improvements in social abilities or cognitive function were noted. There are also ethical issues with further trials, as the eardrum can be damaged during hyperbaric therapy.[54] Despite the lack of evidence, in 2015, the number of people utilizing this therapy has continued to rise.[55]
There is also insufficient evidence to support its use in acute traumatic or surgical wounds.[56]
Hearing issues
[edit]There is limited evidence that hyperbaric oxygen therapy improves hearing in patients with sudden sensorineural hearing loss who present within two weeks of hearing loss. There is some indication that HBOT might improve tinnitus presenting in the same time frame.[57]
Chronic ulcers
[edit]HBOT in diabetic foot ulcers increased the rate of early ulcer healing but does not appear to provide any benefit in wound healing at long-term follow-up. In particular, there was no difference in major amputation rate.[58] For venous, arterial and pressure ulcers, no evidence was apparent that HBOT provides a long-term improvement over standard treatment.[28]
Radiation injury
[edit]There is some evidence that HBOT is effective for late radiation tissue injury of bone and soft tissues of the head and neck. Some people with radiation injuries of the head, neck or bowel show an improvement in quality of life. Importantly, no such effect has been found in neurological tissues. The use of HBOT may be justified to selected patients and tissues, but further research is required to establish the best people to treat and timing of any HBO therapy.[59]
Neuro-rehabilitation
[edit]As of 2012, there was no sufficient evidence to support using hyperbaric oxygen therapy to treat people who have traumatic brain injuries.[60] In acute stroke, HBOT does not show benefit.[61][53] Small clinical trials, however, have shown benefits from HBOT for stroke survivors between 6 months to 3 years after the acute phase.[62][63]
HBOT in multiple sclerosis has not shown benefit and routine use is not recommended.[52][64]
A 2007 review of HBOT in cerebral palsy found no difference compared to the control group.[65][66] Neuropsychological tests also showed no difference between HBOT and room air and based on caregiver report, those who received room air had significantly better mobility and social functioning.[65][66] Children receiving HBOT were reported to experience seizures and the need for tympanostomy tubes to equalize ear pressure, though the incidence was not clear.[65]
Cancer
[edit]In alternative medicine, hyperbaric medicine has been promoted as a treatment for cancer. However, a 2011 study by the American Cancer Society reported no evidence it is effective for this purpose.[67] A 2012 review article in the journal, Targeted Oncology, reports that "there is no evidence indicating that HBO neither acts as a stimulator of tumor growth nor as an enhancer of recurrence. On the other hand, there is evidence that implies that HBO might have tumor-inhibitory effects in certain cancer subtypes, and we thus strongly believe that we need to expand our knowledge on the effect and the mechanisms behind tumor oxygenation."[68]
Migraines
[edit]Low-quality evidence suggests that hyperbaric oxygen therapy may reduce the pain associated with an acute migraine headache in some cases.[69] It is not known which people would benefit from this treatment, and there is no evidence that hyperbaric medicine can prevent future migraines.[69] More research is necessary to confirm the effectiveness of hyperbaric oxygen therapy for treating migraines.[69]
Respiratory distress
[edit]Patients who are having extreme difficulty breathing – acute respiratory distress syndrome – are commonly given oxygen and there have been limited trials of hyperbaric equipment in such cases. Examples include treatment of the Spanish flu[70] and COVID-19.[71]
Contraindications
[edit]The toxicology of the treatment has been reviewed by Ustundag et al.[72] and its risk management is discussed by Christian R. Mortensen, in light of the fact that most hyperbaric facilities are managed by departments of anaesthesiology and some of their patients are critically ill.[73]
An absolute contraindication to hyperbaric oxygen therapy is untreated pneumothorax.[74] The reason is concern that it can progress to tension pneumothorax, especially during the decompression phase of therapy, although treatment on oxygen-based tables may avoid that progression.[75] The COPD patient with a large bleb represents a relative contraindication for similar reasons.[76][page needed] Also, the treatment may raise the issue of occupational health and safety (OHS), for chamber inside attendants, who should not be compressed if they are unable to equalise ears and sinuses.[77]
The following are relative contraindications – meaning that special consideration must be made by specialist physicians before HBO treatments begin:
- Cardiac disease[clarification needed]
- COPD with air trapping – can lead to pneumothorax during treatment.
- Upper respiratory infections – These conditions can make it difficult for the patient to equalise their ears or sinuses, which can result in what is termed ear or sinus squeeze.[74]
- High fevers – In most cases the fever should be lowered before HBO treatment begins. Fevers may predispose to convulsions.[74]
- Emphysema with CO2 retention – This condition can lead to pneumothorax during HBO treatment due to rupture of an emphysematous bulla during decompression. This risk can be evaluated by x-ray.[74][clarification needed]
- History of thoracic (chest) surgery – This is rarely a problem and usually not considered a contraindication. However, there is concern that air may be trapped in lesions that were created by surgical scarring. These conditions need to be evaluated prior to considering HBO therapy.[74]
- Malignant disease: Cancers thrive in blood-rich environments but may be suppressed by high oxygen levels. HBO treatment of individuals who have cancer presents a problem, since HBO both increases blood flow via angiogenesis and also raises oxygen levels. Taking an anti-angiogenic supplement may provide a solution.[78][79] A study by Feldemier, et al. and NIH funded study on Stem Cells by Thom, et al., indicate that HBO is actually beneficial in producing stem/progenitor cells and the malignant process is not accelerated.[80]
- Middle ear barotrauma is always a consideration in treating both children and adults in a hyperbaric environment because of the necessity to equalise pressure in the ears.
Pregnancy is not a relative contraindication to hyperbaric oxygen treatments,[76][page needed] although it may be for underwater diving. In cases where a pregnant woman has carbon monoxide poisoning there is evidence that lower pressure (2.0 ATA) HBOT treatments are not harmful to the fetus, and that the risk involved is outweighed by the greater risk of the untreated effects of CO on the fetus (neurologic abnormalities or death.)[81][82] In pregnant patients, HBO therapy has been shown to be safe for the fetus when given at appropriate levels and "doses" (durations). In fact, pregnancy lowers the threshold for HBO treatment of carbon monoxide-exposed patients. This is due to the high affinity of fetal hemoglobin for CO.[76][page needed]
Therapeutic principles
[edit]The therapeutic consequences of HBOT and recompression result from multiple effects.[9][83]
Clinical pressure (2.0–3.0 Bar)
[edit]The increased overall pressure is of therapeutic value in the treatment of decompression sickness and air embolism as it provides a physical means of reducing the volume of inert gas bubbles within the body;[84] Exposure to this increased pressure is maintained for a period long enough to ensure that most of the bubble gas is dissolved back into the tissues, removed by perfusion and eliminated in the lungs.[83]
The improved concentration gradient for inert gas elimination (oxygen window) by using a high partial pressure of oxygen increases the rate of inert gas elimination in the treatment of decompression sickness.[85][86]
For many other conditions, the therapeutic principle of HBOT lies in its ability to drastically increase partial pressure of oxygen in the tissues of the body. The oxygen partial pressures achievable using HBOT are much higher than those achievable while breathing pure oxygen under normobaric conditions (i.e. at normal atmospheric pressure). This effect is achieved by an increase in the oxygen transport capacity of the blood. At normal atmospheric pressure, oxygen transport is limited by the oxygen binding capacity of hemoglobin in red blood cells and very little oxygen is transported by blood plasma. Because the hemoglobin of the red blood cells is almost saturated with oxygen at atmospheric pressure, this route of transport cannot be exploited any further. Oxygen transport by plasma, however, is significantly increased using HBOT because of the higher solubility of oxygen as pressure increases.[83]
Proangiogenic stem progenitor cell mobilization
[edit]A study suggests that exposure to hyperbaric oxygen (HBOT) might also mobilize stem/progenitor cells from the bone marrow by a nitric oxide-dependent mechanism.[87]
Low pressure hyperoxia, stem progenitor cell mobilization and inflammatory cytokine expression
[edit]A more recent study suggests that stem cell mobilization, similar to that seen in the Thom study, is also invoked at relative normo-baric pressure with a significantly smaller increase in oxygen concentration. This study also found a significant decrease in the expression of the systemic inflammatory cytokine TNF-α in venous blood. These results suggest that hyperbaria may not be required to invoke the transcriptional responses seen at higher partial pressures of oxygen and that the effect is due solely to oxygen.[88]
Hyperbaric chambers
[edit]
Construction
[edit]The traditional type of hyperbaric chamber used for therapeutic recompression and HBOT is a rigid shelled pressure vessel. Such chambers can be run at absolute pressures typically about 6 bars (87 psi), 600,000 Pa or more in special cases.[89] Navies, professional diving organizations, hospitals, and dedicated recompression facilities typically operate these. They range in size from semi-portable, one-patient units to room-sized units that can treat eight or more patients. The larger units may be rated for lower pressures if they are not primarily intended for treatment of diving injuries.[citation needed]
A rigid chamber may consist of:
- a pressure vessel designed to a code such as ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code
- viewports to allow the medical personnel to visually monitor the occupants, and can be used for hand signalling as an auxiliary emergency communications method. The major components are the window (transparent acrylic), the window seat (holds the acrylic window), and retaining ring. Interior lighting can be provided by mounting lights outside the viewports. Viewports are a feature specific to PVHOs due to the need to see the people inside and evaluate their health. Other materials have been attempted, but they consistently fail to maintain their seal or have cracks which would progress rapidly to catastrphophic failure. Acrylic is more likely to have small cracks the operators can see and have time to take mitigation steps instead of failing catastrophically.[90] Counterfeit chambers often do not use acrylic windows.
- one or more human entry hatches – small and circular or wheel-in type hatches for patients on gurneys;[89]
- the entry lock that allows human entry – a separate chamber with two hatches, one to the outside and one to the main chamber, which can be independently pressurized to allow patients to enter or exit the main chamber while it is still pressurized;[89]
- a low volume medical or service airlock for medicines, instruments, and food;[89]
- transparent ports or closed-circuit television that allows technicians and medical staff outside the chamber to monitor the patient inside the chamber;
- an intercom system allowing two-way communication;[89]
- an optional carbon dioxide scrubber – consisting of a fan that passes the gas inside the chamber through a soda lime canister;[89]
- a control panel outside the chamber to open and close valves that control air flow to and from the chamber, and regulate oxygen to hoods or masks;[89]
- an over-pressure relief valve;[89]
- a built-in breathing system (BIBS) to supply and exhaust treatment gas;[89]
- a fire suppression system.[89]
Flexible monoplace chambers are available ranging from collapsible flexible aramid fiber-reinforced chambers which can be disassembled for transport via truck or SUV, with a maximum working pressure of 2 bar above ambient complete with BIBS allowing full oxygen treatment schedules.[91][92][93] to portable, air inflated "soft" chambers that can operate at between 0.3 and 0.5 bars (4.4 and 7.3 psi) above atmospheric pressure with no supplemental oxygen, and longitudinal zipper closure.[94]
Oxygen supply
[edit]
In the larger multiplace chambers, patients inside the chamber breathe from either "oxygen hoods" – flexible, transparent soft plastic hoods with a seal around the neck similar to a space suit helmet – or tightly fitting oxygen masks, which supply pure oxygen and may be designed to directly exhaust the exhaled gas from the chamber. During treatment patients breathe 100% oxygen most of the time to maximise the effectiveness of their treatment, but have periodic "air breaks" during which they breathe chamber air (21% oxygen) to reduce the risk of oxygen toxicity. The exhaled treatment gas must be removed from the chamber to prevent the buildup of oxygen, which could present a fire risk. Attendants may also breathe oxygen some of the time to reduce their risk of decompression sickness when they leave the chamber. The pressure inside the chamber is increased by opening valves allowing high-pressure air to enter from storage cylinders, which are filled by an air compressor. Chamber air oxygen content is kept between 19% and 23% to control fire risk (US Navy maximum 25%).[89] If the chamber does not have a scrubber system to remove carbon dioxide from the chamber gas, the chamber must be isobarically ventilated to keep the CO2 within acceptable limits.[89]
A soft chamber may be pressurized directly from a compressor.[94] or from storage cylinders.[93]
Smaller "monoplace" chambers can only accommodate the patient, and no medical staff can enter. The chamber may be pressurised with pure oxygen or compressed air. If pure oxygen is used, no oxygen breathing mask or helmet is needed, but the cost of using pure oxygen is much higher than that of using compressed air. If compressed air is used, then an oxygen mask or hood is needed as in a multiplace chamber. Most monoplace chambers can be fitted with a demand breathing system for air breaks. In low pressure soft chambers, treatment schedules may not require air breaks, because the risk of oxygen toxicity is low due to the lower oxygen partial pressures used (usually 1.3 ATA), and short duration of treatment.[citation needed]
For alert, cooperative patients, air breaks provided by mask are more effective than changing the chamber gas because they provide a quicker gas change and a more reliable gas composition both during the break and treatment periods.[citation needed]
Treatments
[edit]Initially, HBOT was developed as a treatment for diving disorders involving bubbles of gas in the tissues, such as decompression sickness and gas embolism, It is still considered the definitive treatment for these conditions. The chamber treats decompression sickness and gas embolism by increasing pressure, reducing the size of the gas bubbles and improving the transport of blood to downstream tissues. After elimination of bubbles, the pressure is gradually reduced back to atmospheric levels. Hyperbaric chambers are also used for animals.
As of September 2023, a number of hyperbaric chambers in the US are turning divers with decompression sickness away, and only treating more profitable scheduled cases. The number of hyperbaric medical facilities in the US is estimated at about 1500, of which 67 are treating diving accidents, according to Divers Alert Network. Many facilities only provide hyperbaric treatment for wound care for economic reasons. Emergency hyperbaric services are more expensive to train and staff, and liability is increased.[95]
Protocol
[edit]Emergency HBOT for decompression illness follows treatment schedules laid out in treatment tables. Most cases employ a recompression to 2.8 bars (41 psi) absolute, the equivalent of 18 metres (60 ft) of water, for 4.5 to 5.5 hours with the casualty breathing pure oxygen, but taking air breaks every 20 minutes to reduce oxygen toxicity. For extremely serious cases resulting from very deep dives, the treatment may require a chamber capable of a maximum pressure of 8 bars (120 psi), the equivalent of 70 metres (230 ft) of water, and the ability to supply heliox as a breathing gas.[83]
U.S. Navy treatment charts are used in Canada and the United States to determine the duration, pressure, and breathing gas of the therapy. The most frequently used tables are Table 5 and Table 6. In the UK the Royal Navy 62 and 67 tables are used.
The Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society (UHMS) publishes a report that compiles the latest research findings and contains information regarding the recommended duration and pressure of the longer-term conditions.[96]
Home and out-patient clinic treatment
[edit]
There are several sizes of portable chambers, which are used for home treatment. These are usually referred to as "mild personal hyperbaric chambers", which is a reference to the lower pressure (compared to hard chambers) of soft-sided chambers. The American Medical Association is opposed to home use or any other use of hyperbaric chambers if it is not "in facilities with appropriately trained staff including physician supervision and prescription and only when the intervention has scientific support or rationale" due demonstrated hazard [97]
In the US, these "mild personal hyperbaric chambers" are categorized by the FDA as CLASS II medical devices and requires a prescription in order to purchase one or take treatments.[98] As with any hyperbaric chamber, the FDA require compliance with ASME and NFPA standards. The most common option (but not approved by FDA) some patients choose is to acquire an oxygen concentrator which typically delivers 85–96% oxygen as the breathing gas.
Oxygen is never fed directly into soft chambers but is rather introduced via a line and mask directly to the patient. FDA approved oxygen concentrators for human consumption in confined areas used for HBOT are regularly monitored for purity (±1%) and flow (10 to 15 liters per minute outflow pressure). An audible alarm will sound if the purity ever drops below 80%. Personal hyperbaric chambers use 120 volt or 220 volt outlets. The FDA warns against the use of oxygen concentrators or oxygen tanks with chambers that does not meet ASME and FDA standards, regardless if the concentrators are FDA approved.[99]
Possible complications and concerns
[edit]There are risks associated with HBOT, similar to some diving disorders. Pressure changes can cause a "squeeze" or barotrauma in the tissues surrounding trapped air inside the body, such as the lungs,[75] behind the eardrum,[100][101] inside paranasal sinuses,[100] or trapped underneath dental fillings.[102] Breathing high-pressure oxygen may cause oxygen toxicity.[103] Temporarily blurred vision can be caused by swelling of the lens, which usually resolves in two to four weeks.[104][105]
There are reports that cataracts may progress following HBOT'[106] and rarely, may develop de novo, but this may be unrecognized and under reported. The cause is not fully explained, but evidence suggests that lifetime exposure of the lens to high partial pressure oxygen may be a major factor. Oxidative damage to lens proteins is thought to be responsible. This may be an end-stage of the relatively well documented myopic shift detected in most hyperbaric patients after a course of multiple treatments.
Effects of pressure
[edit]Patients inside the chamber may notice discomfort inside their ears as a pressure difference develops between their middle ear and the chamber atmosphere.[107] This can be relieved by ear clearing using the Valsalva maneuver or other techniques. Continued increase of pressure without equalizing may cause ear drums to rupture, resulting in severe pain. As the pressure in the chamber increases further, the air may become warm.
To reduce the pressure, a valve is opened to allow air out of the chamber. As the pressure falls, the patient's ears may "squeak" as the pressure inside the ear equalizes with the chamber. The temperature in the chamber will fall. The speed of pressurization and de-pressurization can be adjusted to each patient's needs.
Side effects
[edit]Oxygen toxicity is a limitation on both maximum partial pressure of oxygen, and on length of each treatment.
HBOT can accelerate the development of cataracts over multiple repetitive treatments, and can cause temporary relative myopia over the shorter term.[108]
Regulation and legality
[edit]The use of hyperbaric chambers for medical and therapeutic procedures is generally regulated. Authorities have warned of potential risks to patients receiving treatment in unlicensed facilities, notably in Israel,[109] Canada,[110] and the United States.[111] In Italy, the use of hyperbaric chambers for therapy was severely restricted to limited medical settings after a serious fire which killed ten patients in 1997.[112][113]
In some jurisdictions, the use and availability of HBOT is further restricted at the subnational level. In the U.S. state of North Carolina, several cities including Durham, Raleigh and Charlotte have ordered operators of mild hyperbaric oxygen therapy to close to protect public safety due to a risk of fire.[114]
Unlicensed and fraudulent operators have been subject to prosecution. In Australia, Oxymed Australia Pty Ltd and director Malcolm Hooper were ordered to pay AUS $3 million in fines after advertising hyperbaric therapy against the country's Therapeutic Goods Act.[115] In Canada, certain soft-shelled hyperbaric chambers were removed from the market for a potential risk to patients.[116]
Costs
[edit]HBOT is recognized by Medicare in the United States as a reimbursable treatment for 14 UHMS "approved" conditions. A 1-hour HBOT session may cost between $300 and higher in private clinics, and over $2,000 in hospitals. U.S. physicians (M.D. or D.O.) may lawfully prescribe HBOT for "off-label" conditions such as stroke,[117][118] and migraine.[119][120] Such patients are treated in outpatient clinics. In the United Kingdom most chambers are financed by the National Health Service, although some, such as those run by Multiple Sclerosis Therapy Centres, are non-profit. In Australia, HBOT is not covered by Medicare as a treatment for multiple sclerosis.[121] China and Russia treat more than 80 maladies, conditions and trauma with HBOT.[122]
Personnel
[edit]- Hyperbaric medical practitioner - a specialist in hyperbaric medicine
- Diving medical practitioner – a specialist in diving medicine
- Chamber operator – a person competent to operate a hyperbaric chamber
- Hyperbaric nurse – a nurse responsible for administering hyperbaric oxygen therapy to patients and supervising them throughout the treatment.
- Diving medical technician – member of a dive team who is trained in advanced first aid.
- Chamber attendant – a person trained in basic first aid who is medically fit to dive in a chamber, usually a member of a diving team allocated to looking after the diver being treated.
Research
[edit]Aspects under research include radiation-induced hemorrhagic cystitis;[123] and inflammatory bowel disease,[124] rejuvenation.[125]
Some research found evidence that HBOT improves local tumor control, mortality, and local tumor recurrence for cancers of the head and neck.[126]
Some research also found evidence of an increase in stem progenitor cells[80] and a decrease in inflammation.[88]
Neurological
[edit]Tentative evidence shows a possible benefit in cerebrovascular diseases.[127] Rats subjected to HBOT after some time following the acute phase of experimentally-induced stroke showed reduced inflammation, increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor, and evidence of neurogenesis.[128] Another rat study showed improved neurofunctional recovery as well as neurogenesis following the late-chronic phase of experimentally-induced stroke.[129]
The clinical experience and results so far published has promoted the use of HBOT therapy in patients with cerebrovascular injury and focal cerebrovascular injuries.[130] However, the power of clinical research is limited because of the shortage of randomized controlled trials.[127]
Radiation wounds
[edit]A 2010 review of studies of HBOT applied to wounds from radiation therapy reported that, while most studies suggest a beneficial effect, more experimental and clinical research is needed to validate its clinical use.[131]
History
[edit]Hyperbaric air
[edit]Junod built a chamber in France in 1834 to treat pulmonary conditions at pressures between 2 and 4 atmospheres absolute.[132]
During the following century "pneumatic centres" were established in Europe and the USA which used hyperbaric air to treat a variety of conditions.[133]
Orval J Cunningham, a professor of anesthesia at the University of Kansas in the early 1900s observed that people with circulatory disorders did better at sea level than at altitude and this formed the basis for his use of hyperbaric air. In 1918, he successfully treated patients with the Spanish flu with hyperbaric air. In 1930 the American Medical Association forced him to stop hyperbaric treatment, since he did not provide acceptable evidence that the treatments were effective.[133][70]
Hyperbaric oxygen
[edit]The English scientist Joseph Priestley discovered oxygen in 1775. Shortly after its discovery, there were reports of toxic effects of hyperbaric oxygen on the central nervous system and lungs, which delayed therapeutic applications until 1937, when Behnke and Shaw first used it in the treatment of decompression sickness.[133]
In 1955 and 1956 Churchill-Davidson, in the UK, used hyperbaric oxygen to enhance the radiosensitivity of tumours, while Ite Boerema, at the University of Amsterdam, successfully used it in cardiac surgery.[133]
In 1961 Willem Hendrik Brummelkamp et al. published on the use of hyperbaric oxygen in the treatment of clostridial gas gangrene.[134]
In 1962 Smith and Sharp reported successful treatment of carbon monoxide poisoning with hyperbaric oxygen.[133]
The Undersea Medical Society (now Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society) formed a Committee on Hyperbaric Oxygenation which has become recognized as the authority on indications for hyperbaric oxygen treatment.[133]
Incidents
[edit]Fires inside a hyperbaric chamber are incredibly dangerous. A review article published in 1997 found 77 human fatalities in 35 different hyperbaric chamber fires that occurred from 1923 to 1996.[135] Further studies indicate while the treatment is often considered safe, the use of hyperbaric medicine comes with risks to the operating personnel for improper use, urging proper machine maintenance and safety procedures for the device's use.[136]
- 1997: Ten patients and a nurse were killed in Milan, Italy after a fire broke out inside a hyperbaric oxygen chamber.[137]
- 2009: A grandmother and her four year old grandson perished after a hyperbaric chamber caught fire and exploded in Florida. The boy was receiving treatment in the chamber for cerebral palsy and had traveled from Italy where the treatment is outlawed to undergo the procedure.[138]
- 2012: A hyperbaric oxygen chamber exploded in Florida, killing a woman and a thoroughbred horse who was receiving treatment. The explosion occurred after the horse kicked out at the chamber, creating sparks which ignited.[139]
- 2015: A dog was killed in Georgia when the chamber it was receiving treatment in caught fire and exploded. The dog was being treated for arthritis.[140]
- 2016: A fire killed four people who were receiving treatment inside a hyperbaric chamber at Mintohardjo Navy Hospital in Jakarta, Indonesia. The fire was reportedly caused by an electrical short circuit. After the fire broke out, operators used a sprinkler system and an emergency shut off system to rescue the victims, but live-saving efforts were prevented as the machine became engulfed in flames.[141]
- 2016: A man in Victoria, Australia died in a hyperbaric chamber while receiving treatment. The practitioners overseeing his care were found responsible for failing to ensure the patient's safety leading to his death. They were later fined AU$716,750.[142]
See also
[edit]- Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society – US based organisation for research and education in hyperbaric physiology and medicine.
- South Pacific Underwater Medicine Society – Publisher for diving and hyperbaric medicine and physiology
- Decompression chamber – Any pressure vessel for huma occupancy used to decompress a person
- Hyperbaric treatment schedules – Planned hyperbaric exposure using a specified breathing gas as medical treatment
- Transdermal continuous oxygen therapy – Wound closure technique using external oxygen exposure
References
[edit]- ^ Robertson, J.A.; Shlim, D.R. (1991). "Treatment of moderate acute mountain sickness with pressurization in a portable hyperbaric (Gamow™) Bag". Journal of Wilderness Medicine. 2 (4): 268–273. doi:10.1580/0953-9859-2.4.268.
- ^ Butler, G. J.; Al-Waili, N.; Passano, D. V.; Ramos, J.; Chavarri, J.; Beale, J.; Allen, M. W.; Lee, B. Y.; Urteaga, G.; Salom, K. (2011). "Altitude mountain sickness among tourist populations: A review and pathophysiology supporting management with hyperbaric oxygen". Journal of Medical Engineering & Technology. 35 (3–4): 197–207. doi:10.3109/03091902.2010.497890. PMID 20836748.
- ^ Hackett, Peter H.; Roach, Robert C. (2001). "High-Altitude Illness". New England Journal of Medicine. 345 (2): 107–114. doi:10.1056/nejm200107123450206. PMID 11450659.
- ^ "Safety Standard for Pressure Vessels for Human Occupancy". Codes and Standards. American Society of Mechanical Engineers. Retrieved 25 April 2020.
- ^ Federal Food and Drug Agency. "Hyperbaric chamber". Product Classification. US FDA. Retrieved 25 March 2024.
- ^ Benton, Peter; Woodfine, James; Westwood, Paul (January 1996). "Arterial gas embolism following a 1-meter ascent during helicopter escape training: a case report". Aviation and Space Environemental Medicine. 67 (1): 63–64. PMID 8929206. Retrieved 25 March 2024.
- ^ Hampson, Neil; Moon, Richard (September 2020). "Arterial gas embolism breathing compressed air in 1.2 metres of water". Diving and Hyperbaric Medicine. 50 (3): 292–294. doi:10.28920/dhm50.3.292-294. PMC 7819734. PMID 32957133. Retrieved 25 March 2024.
- ^ Betts, J Gordon; Desaix, Peter; Johnson, Eddie; Johnson, Jody E; Korol, Oksana; Kruse, Dean; Poe, Brandon; Wise, James; Womble, Mark D; Young, Kelly A (September 13, 2023). Anatomy & Physiology. Houston: OpenStax CNX. 22.4 Gas exchange. ISBN 978-1-947172-04-3.
- ^ a b Gesell LB (2008). Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Indications. The Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Committee Report (12th ed.). Durham, NC: Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society. ISBN 978-0-930406-23-3.
- ^ "Indications for hyperbaric oxygen therapy". Undersea & Hyperbaric Medical Society. 2011. Retrieved 21 August 2011.
- ^ Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society. "Air or Gas Embolism". Retrieved 2011-08-21.
- ^ Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society. "Carbon Monoxide". Retrieved 2011-08-21.
- ^ Piantadosi CA (2004). "Carbon monoxide poisoning". Undersea & Hyperbaric Medicine. 31 (1): 167–77. PMID 15233173. Archived from the original on 2011-02-03. Retrieved 2008-05-20.
((cite journal)): CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society. "Cyanide Poisoning". Retrieved 2011-08-21.
- ^ Hall AH, Rumack BH (September 1986). "Clinical toxicology of cyanide". Annals of Emergency Medicine. 15 (9): 1067–74. doi:10.1016/S0196-0644(86)80131-7. PMID 3526995.
- ^ Takano T, Miyazaki Y, Nashimoto I, Kobayashi K (September 1980). "Effect of hyperbaric oxygen on cyanide intoxication: in situ changes in intracellular oxidation reduction". Undersea Biomedical Research. 7 (3): 191–97. PMID 7423657. Archived from the original on 2011-02-03. Retrieved 2008-05-20.
((cite journal)): CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society. "Central Retinal Artery Occlusion". Retrieved 2014-05-30.
- ^ Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society. "Clostridal Myositis and Myonecrosis (Gas gangrene)". Retrieved 2011-08-21.
- ^ Hart GB, Strauss MB (1990). "Gas Gangrene – Clostridial Myonecrosis: A Review". J. Hyperbaric Med. 5 (2): 125–44. Archived from the original on 2011-02-03. Retrieved 2008-05-20.
((cite journal)): CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Zamboni WA, Riseman JA, Kucan JO (1990). "Management of Fournier's Gangrene and the role of Hyperbaric Oxygen". J. Hyperbaric Med. 5 (3): 177–86. Archived from the original on 2011-02-03. Retrieved 2008-05-20.
((cite journal)): CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society. "Crush Injury, Compartment syndrome, and other Acute Traumatic Ischemias". Retrieved 2011-08-21.
- ^ Bouachour G, Cronier P, Gouello JP, Toulemonde JL, Talha A, Alquier P (August 1996). "Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in the management of crush injuries: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial". The Journal of Trauma. 41 (2): 333–39. doi:10.1097/00005373-199608000-00023. PMID 8760546.
- ^ Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society. "Decompression Sickness or Illness and Arterial Gas Embolism". Retrieved 2011-08-21.
- ^ Brubakk AO, Neuman TS (2003). Bennett and Elliott's physiology and medicine of diving (5th Rev ed.). United States: Saunders Ltd. p. 800. ISBN 978-0-7020-2571-6.
- ^ Acott C (1999). "A brief history of diving and decompression illness". South Pacific Underwater Medicine Society Journal. 29 (2). ISSN 0813-1988. OCLC 16986801. Archived from the original on 2011-09-05. Retrieved 2008-03-18.
((cite journal)): CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society. "Enhancement of Healing in Selected Problem Wounds". Retrieved 2011-08-21.
- ^ Zamboni WA, Wong HP, Stephenson LL, Pfeifer MA (September 1997). "Evaluation of hyperbaric oxygen for diabetic wounds: a prospective study". Undersea & Hyperbaric Medicine. 24 (3): 175–79. PMID 9308140. Archived from the original on February 8, 2009.
((cite journal)): CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ a b Kranke P, Bennett MH, Martyn-St James M, Schnabel A, Debus SE, Weibel S (June 2015). "Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for chronic wounds" (PDF). The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2015 (6): CD004123. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004123.pub4. PMC 7055586. PMID 26106870.
- ^ Abidia A, Laden G, Kuhan G, Johnson BF, Wilkinson AR, Renwick PM, et al. (June 2003). "The role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in ischaemic diabetic lower extremity ulcers: a double-blind randomised-controlled trial". European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery. 25 (6): 513–18. doi:10.1053/ejvs.2002.1911. PMID 12787692.
- ^ Kalani M, Jörneskog G, Naderi N, Lind F, Brismar K (2002). "Hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) therapy in treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. Long-term follow-up". Journal of Diabetes and Its Complications. 16 (2): 153–58. doi:10.1016/S1056-8727(01)00182-9. PMID 12039398.
- ^ Chen J (2003). "The Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Diabetic Retinopathy". Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 44 (5): 4017–B720. Archived from the original on 2009-01-13. Retrieved 2008-12-16.
- ^ Chang YH, Chen PL, Tai MC, Chen CH, Lu DW, Chen JT (August 2006). "Hyperbaric oxygen therapy ameliorates the blood-retinal barrier breakdown in diabetic retinopathy". Clinical & Experimental Ophthalmology. 34 (6): 584–89. doi:10.1111/j.1442-9071.2006.01280.x. PMID 16925707. S2CID 35547243.
- ^ Basile C, Montanaro A, Masi M, Pati G, De Maio P, Gismondi A (2002). "Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for calcific uremic arteriolopathy: a case series". Journal of Nephrology. 15 (6): 676–80. PMID 12495283.
- ^ Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society. "Severe Anemia".
- ^ Hart GB, Lennon PA, Strauss MB (1987). "Hyperbaric oxygen in exceptional acute blood-loss anemia". J. Hyperbaric Med. 2 (4): 205–10. Archived from the original on 2009-01-16. Retrieved 2008-05-19.
((cite journal)): CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society. "Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss". Retrieved 2014-05-30.
- ^ Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society. "Intracranial Abscess". Retrieved 2011-08-21.
- ^ Lampl LA, Frey G, Dietze T, Trauschel M (1989). "Hyperbaric Oxygen in Intracranial Abscesses". J. Hyperbaric Med. 4 (3): 111–26. Archived from the original on 2009-01-16. Retrieved 2008-05-19.
((cite journal)): CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Chamilos G, Kontoyiannis DP (2015). "Chapter 133: Aspergillus, Candida, and other opportunistic mold infections of the lung". In Grippi MA, Elias JA, Fishman JA, Kotloff RM, Pack AI, Senior RM (eds.). Fishman's Pulmonary Diseases and Disorders (5th ed.). McGraw-Hill. p. 2065. ISBN 978-0-07-179672-9.
- ^ Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society. "Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infections". Retrieved 2011-08-21.
- ^ Escobar SJ, Slade JB, Hunt TK, Cianci P (2005). "Adjuvant hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBO2)for treatment of necrotizing fasciitis reduces mortality and amputation rate". Undersea & Hyperbaric Medicine. 32 (6): 437–43. PMID 16509286. Archived from the original on February 16, 2009.
((cite journal)): CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society. "Refractory Osteomyelitis". Retrieved 2011-08-21.
- ^ Mader JT, Adams KR, Sutton TE (1987). "Infectious diseases: pathophysiology and mechanisms of hyperbaric oxygen". J. Hyperbaric Med. 2 (3): 133–40. Archived from the original on 2009-02-13. Retrieved 2008-05-16.
((cite journal)): CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Kawashima M, Tamura H, Nagayoshi I, Takao K, Yoshida K, Yamaguchi T (2004). "Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in orthopedic conditions". Undersea & Hyperbaric Medicine. 31 (1): 155–62. PMID 15233171. Archived from the original on 2009-02-16. Retrieved 2008-05-20.
((cite journal)): CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society. "Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatments for Complications of radiation Therapy". Retrieved 2011-08-21.
- ^ Zhang LD, Kang JF, Xue HL (July 1990). "Distribution of lesions in the head and neck of the humerus and the femur in dysbaric osteonecrosis". Undersea Biomedical Research. 17 (4): 353–58. OCLC 2068005. PMID 2396333. Archived from the original on 2011-02-03. Retrieved 2008-05-20.
((cite journal)): CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Lafforgue P (October 2006). "Pathophysiology and natural history of avascular necrosis of bone". Joint Bone Spine. 73 (5): 500–07. doi:10.1016/j.jbspin.2006.01.025. PMID 16931094.
- ^ Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society. "Skin Grafts and Flaps Compromised". Retrieved 2011-08-21.
- ^ Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society. "Thermal Burns". Retrieved 2011-08-21.
- ^ Cianci P, Lueders H, Lee H, Shapiro R, Sexton J, Williams C, Green B (1988). "Adjunctive Hyperbaric Oxygen Reduces the Need for Surgery in 40–80% Burns". J. Hyperbaric Med. 3 (2): 97–101. Archived from the original on 2011-03-12. Retrieved 2008-05-16.
((cite journal)): CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ "Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: Don't Be Misled" (PDF). Food and Drug Administration. 22 August 2013. Archived from the original on 22 August 2013.
- ^ a b Bennett M; Heard R (2004). Bennett MH (ed.). "Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for multiple sclerosis". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2011 (1): CD003057. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003057.pub2. PMC 8407327. PMID 14974004.
- ^ a b Bennett MH, Weibel S, Wasiak J, Schnabel A, French C, Kranke P (November 2014). "Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for acute ischaemic stroke". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2014 (11): CD004954. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004954.pub3. PMC 10754477. PMID 25387992.
- ^ Xiong T, Chen H, Luo R, Mu D (October 2016). "Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for people with autism spectrum disorder (ASD)". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 10 (11): CD010922. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010922.pub2. PMC 6464144. PMID 27737490.
- ^ Walker, Joseph Lauvrak. "Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Gets More Popular as Unapproved Treatment". Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 2015-03-14.
- ^ Eskes, Anne; Vermeulen, Hester; Lucas, Cees; Ubbink, Dirk T (2013-12-16). Cochrane Wounds Group (ed.). "Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for treating acute surgical and traumatic wounds". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (12): CD008059. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008059.pub3. PMID 24343585.
- ^ Bennett MH, Kertesz T, Perleth M, Yeung P, Lehm JP (October 2012). "Hyperbaric oxygen for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss and tinnitus". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 10: CD004739. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004739.pub4. PMID 23076907.
- ^ Lauvrak V, Frønsdal KB, Ormstad SS, Vaagbø G, Fure B (2015). Effectiveness of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in patients with Late Radiation Tissue Injury or Diabetic Foot Ulcer. ISBN 978-82-8121-945-8.
- ^ Lin, ZC; Bennett, MH; Hawkins, GC; Azzopardi, CP; Feldmeier, J; Smee, R; Milross, C (15 August 2023). "Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for late radiation tissue injury". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2023 (8): CD005005. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005005.pub5. PMC 10426260. PMID 37585677. Retrieved 19 October 2023.
- ^ Bennett MH, Trytko B, Jonker B (December 2012). "Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for the adjunctive treatment of traumatic brain injury". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 12: CD004609. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004609.pub3. PMID 23235612.
- ^ Carson S, McDonagh M, Russman B, Helfand M (December 2005). "Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for stroke: a systematic review of the evidence". Clinical Rehabilitation. 19 (8): 819–33. doi:10.1191/0269215505cr907oa. PMID 16323381. S2CID 9900873.
- ^ Efrati S, Fishlev G, Golan M (2013). "Hyperbaric oxygen induces late neuroplasticity in post stroke patients--randomized, prospective trial". PLOS One. 8 (1): e53716. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...853716E. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0053716. PMC 3546039. PMID 23335971.
- ^ Rosario ER, Kaplan SE, Rosenberg SS (2018). "The Effect of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Functional Impairments Caused by Ischemic Stroke". Neurology Research International. 2018: 172679. doi:10.1155/2018/3172679. PMC 6198568. PMID 30402285.
- ^ Bennett M, Heard R (April 2010). "Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for multiple sclerosis". CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics. 16 (2): 115–24. doi:10.1111/j.1755-5949.2009.00129.x. PMC 6493844. PMID 20415839.
- ^ a b c McDonagh MS, Morgan D, Carson S, Russman BS (December 2007). "Systematic review of hyperbaric oxygen therapy for cerebral palsy: the state of the evidence". Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology. 49 (12): 942–47. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8749.2007.00942.x. PMID 18039243.
- ^ a b Collet JP, Vanasse M, Marois P, Amar M, Goldberg J, Lambert J, et al. (February 2001). "Hyperbaric oxygen for children with cerebral palsy: a randomised multicentre trial. HBO-CP Research Group". Lancet. 357 (9256): 582–86. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(00)04054-X. PMID 11558483. S2CID 18668055.
- ^ "Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy". American Cancer Society. 14 April 2011. Retrieved 14 February 2015.
- ^ Moen I, Stuhr LE (December 2012). "Hyperbaric oxygen therapy and cancer – a review". Targeted Oncology. 7 (4): 233–42. doi:10.1007/s11523-012-0233-x. PMC 3510426. PMID 23054400.
- ^ a b c Bennett MH, French C, Schnabel A, Wasiak J, Kranke P, Weibel S (December 2015). "Normobaric and hyperbaric oxygen therapy for the treatment and prevention of migraine and cluster headache". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2016 (12): CD005219. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005219.pub3. PMC 8720466. PMID 26709672.
- ^ a b Sellers, L. M. (1964). "The Fallibility of the Forrestian Principle. "Semper Primus Pervenio Maxima Cum Vi". (Orval James Cunningham)." Trans Am Laryngol Rhinol Otol Soc 23: 385–405
- ^ Harch PG (13 April 2020), "Hyperbaric oxygen treatment of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) respiratory failure", Medical Gas Research, 10 (2): 61–62, doi:10.4103/2045-9912.282177, PMC 7885706, PMID 32541128, S2CID 216380932
- ^ Ustundag A, Duydu Y, Aydin A, Eken A, Dundar K, Uzun G (Oct 2008). "Evaluation of the potential genotoxic effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy". Toxicology Letters. 180: S142. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2008.06.792.
- ^ Mortensen, Christian Risby (March 1982). "Hyperbaric oxygen therapy". The Western Journal of Medicine. 136 (3): 333–37. doi:10.1016/j.cacc.2008.07.007. PMC 1273677. PMID 18749067.
- ^ a b c d e Jain KK. "Indications, Contraindications, and Complications of HBO Therapy" (PDF). Textbook of Hyperbaric Medicine. pp. 75–80. Retrieved 22 September 2016.
- ^ a b Broome JR, Smith DJ (November 1992). "Pneumothorax as a complication of recompression therapy for cerebral arterial gas embolism". Undersea Biomedical Research. 19 (6): 447–55. PMID 1304671. Archived from the original on 2011-02-03. Retrieved 2008-05-23.
((cite journal)): CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ a b c Marx JA, ed. (2002). "chapter 194". Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice (5th ed.). Mosby. ISBN 978-0323011853.
- ^ Liu YH, Hsia TC, Liu JC, Chen W (December 2008). "Fracture of the maxillary bone during hyperbaric oxygen therapy". CMAJ. 179 (12): 1351. doi:10.1503/cmaj.080713. PMC 2585132. PMID 19047622.
- ^ Takenaka S, Arimura T, Higashi M, Nagayama T, Ito E (August 1980). "Experimental study of bleomycin therapy in combination with hyperbaric oxygenation". Nihon Gan Chiryo Gakkai Shi. 15 (5): 864–75. PMID 6159432.
- ^ Stubbs JM, Johnson EG, Thom SR (2005). "Trends Of Treating Patients, That Have Received Bleomycin Therapy In The Past, With Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment (Hbot) And A Survey Of Considered Absolute Contraindications To Hbot". Undersea Hyperb Med Abstract. 32 (supplement). Archived from the original on February 16, 2009. Retrieved 2008-05-23.
((cite journal)): CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ a b Feldmeier J, Carl U, Hartmann K, Sminia P (Spring 2003). "Hyperbaric oxygen: does it promote growth or recurrence of malignancy?". Undersea & Hyperbaric Medicine. 30 (1): 1–18. PMID 12841604.
- ^ Van Hoesen KB, Camporesi EM, Moon RE, Hage ML, Piantadosi CA (February 1989). "Should hyperbaric oxygen be used to treat the pregnant patient for acute carbon monoxide poisoning? A case report and literature review". JAMA. 261 (7): 1039–43. doi:10.1001/jama.1989.03420070089037. PMID 2644457.
- ^ Elkharrat D, Raphael JC, Korach JM, Jars-Guincestre MC, Chastang C, Harboun C, Gajdos P (1991). "Acute carbon monoxide intoxication and hyperbaric oxygen in pregnancy". Intensive Care Medicine. 17 (5): 289–92. doi:10.1007/BF01713940. PMID 1939875. S2CID 25109979.
- ^ a b c d U.S. Navy Supervisor of Diving (Apr 2008). "20" (PDF). U.S. Navy Diving Manual. SS521-AG-PRO-010, revision 6. Vol. 5. U.S. Naval Sea Systems Command. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 31, 2014. Retrieved 2009-06-29.
- ^ Jørgensen TB, Sørensen AM, Jansen EC (April 2008). "Iatrogenic systemic air embolism treated with hyperbaric oxygen therapy". Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica. 52 (4): 566–68. doi:10.1111/j.1399-6576.2008.01598.x. PMID 18339163. S2CID 11470093.
- ^ Behnke AR (1967). "The isobaric (oxygen window) principle of decompression". Trans. Third Marine Technology Society Conference, San Diego. The New Thrust Seaward. Washington DC: Marine Technology Society. Archived from the original on August 20, 2008. Retrieved 20 July 2016.
((cite conference)): CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Van Liew HD, Conkin J, Burkard ME (September 1993). "The oxygen window and decompression bubbles: estimates and significance". Aviation, Space, and Environmental Medicine. 64 (9 Pt 1): 859–65. PMID 8216150.
- ^ Thom SR, Bhopale VM, Velazquez OC, Goldstein LJ, Thom LH, Buerk DG (April 2006). "Stem cell mobilization by hyperbaric oxygen". American Journal of Physiology. Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 290 (4): H1378–86. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00888.2005. PMID 16299259. S2CID 29013782.
- ^ a b MacLaughlin KJ, Barton GP, Braun RK, Eldridge MW (July 2019). "Effect of intermittent hyperoxia on stem cell mobilization and cytokine expression". Medical Gas Research. 2019 Jul-Sep (9(3)): 139–144. doi:10.4103/2045-9912.266989. PMC 6779002. PMID 31552878.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l U.S. Navy Supervisor of Diving (April 2008). "Chapter 21: Recompression Chamber Operation" (PDF). U.S. Navy Diving Manual. Volume 5: Diving Medicine and Recompression Chamber Operations. SS521-AG-PRO-010, Revision 6. U.S. Naval Sea Systems Command. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 31, 2014. Retrieved 2009-06-29.
- ^ Kemper, Bart; Cross, Linda (September 2020). "Developing "Design by Analysis" Methodology for Windows for Pressure Vessels for Human Occupancy". ASCE-ASME Journal of Risk and Uncertainty in Engineering Systems, Part B: Mechanical Engineering. 6 (3). doi:10.1115/1.4046742.
- ^ Malnati P (30 April 2015). "Uncompromising composite hyperbaric oxygen chamber closes the gap". compositesworld.com newsletter. Composites World. Retrieved 29 March 2016.
- ^ Staff (2014). "Hematocare : The revolution at 3 ata". Gaumond Medical Group Inc. Retrieved 29 March 2016.
- ^ a b Staff. "Hyperlite folding portable hyperbaric chambers" (PDF). Technical specifications. London: SOS Ltd. Retrieved 29 March 2016.
- ^ a b www.oxyhealth.com. "Portable Hyperbaric Chambers | Hyperbaric Oxygen Chamber | Hyperbaric Oxygen". Oxyhealth.com. Retrieved 2010-09-25.
- ^ Stewart, Ashley (6 September 2023). "Hyperbaric Chambers Are Turning Away Divers. Will There Be One Nearby When You Need It?". gue.com. Retrieved 7 October 2023.
- ^ "Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society". Uhms.org. Retrieved 2011-08-21.
- ^ "Oppose Unsafe Use of "Mild Hyperbaric Therapy" D-270.986". AMA Policy Finder. American Medical Association. Retrieved 25 March 2024.
- ^ "Product Classification, Chamber, Hyperbaric". United States Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 2011-08-22.
- ^ "Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: Get the Facts". FDA Consumer Updates. US FDA. 26 July 2021.
- ^ a b Fitzpatrick DT, Franck BA, Mason KT, Shannon SG (1999). "Risk factors for symptomatic otic and sinus barotrauma in a multiplace hyperbaric chamber". Undersea & Hyperbaric Medicine. 26 (4): 243–47. PMID 10642071. Archived from the original on 2011-08-11. Retrieved 2008-05-23.
((cite journal)): CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Fiesseler FW, Silverman ME, Riggs RL, Szucs PA (2006). "Indication for hyperbaric oxygen treatment as a predictor of tympanostomy tube placement". Undersea & Hyperbaric Medicine. 33 (4): 231–25. PMID 17004409. Archived from the original on 2011-02-03. Retrieved 2008-05-23.
((cite journal)): CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Stein L (2000). "Dental Distress. The 'Diving Dentist' Addresses the Problem of a Diving-Related Toothache" (PDF). Alert Diver (January/ February): 45–48. Retrieved 2008-05-23.
- ^ Smerz RW (2004). "Incidence of oxygen toxicity during the treatment of dysbarism". Undersea & Hyperbaric Medicine. 31 (2): 199–202. PMID 15485081. Archived from the original on 2011-05-13. Retrieved 2010-01-02.
((cite journal)): CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Butler FK (1995). "Diving and hyperbaric ophthalmology". Survey of Ophthalmology. 39 (5): 347–66. doi:10.1016/S0039-6257(05)80091-8. PMID 7604359.
- ^ Butler FK, White E, Twa M (1999). "Hyperoxic myopia in a closed-circuit mixed-gas scuba diver". Undersea & Hyperbaric Medicine. 26 (1): 41–45. PMID 10353183. Archived from the original on 2009-06-09. Retrieved 2008-05-23.
((cite journal)): CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Gesell LB, Adams BS, Kob DG (2000). "De Novo Cataract Development Following A Standard Course Of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy". Undersea Hyperb Med Abstract. 27 (supplement): 389–92. PMID 18251434. Archived from the original on February 16, 2009. Retrieved 2008-06-01.
((cite journal)): CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Lehm Jan P, Bennett Michael H (2003). "Predictors of middle ear barotrauma associated with hyperbaric oxygen therapy". South Pacific Underwater Medicine Society Journal. 33: 127–33. Archived from the original on July 22, 2009. Retrieved 2009-07-15.
((cite journal)): CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Bennett, Michael H.; Cooper, Jeffrey S. (21 June 2022). "Hyperbaric Cataracts". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. StatPearls Publishing LLC. PMID 29261974. Retrieved 30 July 2022.
- ^ "Health Ministry warns public not to go to unlicensed hyperbaric oxygen chambers". The Jerusalem Post | JPost.com. 2023-12-17. Retrieved 2024-05-22.
- ^ Government of Canada, Health Canada (2021-10-28). "Unlicensed soft-shelled hyperbaric chambers may pose serious health risks - Recalls, advisories and safety alerts – Canada.ca". recalls-rappels.canada.ca. Retrieved 2024-05-22.
- ^ Office of the Commissioner (July 26, 2021). "Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: Get the Facts". FDA – via U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
- ^ "Italian Authorities Still Plan to Prosecute Substance Abuse Cases". Washington Post. 2024-01-31. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved 2024-05-22.
- ^ Colvin, AP (January 3, 1998). "Fire-safety standards for hyperbaric oxygen facilities". The Lancet. 351 (9095): 69. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(05)78048-x. ISSN 0140-6736. PMID 9433452.
- ^ Brosseau, Carli (July 5, 2022). "Durham joins NC cities barring 'mild hyperbaric oxygen therapy.' Find out why". The News & Observer.
- ^ Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care (December 3, 2021). "Oxymed Australia Pty Ltd and director Malcolm Hooper ordered to pay $3 million for unlawful advertising of hyperbaric oxygen therapy devices". Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration. Retrieved May 22, 2024.
- ^ KelownaNow. "Health Canada seizes several unlicensed hyperbaric chambers due to serious health risks". KelownaNow. Retrieved 2024-05-22.
- ^ Jain KK (1989). "Effect of Hyperbaric Oxygenation on Spasticity in Stroke Patients". J. Hyperbaric Med. 4 (2): 55–61. Archived from the original on 2008-11-01. Retrieved 2008-08-06.
((cite journal)): CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Singhal AB, Lo EH (February 2008). "Advances in emerging nondrug therapies for acute stroke 2007". Stroke. 39 (2): 289–91. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.511485. PMC 3705573. PMID 18187678.
- ^ Eftedal OS, Lydersen S, Helde G, White L, Brubakk AO, Stovner LJ (August 2004). "A randomized, double blind study of the prophylactic effect of hyperbaric oxygen therapy on migraine". Cephalalgia. 24 (8): 639–44. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2004.00724.x. PMID 15265052. S2CID 22145164.
- ^ Fife WP, Fife CE (1989). "Treatment of Migraine with Hyperbaric Oxygen". J. Hyperbaric Med. 4 (1): 7–15. Archived from the original on 2009-06-09. Retrieved 2008-08-06.
((cite journal)): CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ IN-DEEP. "Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for MS". Making Sense of MS Research. Retrieved 8 November 2012.
- ^ Textbook of Hyperbaric Medicine KK Jane, 5th Edition, 2010
- ^ Yoshida T, Kawashima A, Ujike T, Uemura M, Nishimura K, Miyoshi S (July 2008). "Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for radiation-induced hemorrhagic cystitis". International Journal of Urology. 15 (7): 639–41. doi:10.1111/j.1442-2042.2008.02053.x. PMID 18643783.
- ^ Noyer CM, Brandt LJ (February 1999). "Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for perineal Crohn's disease". The American Journal of Gastroenterology. 94 (2): 318–21. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.1999.00848.x. PMID 10022622. S2CID 9674423.
- ^ Yafit Hachmo et al., (2020). Hyperbaric oxygen therapy increases telomere length and decreases immunosenescence in isolated blood cells : a prospective trial. Aging (Albany NY). PMID 33206062 doi:10.18632/aging.202188
- ^ Bennett MH, Feldmeier J, Smee R, Milross C (April 2018). "Hyperbaric oxygenation for tumour sensitisation to radiotherapy". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 4 (7): CD005007. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd005007.pub4. PMC 6494427. PMID 29637538.
- ^ a b Fischer BR, Palkovic S, Holling M, Wölfer J, Wassmann H (January 2010). "Rationale of hyperbaric oxygenation in cerebral vascular insult". Current Vascular Pharmacology. 8 (1): 35–43. doi:10.2174/157016110790226598. PMID 19485935.
- ^ Lee Y, Chio C, Tsai K (2013). "Long course hyperbaric oxygen stimulates neurogenesis and attenuates inflammation after ischemic stroke". Mediators of Inflammation. 2013: 512978. doi:10.1155/2013/512978. PMC 3595722. PMID 23533308.
- ^ Hu Q, Liang X, Zhang JH (2014). "Delayed hyperbaric oxygen therapy promotes neurogenesis through reactive oxygen species/hypoxia-inducible factor-1α/β-catenin pathway in middle cerebral artery occlusion rats". Stroke. 45 (6): 1807–1814. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.114.005116. PMC 4102647. PMID 24757104.
- ^ Michalski D, Härtig W, Schneider D, Hobohm C (February 2011). "Use of normobaric and hyperbaric oxygen in acute focal cerebral ischemia – a preclinical and clinical review". Acta Neurologica Scandinavica. 123 (2): 85–97. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0404.2010.01363.x. PMID 20456243. S2CID 32844269.
- ^ Spiegelberg L, Djasim UM, van Neck HW, Wolvius EB, van der Wal KG (August 2010). "Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in the management of radiation-induced injury in the head and neck region: a review of the literature". Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. 68 (8): 1732–39. doi:10.1016/j.joms.2010.02.040. PMID 20493616.
- ^ "Aerotherapeutics". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 1 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 271.
- ^ a b c d e f Sharkey S (April 2000). "Current indications for hyperbaric oxygen therapy". ADF Health. 1 (2). Retrieved 18 December 2013.
- ^ Brummelkamp WH, Hogendijk L, Boerema I (1961). "Treatment of anaerobic infections (clostridial myositis) by drenching the tissues with oxygen under high atmospheric pressure". Surgery. 49: 299–302.
- ^ Sheffield, P. J.; Desautels, D. A. (September 1997). "Hyperbaric and hypobaric chamber fires: a 73-year analysis". Undersea & Hyperbaric Medicine: Journal of the Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society, Inc. 24 (3): 153–164. ISSN 1066-2936. PMID 9308138 – via Pub Med National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Mago, Vishal (January–March 2024). "Safety of Hyperbaric Medicine in Clinical Scenarios". Annals of African Medicine. 23 (1): 1–4. doi:10.4103/aam.aam_16_22. ISSN 1596-3519. PMC 10922184. PMID 38358163.
- ^ Simini, Bruno (November 8, 1997). "Milan fire fuels concerns over hyperbaric oxygen facilities". The Lancet. 350 (9088): 1375. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(05)65155-0. ISSN 0140-6736.
- ^ "Men Charged In Fatal Hyperbaric Chamber Explosion - CBS Miami". www.cbsnews.com. 2012-04-25. Retrieved 2024-05-13.
- ^ "Equine hyperbaric oxygen chamber explosion in Florida kills woman and horse". DVM 360. 2012-02-22. Retrieved 2024-05-13.
- ^ "Vet blames dog for hyperbaric chamber explosion". FOX 5 Atlanta. 2016-04-12. Retrieved 2024-05-13.
- ^ Post, The Jakarta. "Fire kills 4 inside hyperbaric chamber - National". The Jakarta Post. Retrieved 2024-05-22.
- ^ "Hyperbaric company and director fined $726,750". WorkSafe Victoria. Retrieved 2024-05-22.
Further reading
[edit]- Office of the Commissioner (26 July 2021). "Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: Get the Facts". Food and Drug Administration.
- Kindwall EP, Whelan HT (2008). Hyperbaric Medicine Practice (3rd ed.). Flagstaff, AZ: Best Publishing Company. ISBN 978-1-930536-49-4.
- Mathieu D (2006). Handbook on Hyperbaric Medicine. Berlin: Springer. ISBN 978-1-4020-4376-5.
- Neubauer RA, Walker M (1998). Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy. Garden City Park, NY: Avery Publishing Group. ISBN 978-0-89529-759-4.
- Jain KK, Baydin SA (2004). Textbook of hyperbaric medicine (4th ed.). Hogrefe & Huber. ISBN 978-0-88937-277-1. (6th edition from Springer in press 2016)
- Harch PG, McCullough V (2010). The Oxygen Revolution. Long Island City, NY: Hatherleigh Press. ISBN 978-1-57826-326-4.
External links
[edit]- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy from eMedicine
- Duke University Medical Center Archives contains collections of multiple individuals who worked with hyperbaric medicine
- Dunning, Brian (November 19, 2019). "Skeptoid #702: Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy". Skeptoid.
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
Tests and procedures involving the respiratory system | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surgery |
| ||||||||||
| Tests |
| ||||||||||
| Other procedures |
| ||||||||||