The Hungary Portal




Hungary (Hungarian: Magyarország [ˈmɒɟɒrorsaːɡ] ⓘ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning 93,030 square kilometres (35,920 sq mi) of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and Slovenia to the southwest, and Austria to the west. Hungary has a population of 9.6 million, mostly ethnic Hungarians and a significant Romani minority. Hungarian is the official language, and Budapest is the country's capital and largest city.
Prior to the foundation of the Hungarian state, various peoples settled in the territory of present-day Hungary, most notably the Celts, Romans, Huns, Germanic peoples, Avars and Slavs. The Principality of Hungary was established in the late 9th century by Álmos and his son Árpád through the conquest of the Carpathian Basin. King Stephen I ascended the throne in 1000, converting his realm to a Christian kingdom. The medieval Kingdom of Hungary was a European power, reaching its height in the 14th-15th century. After a long period of Ottoman wars, Hungary’s forces were defeated at the Battle of Mohács and its capital was captured in 1541, opening roughly a 150 years long period when the country was divided into three parts: Royal Hungary loyal to the Habsburgs, Ottoman Hungary and the largely independent Principality of Transylvania. The reunited Hungary came under Habsburg rule at the turn of the 18th century, fighting a war of independence in 1713–1711, and a war of independence in 1848–1849 until a compromise allowed the formation of the Austro-Hungarian Monarchy in 1867, a major power into the early 20th century. Austria-Hungary collapsed after World War I, and the subsequent Treaty of Trianon in 1920 established Hungary's current borders, resulting in the loss of 71% of its historical territory, 58% of its population, and 32% of its ethnic Hungarians.
In the interwar period, after initial turmoil, Miklós Horthy ascended as a determining politician, representing the monarchy as regent in place of the Habsburgs. Hungary joined the Axis powers in World War II, suffering significant damage and casualties. As a result, the Hungarian People's Republic was established as a satellite state of the Soviet Union. Following the failed 1956 revolution, Hungary became a comparatively freer, though still repressed, member of the Eastern Bloc. In 1989, concurrently with the Revolutions of 1989, Hungary peacefully transitioned into a democratic parliamentary republic, joining the European Union in 2004 and being part of the Schengen Area since 2007.
Hungary is a high-income economy with universal health care and tuition-free secondary education. Hungary has a long history of significant contributions to arts, music, literature, sports, science and technology. It is a popular tourist destination in Europe, drawing 24.5 million international tourists in 2019. It is a member of numerous international organisations, including the Council of Europe, NATO, United Nations, World Health Organization, World Trade Organization, World Bank, Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, and the Visegrád Group. (Full article...)
Joel Brand (Hungarian: Brand Jenő; 25 April 1906 – 13 July 1964) was a member of the Budapest Aid and Rescue Committee (Va'adat ha-Ezra ve-ha-Hatzala be-Budapest or Va'ada), an underground Zionist group in Budapest, Hungary, that smuggled Jews out of German-occupied Europe to the relative safety of Hungary, during the Holocaust. When Germany invaded Hungary in March 1944, Brand became known for his efforts to save the Jewish community from deportation to the Auschwitz concentration camp in occupied Poland and the gas chambers there.
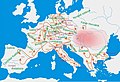
In April 1944 Brand was approached by SS-Obersturmbannführer Adolf Eichmann, head of the German Reich Security Head Office department IV B4 (Jewish affairs), who had arrived in Budapest to organize the deportations. Eichmann proposed that Brand broker a deal between the SS and the United States or Britain, in which the Nazis would exchange one million Jews for 10,000 trucks for the Eastern front and large quantities of tea and other goods. It was the most ambitious of a series of proposals between the SS and Jewish leaders. Eichmann called it "Blut gegen Waren" ("blood for goods"). (Full article...)Selected article -
People
- Musicians
Béla Bartók – János Bihari – Ernő Dohnányi – Béni Egressy – Ferenc Erkel – Zoltán Kocsis – Zoltán Kodály – Franz Liszt - Eugene Ormandy - George Szell - András Schiff
- Painters
Gyula Benczúr – Tivadar Csontváry Kosztka – Béla Czóbel – Árpád Feszty – Károly Lotz – Viktor Madarász – Mihály Munkácsy – József Rippl-Rónai – Pál Szinyei Merse – István Szőnyi – Victor Vasarely
- Photographers
Brassaï – Cornell Capa – Robert Capa – Lucien Hervé – André Kertész – László Moholy-Nagy – Martin Munkácsi
- Scientists
Béla H. Bánáthy – Zoltán Bay – Georg von Békésy – Farkas Bolyai – János Bolyai – Károly Bund – József Eötvös – Loránd Eötvös – Dennis Gabor – John Charles Harsanyi – George de Hevesy – Alexander Csoma de Kőrös – László Lovász – John von Neumann – George Andrew Olah – Ernő Rubik – Hans Selye – Ignaz Semmelweis – Charles Simonyi – János Szentágothai – Albert Szent-Györgyi – Leó Szilárd – Edward Teller – Eugene Wigner
- Writers and poets
Endre Ady – János Arany – József Eötvös – György Faludy – Béla Hamvas – Mór Jókai – Attila József – Ferenc Kazinczy – Imre Kertész – János Kodolányi – Ferenc Kölcsey – Imre Madách – Sándor Márai – Ferenc Molnár – Sándor Petőfi – Miklós Radnóti – Magda Szabó – Antal Szerb – Miklós Vámos – Mihály Vörösmarty
- Statesmen, Politicians and Military
Gyula Andrássy – Lajos Batthyány – Gabriel Bethlen – Stephen Bocskay – Matthias Corvinus – Ferenc Deák – Miklós Horthy – Lajos Kossuth – Ferenc Nagy – Imre Nagy – Bertalan Szemere – István Széchenyi – Miklós Wesselényi – Vilmos Nagy of Nagybaczon
- Sportspeople
József Bozsik – Krisztina Egerszegi – Zoltán Gera – Dezső Gyarmati – Ágnes Keleti – Péter Lékó – Csaba Mérő – Tibor Nyilasi – László Papp – Judit Polgár – Zsuzsa Polgár – Ferenc Puskás
- Film & Stage
Nimród Antal – Michael Curtiz – John Garfield – Miklós Jancsó – Sir Alexander Korda – Peter Lorre – Béla Lugosi – Emeric Pressburger – Miklós Rózsa – Andy G. Vajna – Gábor Zsazsa

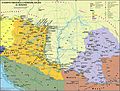
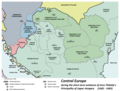
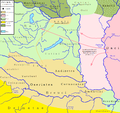
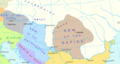
Béla IV (1206 – 3 May 1270) was King of Hungary and Croatia between 1235 and 1270, and Duke of Styria from 1254 to 1258. As the oldest son of King Andrew II, he was crowned upon the initiative of a group of influential noblemen in his father's lifetime in 1214. His father, who strongly opposed Béla's coronation, refused to give him a province to rule until 1220. In this year, Béla was appointed Duke of Slavonia, also with jurisdiction in Croatia and Dalmatia. Around the same time, Béla married Maria, a daughter of Theodore I Laskaris, Emperor of Nicaea. From 1226, he governed Transylvania as duke. He supported Christian missions among the pagan Cumans who dwelled in the plains to the east of his province. Some Cuman chieftains acknowledged his suzerainty and he adopted the title of King of Cumania in 1233. King Andrew died on 21 September 1235 and Béla succeeded him. He attempted to restore royal authority, which had diminished under his father. For this purpose, he revised his predecessors' land grants and reclaimed former royal estates, causing discontent among the noblemen and the prelates.
The Mongols invaded Hungary and annihilated Béla's army in the Battle of Mohi on 11 April 1241. He escaped from the battlefield, but a Mongol detachment chased him from town to town as far as Trogir on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. Although he survived the invasion, the Mongols devastated the country before their unexpected withdrawal in March 1242. Béla introduced radical reforms in order to prepare his kingdom for a second Mongol invasion. He allowed the barons and the prelates to erect stone fortresses and to set up their private armed forces. He promoted the development of fortified towns. During his reign, thousands of colonists arrived from the Holy Roman Empire, Poland and other neighboring regions to settle in the depopulated lands. Béla's efforts to rebuild his devastated country won him the epithet of "second founder of the state" (Hungarian: második honalapító). (Full article...)Selected picture
Wikiprojects
Related projects:
Related portals
Things you can do
| The following stub articles would benefit from expansion. | |
Topics
Categories
New articles
Rules | Match log | Results page (for watching) | Last updated: 2024-02-07 20:40 (UTC)
Note: The list display can now be customized by each user. See List display personalization for details.
- Equestrian events at the 1936 Summer Olympics (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Raydann (talk · contribs · new pages (50)) started on 2024-02-07, score: 20
- Siege of Esztergom (1685) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Vbbanaz05 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-02-07, score: 30
- Ignác Amsel (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Svartner (talk · contribs · new pages (164)) started on 2024-02-07, score: 90
- Siege of Kanizsa (1690) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SebbeKg (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-02-07, score: 90
- Battle of Zsarnóca (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SebbeKg (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-02-07, score: 50
- Jean Hathaway (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by PigeonChickenFish (talk · contribs · new pages (57)) started on 2024-02-06, score: 60
- Giuseppe Salvatore Pianell (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Manoru007 (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-02-06, score: 20
- Deaths in January 2024 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rusted AutoParts (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-02-06, score: 40
- Mickiewicz Falls (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by PavKls (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2024-02-06, score: 50
- Jenő Medgyessy (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Svartner (talk · contribs · new pages (164)) started on 2024-02-06, score: 70
- Siege of Nitra (1664) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SebbeKg (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-02-06, score: 70
- Siege of Kanizsa (1664) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SebbeKg (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-02-06, score: 70
- The Village Scene (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Whispyhistory (talk · contribs · new pages (9)) started on 2024-02-06, score: 20
- Jeux sans frontières (season 30) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Gonnym (talk · contribs · new pages (40)) started on 2024-02-05, score: 40
- Lovro Šitović (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Governor Sheng (talk · contribs · new pages (38)) started on 2024-02-05, score: 20
- Winter Campaign of Austro-Turkish War (1663–1664) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Vbbanaz05 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-02-05, score: 180
- Palermo Airport (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Amakuru (talk · contribs · new pages (57)) started on 2024-02-05, score: 30
- Ottoman-Habsburg War (1565-1568) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SebbeKg (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-02-05, score: 140
- Pest County 6th constituency (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tutwakhamoe (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-02-05, score: 90
- I'll Make You Happy (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tassedethe (talk · contribs · new pages (83)) started on 2024-02-04, score: 20
- Vladimír Janoušek (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by NoJin (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-02-04, score: 30
- Róbert Gragger (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Shhhnotsoloud (talk · contribs · new pages (29)) started on 2024-02-04, score: 20
- Etta Becker-Donner (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Alperen (talk · contribs · new pages (16)) started on 2024-02-04, score: 20
- The Vina Player (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Whispyhistory (talk · contribs · new pages (9)) started on 2024-02-04, score: 20
- Wojciech Komorowski (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SebbeKg (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-02-04, score: 20
- Mette Sjøberg (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Fregerslev (talk · contribs · new pages (22)) started on 2024-02-04, score: 20
- Janka Zirzen (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Thirukannan (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-02-03, score: 90
- Joseph Körösi (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Josephine1915 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-02-03, score: 50
- Bulcsú Révész (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hildreth gazzard (talk · contribs · new pages (98)) started on 2024-02-03, score: 40
- Judit Gervain (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Muspilli (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-02-03, score: 20
- Lee Aaliya (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Dainshku (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2024-02-03, score: 20
- Xaivian Lee (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by BullDawg2021 (talk · contribs · new pages (18)) started on 2024-02-03, score: 20
- Adalbert László Arany (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Alperen (talk · contribs · new pages (16)) started on 2024-02-02, score: 60
- 2025 Formula One World Championship (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DualSkream (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-02-01, score: 20
- 2024 IHF Men's Olympic Qualification Tournaments (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Kante4 (talk · contribs · new pages (68)) started on 2024-02-02, score: 20
- Ukrainian-Polish conflict in Volhynia (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Olek Novy (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2024-02-02, score: 20
- Fox (international) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by TemaGub2002 (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-02-02, score: 20
- Tetiana Lazarenko (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ілля Криворучко (talk · contribs · new pages (18)) started on 2024-02-02, score: 20
- Population 11 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Phinbart (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-02-01, score: 20
- Tibor Ág (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Alperen (talk · contribs · new pages (16)) started on 2024-02-01, score: 100
- Ág Tibor (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Alperen (talk · contribs · new pages (16)) started on 2024-02-01, score: 100
- 2023 World Athletics Championships – World Team (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tfisher93 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-02-01, score: 20
- Anhelina Khmil (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ілля Криворучко (talk · contribs · new pages (18)) started on 2024-02-01, score: 20
- Joseph Chrysostomus Pauer (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Governor Sheng (talk · contribs · new pages (38)) started on 2024-01-31, score: 30
- List of CSI: Vegas episodes (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 86.1.199.26 (talk · contribs · new pages (11)) started on 2024-01-30, score: 20
- Óscar Ortubé (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Gianlu2790 (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2024-01-31, score: 20
- József Vida (banker) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Pete 4583 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-01-31, score: 50
- Hutsul Uprising (1919) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Галай Артём (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-01-31, score: 40
- Nazareno Sasia (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Pietaster (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-01-31, score: 30
- Valdiléia Martins (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Pietaster (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-01-31, score: 30
- Deaths in 1979 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by ItsCheck (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-01-31, score: 20
- Crisis of the Piast dynasty (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SebbeKg (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-01-31, score: 30
- Berlin Conference (November 2–6, 1917) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Juan José Arcila M (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-01-31, score: 40
- CSI: Vegas (season 2) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 86.1.199.26 (talk · contribs · new pages (11)) started on 2024-01-30, score: 20
- Julius Mannaberg (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Eli185.2 (talk · contribs · new pages (14)) started on 2024-01-27, score: 70
- Miklós Benedek (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Spinster300 (talk · contribs · new pages (28)) started on 2024-01-30, score: 90
- 2008–09 Baktalórántháza VSE season (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rakeck (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-01-30, score: 260
- Lajos Kazár (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by HUR752 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-01-30, score: 90
- Pongrác Szentmiklósi (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by TheReablikin (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-01-30, score: 40
- Berlin Conference (March 26-27, 1917) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Juan José Arcila M (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-01-29, score: 40
- Pyotr Sergiev (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rahammz (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-01-29, score: 30
- Mle Collins (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jankec666 (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-01-29, score: 90
- Dragan Pechmalbec (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Williehuggies (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2024-01-29, score: 20
- Klara Valko (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by HRShami (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2024-01-29, score: 40
- 2023–24 synchronized skating season (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by MeSpnt (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-01-29, score: 20
- Gyula Tóth (politician) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jmanlucas (talk · contribs · new pages (31)) started on 2024-01-28, score: 80
- Josef Reither (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Thürneustift (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-01-28, score: 20
- Johann Steinböck (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Thürneustift (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-01-28, score: 20
- Ibrahim Ghanem (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Pehlivanmeydani (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-01-28, score: 20
- Doina lui Lucaciu (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Biruitorul (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-01-28, score: 20
- 2024 in ice hockey (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Xegma (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-01-28, score: 30
- Corus Chess Tournament 2008 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Chessrat (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-01-28, score: 20
- Corus Chess Tournament 2006 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Chessrat (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-01-28, score: 40
- Corus Chess Tournament 2005 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Chessrat (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-01-28, score: 20
- Corus Chess Tournament 2004 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Chessrat (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-01-28, score: 20
- Corus Chess Tournament 2003 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Chessrat (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-01-28, score: 40
- Andrew Kaplon (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Norden1990 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-01-27, score: 120
- 2023–24 Middle Tennessee Blue Raiders women's basketball team (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RedSox39 (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2024-01-27, score: 20
- Eduard Hartmann (politician) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Thürneustift (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-01-27, score: 20
- Haru Kakiuchi (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rainbowed-Sunned-Spirit (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-01-27, score: 30
- Edith Hoffmann (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Spinster300 (talk · contribs · new pages (28)) started on 2024-01-27, score: 100
- Acanthus hungaricus (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tom Radulovich (talk · contribs · new pages (114)) started on 2024-01-27, score: 20
- Fra Paalman (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Global Archives (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-01-27, score: 20
- Lyubov Korol' (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ілля Криворучко (talk · contribs · new pages (18)) started on 2024-01-27, score: 20
- The Hungarian Brothers (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Lord Cornwallis (talk · contribs · new pages (161)) started on 2024-01-27, score: 20
- Ottoman-Habsburg War (1551–1562) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SebbeKg (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-01-25, score: 210
- City Assembly of Novi Sad (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Nickpunk (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-01-26, score: 20
- Andriy Oleynyk (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ілля Криворучко (talk · contribs · new pages (18)) started on 2024-01-26, score: 20
- Sergiy Bilov (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ілля Криворучко (talk · contribs · new pages (18)) started on 2024-01-26, score: 20
- Corus Chess Tournament 2010 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Greenman (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-01-26, score: 20
- 2011–12 Rákospalotai EAC season (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rakeck (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-01-26, score: 260
- Yukiko Umeno (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Family27390 (talk · contribs · new pages (40)) started on 2024-01-26, score: 40
- Ottoman-Habsburg War (1551-1562) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SebbeKg (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-01-25, score: 210
- Ottoman-Habsburg War (1540–1547) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SebbeKg (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-01-25, score: 150
- Big ring (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 65.92.247.66 (talk · contribs · new pages (16)) started on 2024-01-12, score: 20
- Wasservogel (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Miracle Pen (talk · contribs · new pages (128)) started on 2024-01-25, score: 20
- AG1 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Fourthords (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2024-01-25, score: 20
- Ottoman-Habsburg War (1540-1547) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SebbeKg (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-01-25, score: 160
- 2024 Magyar Kupa (men's basketball) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Cakesam (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-01-25, score: 160
- Pension systems by country (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Borysk5 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-01-24, score: 20
- József-Csaba Pál (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by TudorTulok (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-01-24, score: 20
- Republic of Ireland women's national football team results (2020–present) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Louelle.ivy (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-01-24, score: 20
- List of foreign ministers in 2023 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Snickers2686 (talk · contribs · new pages (11)) started on 2024-01-16, score: 20
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus