| Part of a series on the |
| American Revolution |
|---|
 |
|
|
Timeline of the American Revolution—timeline of the political upheaval culminating in the 18th century in which Thirteen Colonies in North America joined together for independence from the British Empire, and after victory in the Revolutionary War combined to form the United States of America. The American Revolution includes political, social, and military aspects. The revolutionary era is generally considered to have begun with the passage of the Stamp Act in 1765 and ended with the ratification of the United States Bill of Rights in 1791. The military phase of the revolution, the American Revolutionary War, lasted from 1775 to 1783.
1600s
[edit]1629
[edit]- The Cambridge Agreement (August 29, 1629)
1683
[edit]- The Lords of Trade issues quo warranto writs for the charters of several North American colonies, including Massachusetts (June 3)
1684
[edit]- Revocation of the Charter by Charles II. For technical reasons the Massachusetts writ is never served, and the agreement is formally vacated when the chancery court issues a scire facias writ formally annulling the charter. The proceedings are arranged so that the time for the colonial authorities to defend the charter expires before they even learn of the event (June 18)
1686
[edit]- Charter arrives in Boston establishing the Dominion of New England in America (May 14)
1689
[edit]- 1689 Boston revolt, Leaders of the former Massachusetts Bay Colony reclaim control of the government. In other colonies, members of governments displaced return to power (April 18)
1691
[edit]- William III and Mary II approve the charter formally establishing the Province of Massachusetts Bay (October 7)
1740s and 1750s
[edit]
1747
[edit]- Ohio Company of Virginia formed
1754
[edit]- Outbreak of the French and Indian War; colonial militias play a role
- Albany Congress, the first time in the 18th century that American colonial representatives meet to discuss some manner of formal union; attempts to gain Iroquois support (June 18–July 11)
1757
[edit]- Prime Minister William Pitt commits to all-out effort in the war
1759
[edit]- Quebec, capital of New France falls to the British
1760s
[edit]1760
[edit]- Pierre de Rigaud, Governor of New France, capitulates to Field Marshal Jeffrey Amherst. This ends most fighting in North America between France and Great Britain in the French and Indian War. Amherst becomes the first British Governor-General of territories that would later become Canada plus lands (Ohio Country and Illinois Country) west of the American Colonies (September 8)
- King George II of Great Britain dies and is succeeded by his grandson George III (October 25)
1763
[edit]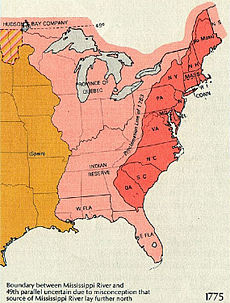
- The Treaty of Paris formally ends the Seven Years' War, called in North America the French and Indian War. France cedes most of its territories in North America to Great Britain, but Louisiana west of the Mississippi River is ceded to Spain (February 10); George III is dissatisfied with the terms of the treaty, which he deems favorable to the losing powers France and Spain rather than the winner, Great Britain.
- Pontiac's War is launched by a Native American confederation in the Great Lakes region under the overall command of the eponymous Ottawa chief. Previously allied with France, they were dissatisfied by the policies of the British under Amherst (April 25, 1763 – July 25, 1766)
- King George's Royal Proclamation of 1763 establishes administration in territories newly ceded by France. To prevent further violence between settlers and Native Americans, the Proclamation sets a western boundary on the American colonies (October 7)
- Navigation Acts are re-enforced by George Grenville as a part of his attempt to reassert unified economic control over the British Empire following the Seven Years' War
1764
[edit]- The Sugar Act (April 5), intended to raise revenues, and the Currency Act (September 1), prohibiting the colonies from issuing paper money, are passed by Parliament. These Acts, coming during the economic slump that followed the French and Indian War, are resented by the colonists and lead to protest
1765
[edit]- Parliament enacts (March 22) the Stamp Act to impose control and help defray the cost of keeping troops in America to control the colonists, imposing a tax on many types of printed materials used in the colonies. Seen as a violation of rights, the Act sparks violent demonstrations in several Colonies. Virginia's House of Burgesses adopts (May 29) the Virginia Resolves claiming that, under British law, Virginians could be taxed only by an assembly to which they had elected representatives
- Parliament enacts (March 24) the Quartering Act, requiring the Colonies to provide housing, food, and other provisions to British troops. The act is resisted or circumvented in most of the colonies. In 1767 and again in 1769, Parliament suspended the governor and legislature of New York for failure to comply
- Delegates from nine colonies attend the Stamp Act Congress which adopts (October 19) a Declaration of Rights and Grievances and petitions Parliament and the king to repeal the Act
1766
[edit]- Although British Parliament repeals the unpopular Stamp Act of the previous year, in the simultaneous Declaratory Act, Parliament asserts its "full power and authority to make laws and statutes ... to bind the colonies and people of America ... in all cases whatsoever", which is designed to overrule actions by the legislative assemblies of each colony, which had traditionally held authority (March 18)
- Liberty pole erected in New York City commons in celebration of the Stamp Act repeal (May 21). An intermittent skirmish with the British garrison over the removal of this and other poles, and their replacement by the Sons of Liberty, rages until the Province of New York is under the control of the revolutionary New York Provincial Congress in 1775
1767
[edit]- Parliament aims to assert its right to tax the American colonies after the failure of the Sugar Act and Stamp Act. The Townshend Acts, named for Chancellor of the Exchequer Charles Townshend, are passed by Parliament, placing duties on many items imported into America (June 29). The American colonists, who were denied any representation in Parliament, strongly condemned the Acts as an egregious abuse of power.
1768
[edit]- Britain's Secretary of State for the Colonies, Lord Hillsborough, orders colonial governors to stop their own assemblies from endorsing Adams' circular letter (April). Hillsborough also orders the governor of Massachusetts to dissolve the general court if the Massachusetts assembly does not revoke the letter. By month's end, the assemblies of New Hampshire, Connecticut and New Jersey have endorsed the letter
- A British warship, HMS Romney, armed with 50 cannon sailed into Boston harbor after a call for help from custom commissioners who were constantly being harassed by Boston agitators (May). A customs official was later locked up in the cabin of Liberty, a sloop owned by John Hancock (June). Imported wine was unloaded illegally into Boston without payment of duties. Following this incident, customs officials seized Hancock's sloop as HMS Liberty (1768). After threats of violence from Bostonians, the customs officials escaped to an island off Boston, then requested the intervention of British troops
- The governor of Massachusetts dissolves the general court (July) after the legislature defies his order to revoke Adams' circular letter. In August, in Boston and New York, merchants agree to boycott most British goods until the Townshend Acts are repealed. In September, at a town meeting in Boston, residents are urged to arm themselves. Later in September, British warships sail into Boston Harbor, then two regiments of British infantry land in Boston and set up permanent residence to keep order
1769
[edit]- To the Betrayed Inhabitants of the City and Colony of New York broadside published anonymously by local Son of Liberty Alexander McDougall (December 16)
1770s
[edit]1770
[edit]
- Golden Hill incident in which British troops wound civilians, including one death (January 19)
- Lord North becomes Prime Minister of Great Britain (January 28)
- Shooting of Christopher Seider (February 22)
- Boston Massacre (March 5)
1771
[edit]- Battle of Alamance in North Carolina (May 16)
1772
[edit]- Samuel Adams organizes the Committees of Correspondence
- Pine Tree Riot (April 13–14)
- The Watauga Association in what would become Tennessee declares itself independent (May)
- Gaspee Affair (June 9)
- Somerset v Stewart A British court ruling confirms that there is nothing in English common law that supports slavery in England (June 22)
1773
[edit]- James Rivington's New-York Gazeteer begins publication (April 22)
- Parliament passes the Tea Act, requiring the colonies to buy tea solely from the East India Company rather than a variety of sources (May 10)
- Association of the Sons of Liberty in New York published by local Sons of Liberty (December 15)
- Colonists in all major ports refuse to allow tea to be landed
- Boston Tea Party (December 16)
1774
[edit]- Benjamin Franklin, Massachusetts' agent in London, is ridiculed before Parliament (January 29)[1]
- Lord Dunmore's War (May–October)
- British pass Intolerable Acts, including:
- Boston Port Act (March 31)
- Administration of Justice Act (May 20)
- Massachusetts Government Act (May 20)
- A second Quartering Act (June 2)
- Quebec Act (June 22)
- Powder Alarm, General Gage's secret raid on the Cambridge powder magazine (September 1)
- First Continental Congress, (September 5 – October 26); 12 colonies send delegates; major actions:
- Declaration and Resolves, also known as Declaration of Rights (October 14)[2]
- Continental Association (October 20)[3]
- Petition to the King (October 26)
- Suffolk Resolves, Suffolk County, Massachusetts (September 9)
- Burning of the Peggy Stewart (October 19)
- Greenwich Tea Party (December 22)
1775
[edit]
- Conciliatory Resolution (February 27) in Parliament
- Paul Revere's Midnight Ride (April 18)
- Battles of Lexington and Concord, followed by the Siege of Boston (April 19)
- Gunpowder Incident (April 20)
- Skenesboro, New York (now Whitehall, New York) captured by Lieutenant Samuel Herrick (May 9)
- Fort Ticonderoga captured by Ethan Allen, Benedict Arnold and the Green Mountain Boys (May 10)
- Second Continental Congress meets (May 10)
- Battle of Machias (June 11–12)
- Congress votes to create Continental Army out of the militia units around Boston and appointed George Washington of Virginia as commanding general. This would later become the modern United States Army (June 14)
- Battle of Bunker Hill (June 17)
- Washington arrives in Cambridge, Massachusetts to take command of the Continental Army (July 2)
- Declaration of the Causes and Necessity of Taking Up Arms issued (July 6)
- Olive Branch Petition sent to King George III (July 8)
- King George III issues a proclamation declaring the colonies in rebellion (August 23)
- Continental Navy established by the Second Continental Congress (October 13)
- Snow Campaign (November–December)
- Dunmore's Proclamation issued by Lord Dunmore, colonial governor of Virginia, offering freedom to slaves that abandon their Patriot masters and fight for the British (November 7)
- Continental Marines established by Continental Congress. They would become the modern day United States Marine Corps (November 10)
- Battle of Kemp's Landing (November 15)
- Siege of Savage's Old Fields (November 19–21)
- Henry Knox transported fifty-nine captured cannons (taken from Fort Ticonderoga and Fort Crown Point) from upstate New York to Boston, Massachusetts; took 56 days to complete (December 5, 1775 – January 24, 1776)
- Battle of Great Bridge (December 9)
- British forces repulse an attack by Continental Army generals Richard Montgomery and Benedict Arnold at the Battle of Quebec (December 31)
1776
[edit]- Burning of Norfolk (January 1)
- New Hampshire ratifies the first state constitution (January 5)
- Thomas Paine publishes Common Sense (January 10)
- David Mathews appointed Mayor of New York, the highest ranking civilian officer for English North America for the duration of the Revolution
- Battle of Moore's Creek Bridge (February 27)
- Battle of the Rice Boats (March 2–3)
- Battle of Nassau (March 3–4)
- Fortification of Dorchester Heights results in British forces evacuating Boston (March 4–5)
- British evacuate Boston (March 17)
- The Continental Army departs its first winter encampment at Cambridge, Massachusetts (April 4)
- Congress opens American ports to trade with all other nations except Britain (April 6)
- Pennsylvania Provincial Conference (June 18–25)
- Battle of Sullivan's Island (June 28)
- Thomas Hickey hanged for role in plot to assassinate George Washington (June 28). British Colonial Loyalist New York Mayor David Mathews previously arrested in Flatbush, Brooklyn for his role in the plot (June 22)
- Battle of Turtle Gut Inlet (June 29)
- Largest assembly of British naval fleet in history commences off the coasts of Staten Island, Brooklyn and New Jersey (July 3)

- Second Continental Congress enacts (July 2) a resolution declaring independence from the British Empire, and then approves (July 4) the written "United States Declaration of Independence"
- Sons of Liberty order enslaved African Americans to topple the statue of King George III in Bowling Green (July 9)
- Battle of Long Island, a.k.a. Battle of Brooklyn (August 27)
- British prison ships begin in Wallabout Bay, New York
- Staten Island Peace Conference (September 11)
- Landing at Kip's Bay (September 15)
- Battle of Harlem Heights (September 16)
- Great Fire of New York (September 21–22)
- Nathan Hale captured and executed for espionage (September 22)
- Battle of Valcour Island (October 11)
- Battle of Pell's Point (October 18)
- Battle of White Plains (October 29)
- Battle of Fort Cumberland (November 10–29)
- Battle of Fort Washington (November 16)
- Battle of Fort Lee (November 20)
- Ambush of Geary (December 14)
- Battle of Iron Works Hill (December 23–26)

- Battle of Trenton (December 26)
1777
[edit]- Battle of the Assunpink Creek, also known as the Second Battle of Trenton (January 2)
- Battle of Princeton (January 3)
- Continental Army enters second winter encampment of the war at Morristown (January 6)
- Forage War (January–March):
- Battle of Millstone (January 20)
- Battle of Drake's Farm (February 1)
- Battle of Quibbletown (February 8)
- Battle of Spanktown (February 23)
- Battle of Bound Brook (April 13)
- British regulars, under Major General William Tryon, burn and loot Danbury, Connecticut (April 26)
- Battle of Ridgefield (April 27)
- Battle of Thomas Creek (May 17)
- Meigs Raid (May 23)
- First Middlebrook encampment (May 28 – July 2)
- Battle of Short Hills (June 26)
- Fort Ticonderoga abandoned by the Americans due to advancing British troops placing cannon on Mount Defiance (July 5)
- British retake Fort Ticonderoga (July 6)
- Battle of Hubbardton (July 7)
- Delegates in Vermont, which was not one of the Thirteen Colonies, establish a republic and adopt a constitution, the first in what is now the territory of the United States to prohibit slavery (July 8)
- Battle of Fort Anne (July 8)
- Siege of Fort Stanwix (August 2–23)
- Battle of Oriskany (August 6)
- Battle of Machias (1777) (August 13–14)
- Battle of Bennington (August 16)
- Battle of Staten Island (August 22)
- Siege of Fort Henry (September 1)
- Battle of Cooch's Bridge (September 3)
- Battle of Brandywine (September 11)
- Battle of the Clouds (September 16)
- Battle of Paoli (Paoli Massacre) (September 20)
- British occupation of Philadelphia (September 26)
- Battle of Germantown (October 4)

- Battle of Forts Clinton and Montgomery (October 6)
- Two Battles of Saratoga (September 19 and October 7) conclude with the surrender of the British army under General Burgoyne.
- Battle of Red Bank (October 22)
- Articles of Confederation adopted by the Second Continental Congress (November 15)
- Capture of Fort Mifflin, (November 16) and Fort Mercer, (November 18)
- Battle of Gloucester (1777) (November 25)
- Battle of White Marsh (December 5 – December 8)
- Battle of Matson's Ford (December 11)
- Rivington's Gazetter renamed Royal Gazette (December 13)
- Continental Army in third winter quarters at Valley Forge (December 19, 1777 – June 19, 1778)
1778
[edit]- Treaty of Amity and Commerce and Treaty of Alliance with France (February 6)
- France is the first foreign country to recognise the flag of the United States, on the ship of John Paul Jones (February 14)
- Battle of Quinton's Bridge (March 18)
- John Paul Jones, in command of the Ranger, attacks Whitehaven in England, America's first naval engagement outside North America (April 20)
- The Great Chain across the Hudson is completed (April 30)
- Battle of Crooked Billet (May 1)
- Battle of Barren Hill (May 20)
- Battle of Cobleskill (May 30)
- British occupation of Philadelphia (ends June)
- Whaleboat attack on Flatbush, Brooklyn to kidnap New York Mayor David Mathews and other British and Loyalist figures partially succeeds in securing Captain James Moncrief and Theophylact Bache, President of the New York Chamber of Commerce, for future prisoner exchange (June)
- Battle of Monmouth (June 28)
- Battle of Wyoming (July 3)
- Battle of Ushant (July 27)
- Battle of Rhode Island (August 29)
- Baylor Massacre (September 27)
- Culper Spy Ring is begun (October)
- Battle of Chestnut Neck (October 6)
- Affair at Little Egg Harbor (October 15)
- Cherry Valley massacre (November 11)
- Capture of Savannah, British successfully launch their southern strategy (December 29)
- Majority of Continental Army in fourth winter quarters at Middlebrook Cantonment (November 30, 1778 – June 3, 1779)
- Major General Israel Putnam chooses Redding, Connecticut as his winter encampment to keep an eye on the storehouses in Danbury, Connecticut (1778–1779)
1779
[edit]- Battle of Beaufort (February 3, 1779)
- Battle of Kettle Creek (February 14)
- Siege of Fort Vincennes (February 23–25)
- Chesapeake raid (May 10–24)
- Battle of Stono Ferry (June 20)
- Tryon's raid (July 3–14)
- Tryon's division lands in East Haven, Connecticut, met with spirited resistance from a band of local militia, take Black Rock Fort (July 5)
- Battle of Fairfield destroys 54 barns, 47 storehouses, burned 83 homes, two churches, and municipal buildings including a schoolhouse, the courthouse and the local jail (July 7)
- Battle of Norwalk weakly opposed by about 50 local militia, easily dispersed. The destruction of the village and its commercial infrastructure destroyed (July 11)
- Battle of Stony Point (July 16)
- Battle of Minisink (July 22)
- Penobscot Expedition (July 24 – August 14)
- Battle of Paulus Hook (August 19)
- Sullivan Expedition (June 18 – October 3)
- Battle of Newtown (August 29)
- Siege of Savannah (September 16 – October 18)
- Battle of Baton Rouge (September 21)
- Battle of Flamborough Head (September 23)
- Continental Army in fifth winter quarters at Morristown (December 1779 – May 1780)
1780s
[edit]1780
[edit]
- Congress establishes the Court of Appeals in Cases of Capture to provide for final adjudication of appeals from state court prize cases involving disposition of ships and cargo allegedly seized from the British (January 15)
- Battle of Cape St. Vincent (January 16)
- A stockade known as Fort Nashborough is founded on the banks of the Cumberland River (January 28). Two years later, the site is renamed Nashville
- Some 8,000 British forces under General Henry Clinton arrive in Charleston, South Carolina, from New York (February 1)
- New York cedes to Congress its western claims, including territory west of Lake Ontario (February 1). In 1792, New York will sell the Erie Triangle to Pennsylvania
- Battle of Young's House (February 3) (In the north)
- Bombardment of Fort Charlotte, after a two-week siege, Spanish general, colonial governor of Louisiana, and Viceroy of New Spain Bernardo de Gálvez captures Fort Charlotte, taking the port of Mobile (in present-day Alabama) from the British (March 14). Fort Charlotte was the last remaining British frontier post capable of threatening New Orleans in Spanish Louisiana. Its fall drove the British from the western reaches of West Florida and reduced the British military presence in West Florida to its capital, Pensacola.
- Siege of Charleston (March 29 – May 12)
- British Army troops under General Henry Clinton and naval forces under Admiral Mariot Arbuthnot besiege Charleston, South Carolina. British ships sail past Fort Moultrie on Sullivan's Island to occupy Charleston Harbor (April 8)
- Battle of Monck's Corner (April 14)
- Battle of Lenud's Ferry (May 6)
- Fort Moultrie falls to the British (May 7)
- American General Benjamin Lincoln surrenders Charleston to the British. The British lose 255 men while capturing a large American garrison (May 12)
- Bird's invasion of Kentucky (May 25 – August 4) (In the west)
- Battle of Waxhaws; a clash between Continental Army forces under Abraham Buford and a mainly Loyalist force led by Banastre Tarleton occurs near Lancaster, South Carolina in the Waxhaws area (close to present-day Buford). The British destroyed the American forces (May 29)
- Alexander's Old Field in Beckhamville, South Carolina (June 6)
- Battle of Connecticut Farms (June 7) (In the north)
- Battle of Mobley's Meeting House (June 10)
- Battle of Ramsour's Mill (June 20)
- Battle of Springfield; with the attempted British invasion of New Jersey stopped at Connecticut Farms and Springfield, major fighting in the North ends (June 23)
- Robert Morris is appointed Superintendent of Finance, a post akin to Prime Minister, by Congress (June 27)
- Expédition Particulière (July 11)
- Battle of Williamson's Plantation (AKA Huck's Defeat) (July 12)
- Battle of Bull's Ferry (July 20–21) (In the north)
- Battle of Colson's Mill (July 21)
- Battle of Rocky Mount (August 1)
- Battle of Hanging Rock (August 6)
- Battle of Piqua (August 8) (In the west)
- Battle of Camden, British General Cornwallis gains a humiliating victory over Gates in South Carolina (August 16)
- Battle of Fishing Creek (August 18)
- Battle of Musgrove Mill (August 18)
- Battle of Black Mingo (August 28)
- Battle of Wahab's Plantation (September 21)
- Major John André captured and the treason of Benedict Arnold is exposed (September 23)
- Battle of Charlotte (September 26)
- John André executed as a spy (October 2)
- Battle of Kings Mountain (October 7)
- Royalton Raid (October 16)
- Battle of Klock's Field (October 19)
- Battle of Fishdam Ford (November 9)
- Battle of Blackstock's Farm (November 20)
- Continental Army enters sixth winter with encampments in New York's Hudson Highlands, Pompton, and Morristown, New Jersey (December)
1781
[edit]- The future King William IV, the only active member of the British Royal Family to visit the former 13 colonies, takes up residence in the Rose and Crown Tavern on Staten Island.
- Pennsylvania Line Mutiny (January 1–29)
- Raid on Richmond (January 1–19)
- Battle of Cowpens (January 17)
- Pompton Mutiny (January 20)
- Battle of Cowan's Ford (February 1)
- Pyle's Massacre (February 24)
- Articles of Confederation ratified (March 1)
- Skirmish at Waters Creek (March 8)
- Battle of Guilford Court House (March 15)
- Battle of Cape Henry (March 16)
- Battle of Blandford (April 25)
- Battle of Hobkirk's Hill (April 25)
- Action at Osborne's (April 27)
- Siege of Augusta (May 22 – June 6)
- Siege of Ninety-Six (May 22 – June 19)
- Battle of Spencer's Ordinary (June 26)
- Battle of Green Spring (July 6)
- Francisco's Fight (July 9–24)
- Battle of the Chesapeake (September 5)
- Battle of Groton Heights (September 6)
- Battle of Eutaw Springs (September 8)
- The British surrender at Yorktown (October 19)
- Continental Army returns to Hudson Highlands and Morristown New Jersey for its seventh winter encampment (December)
- Bank of North America chartered (December 31)
1782
[edit]- The British House of Commons votes against further war, informally recognizing American independence (February 27)
- Gnadenhutten massacre (March 8)
- Battle of Little Mountain (March 22)
- Newburgh letter sent to George Washington by Lewis Nicola (May 22)
- Crawford expedition (May 25 – June 12)
- Siege of Bryan Station (August 15–17)
- Battle of Blue Licks (August 19)
- Battle of the Combahee River (August 27)
- Siege of Fort Henry (1782) (September 11–13)
- Continental Army moves into its eighth and final winter quarters, at the New Windsor Cantonment and in the Hudson Highlands (November)
- Preliminary Articles of Peace are signed by British negotiator Richard Oswald and representatives of the United States of America (November 30)
- British evacuate Charleston, South Carolina (December 14)
- Last skirmish of the conflict takes place near Cedar Bridge Tavern in Barnegat Township, New Jersey (December 27)
1783
[edit]
- Newburgh Conspiracy (March 10–15)
- Pennsylvania Mutiny of 1783 (June 20–24)
- The Treaty of Paris (1783) ends the American Revolutionary War (September 3)
- The British evacuate New York, marking the end of British rule. British loyalist refugees retreat to Quebec and Nova Scotia. General George Washington triumphantly returns with the Continental Army (November 25).
- George Washington resigns as commander-in-chief of the Continental Army (December 23)
1784
[edit]- The Treaty of Paris is ratified by the Congress (January 14)
- Jay–Gardoqui Treaty with Spain fails to be ratified. Negotiations continued until 1786
- The Treaty of Paris is ratified by the British (April 9)
- Ratified treaties are exchanged in Paris between the two nations (May 12)
- "The State of Frankland," later known as Franklin, secedes from North Carolina (August 23)
- Robert Morris resigns as Superintendent of Finance and is not replaced (November 1)
1785
[edit]- Congress refuses admission of the State of Franklin to the Union (May 16)
- Treaty of Hopewell (November 28)
1786
[edit]- Shays' Rebellion (August 29 – June 1787)
- Annapolis Convention fails (September 11–14)
1787
[edit]- Northwest Ordinance enacted (July 13)

- Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia (May 25 - September 17)
- Delaware (December 7), Pennsylvania (December 12), and New Jersey (December 18) ratify the Constitution
1788
[edit]- North Carolina reasserted it claim to its Overmountain region, at which time Franklin ceases to exist
- Georgia, Connecticut, Massachusetts, Maryland, South Carolina, New Hampshire, Virginia and New York ratify the Constitution
- United States Constitution ratified (June 21)
- Cyrus Griffin resigns as "President of the United States in Congress Assembled" (November 2), and with the exceptions of John Jay and John Knox remaining as Secretaries of Foreign Affairs and War respectively; and Michael Hillegas remaining as Treasurer, the United States of America temporarily ceases to exist.[citation needed]
- The first federal Elections for the House of Representatives begin
- 1788–89 United States presidential election (December 15, 1788 – January 10, 1789). George Washington is elected president, and John Adams is elected vice president.
1789
[edit]- Philip Pell, only member in attendance, adjourns the Congress of the Confederation sine die (March 2)
- Members of the 1st United States Congress begin to take their seats at Federal Hall, New York (March 4)
- House of Representatives first achieves a quorum and elects its officers (April 1)
- Senate first achieves a quorum and elects its officers (April 6)
- Joint session of Congress counts the Electoral College ballots, certifies that George Washington has been unanimously elected President of the United States (April 6)
- Adams becomes the first vice president (April 21)
- Washington becomes the first president, at Federal Hall in New York City (April 30)
- The Tariff Act of 1789 is signed into law (July 4)
- Charles Thomson resigns as secretary of Congress and hands over the Great Seal, bringing an end to the Confederation Congress (July)
- Judiciary Act of 1789 (September 24)
- Congress approves twelve articles of amendment to the Constitution, the Bill of Rights (September 25)
- North Carolina becomes the 12th state to ratify the Constitution, with a vote of 194–77 (November 21)
1790s
[edit]1791
[edit]- Bill of Rights ratified. (December 15)
1792
[edit]- 1792 United States presidential election: George Washington reelected president, John Adams reelected vice president.
1793
[edit]- President Washington and Vice President Adams begin their second terms (March 4).
1795
[edit]- Jay's Treaty ratified in June toward resolving post Revolution tensions between the United States and Great Britain. First use of arbitration in modern diplomatic history for Canada–United States border disputes.
1796
[edit]- Six Northwest Territory forts and two Upstate New York forts that remained under British control are ceded to the United States.
- 1796 United States presidential election: John Adams is elected president, Thomas Jefferson elected vice president.
1797
[edit]- Adams becomes the second president, Jefferson becomes the second vice president (March 4).
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Founders Online: The Final Hearing before the Privy Council Committee for Plant …".
- ^ Declaration and Resolves of the First Continental Congress, New Haven, Connecticut: Lillian Goldman Law Library, Yale Law School: Avalon Project, October 14, 1774, retrieved January 10, 2022
- ^ Continental Congress (October 20, 1774). "Continental Association (Articles of Association)". Founders Online (founders.archives.gov). National Archives. Retrieved January 10, 2022.
Further reading
[edit]- Cullen, Joseph P. The concise illustrated history of the American Revolution (1972) for secondary schools online 136pp
- Fremont-Barnes, Gregory, and Richard Alan Ryerson, eds. The Encyclopedia of the American Revolutionary War: A Political, Social, and Military History (5 vol. 2006)
- George, Lynn. A Timeline of the American Revolution (2002) 24pp; for middle schools online
- Morris, Richard B. Encyclopedia of American History (7th ed. 1996) online, detailed timeline
External links
[edit]Wikimedia Commons has media related to American Revolution.
| Year | |
|---|---|
| General | |
| Military | |
| Groups | |
| Industry |
|