| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
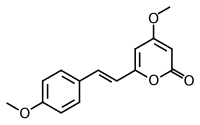
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-Methoxy-6-[(E)-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethen-1-yl]-2H-pyran-2-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.211.821 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H14O4 | |
| Molar mass | 258.273 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Yangonin is one of the six major kavalactones found in the kava plant.[1] It has been shown to possess binding affinity for the cannabinoid receptor CB1 (Ki = 0.72 μM), and selectivity vs. the CB2 receptor (Ki >10 μM) where it behaves as an agonist. The CB1 receptor affinity of yangonin suggests that the endocannabinoid system might contribute to the complex human psychopharmacology of the traditional kava drink and the anxiolytic preparations obtained from the kava plant.[2]
Like other kavalactones, yangonin has been found to potentiate GABAA receptors.[3] This may contribute to the anxiolytic properties of yangonin and kava as a whole.
Further in vitro studies have also demonstrated yangonin to be an inhibitor of monoamine oxidase,[citation needed] with a moderate preference for isozyme B, which could open the door to a wide range of interactions.
