 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Biacalein; Noroxylin |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.164.911 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
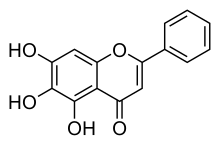
| Formula | C15H10O5 |
| Molar mass | 270.240 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Baicalein (5,6,7-trihydroxyflavone) is a flavone, a type of flavonoid,[1] originally isolated from the roots of Scutellaria baicalensis and Scutellaria lateriflora. It is also a constituent of Oroxylum indicum (Indian trumpetflower) and thyme.[2] It is the aglycone of baicalin.