| Eugeroic | |
|---|---|
| Drug class | |
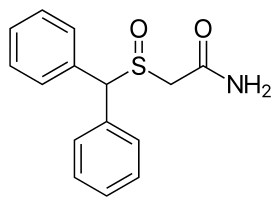 The chemical structure of modafinil, the prototypical drug of this class | |
| Class identifiers | |
| Synonyms | Wakefulness-promoting agent Wakefulness-promoting drug |
| Use | Promote wakefulness and alertness |
| ATC code | N06B |
| Legal status | |
| In Wikidata | |
Eugeroics (originally "eugrégorique" or "eugregoric"),[1] also known as wakefulness-promoting agents and wakefulness-promoting drugs, are a class of drugs that promote wakefulness and alertness.[2][3] They are medically indicated for the treatment of certain sleep disorders including excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS) in narcolepsy or obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).[2][3] Eugeroics are also often prescribed off-label for the treatment of EDS in idiopathic hypersomnia.[4] In contrast to classical psychostimulants, such as methylphenidate and amphetamine, which are also used in the treatment of these disorders, eugeroics typically do not produce marked euphoria, and, consequently, have a lower addictive potential.[2][3][5]
Modafinil and armodafinil are each thought to act as selective, weak, atypical dopamine reuptake inhibitors (DRI),[2][3] whereas adrafinil acts as a prodrug for modafinil. Other eugeroics include solriamfetol, which acts as a norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI),[6][7] and pitolisant, which acts as a histamine 3 (H3) receptor antagonist/inverse agonist.[8][9][10]
Recent research
[edit]Cephalon, the original U.S. market rights holder of modafinil, has demonstrated initiative in the development of a successor to the prototypical eugeroic.[11] Of the more than twenty compounds preclinically tested in Cephalon's three-part drug discovery series, the compound fluorenol was selected as a lead. Fluorenol was found to induce wakefulness to a greater degree than modafinil, despite possessing a lower affinity for the dopamine transporter.[12]
All currently marketed eugeroics are classified as central nervous system stimulants and possess some (attenuated) stimulant-like properties.[13][14] It is expected that future developments will further distinguish eugeroics from classical CNS stimulants.[15][11]
Examples
[edit]Marketed
[edit]- Armodafinil (Nuvigil)
- Modafinil (Provigil)
- Pitolisant (Wakix)[16]
- Solriamfetol (Sunosi)[14]
Discontinued
[edit]- Adrafinil (Olmifon)
Never marketed
[edit]- Flmodafinil (CRL-40,940)
- Fluorafinil (CRL-40,941)
- Fluorenol
- Methylbisfluoromodafinil
In development
[edit]- Selective orexin receptor agonists (two are currently under development by Takeda, danavorexton and TAK-994)[17]
- CE-123 is under patent by Red Bull.[18]
References
[edit]- ^ Milgram, Norton W.; Callahan, Heather; Siwak, Christina (2006). "Adrafinil: A Novel Vigilance Promoting Agent". CNS Drug Reviews. 5 (3): 193–212. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.1999.tb00100.x. ISSN 1080-563X.
- ^ a b c d "Provigil: Prescribing information" (PDF). United States Food and Drug Administration. Cephalon, Inc. January 2015. Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- ^ a b c d "Nuvigil: Prescribing information" (PDF). United States Food and Drug Administration. Cephalon, Inc. April 2015. Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- ^ "Practice Parameters for the Treatment of Narcolepsy and other Hypersomnias of Central Origin" (PDF). American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM). September 2007.
- ^ Taneja, Indu; Haman, Kirsten; Shelton, Richard C.; Robertson, David (February 2007). "A randomized, double-blind, crossover trial of modafinil on mood". Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology. 27 (1): 76–79. doi:10.1097/jcp.0b013e31802eb7ea. ISSN 0271-0749. PMID 17224718. S2CID 40801601.
- ^ Stahl, Stephen M.; Pradko, James F.; Haight, Barbara R.; Modell, Jack G.; Rockett, Carol B.; Learned-Coughlin, Susan (2004-08-13). "A Review of the Neuropharmacology of Bupropion, a Dual Norepinephrine and Dopamine Reuptake Inhibitor". The Primary Care Companion to the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 06 (4): 159–166. doi:10.4088/PCC.v06n0403. ISSN 1523-5998. PMC 514842. PMID 15361919.
- ^ Stahl, Stephen M. (2009-03-02). Stahl's Illustrated Antidepressants. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-75852-9.
- ^ Schwartz, Jean-Charles (2011). "The histamine H3 receptor: from discovery to clinical trials with pitolisant: H3 Receptor: from discovery to clinical trials". British Journal of Pharmacology. 163 (4): 713–721. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01286.x. PMC 3111674. PMID 21615387.
- ^ Kollb-Sielecka, Marta; Demolis, Pierre; Emmerich, Joseph; Markey, Greg; Salmonson, Tomas; Haas, Manuel (2017). "The European Medicines Agency review of pitolisant for treatment of narcolepsy: summary of the scientific assessment by the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use". Sleep Medicine. 33: 125–129. doi:10.1016/j.sleep.2017.01.002. PMID 28449891.
- ^ Inocente, Clara; Arnulf, Isabelle; Bastuji, Hélène; Thibault-Stoll, Anne; Raoux, Aude; Reimão, Rubens; Lin, Jian-Sheng; Franco, Patricia (2012). "Pitolisant, an Inverse Agonist of the Histamine H3 Receptor: An Alternative Stimulant for Narcolepsy-Cataplexy in Teenagers With Refractory Sleepiness". Clinical Neuropharmacology. 35 (2): 55–60. doi:10.1097/WNF.0b013e318246879d. ISSN 0362-5664. PMID 22356925. S2CID 36336966.
- ^ a b Dunn, Derek; Hostetler, Greg; Iqbal, Mohamed; Messina-McLaughlin, Patricia; Reiboldt, Alyssa; Lin, Yin Guo; Gruner, John; Bacon, Edward R.; Ator, Mark A.; Chatterjee, Sankar (2012-03-15). "Wake-promoting agents: search for next generation modafinil: part I". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 22 (6): 2312–2314. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.12.099. ISSN 1464-3405. PMID 22264475.
- ^ Dunn, Derek; Hostetler, Greg; Iqbal, Mohamed; Marcy, Val R.; Lin, Yin Guo; Jones, Bruce; Aimone, Lisa D.; Gruner, John; Ator, Mark A.; Bacon, Edward R.; Chatterjee, Sankar (2012-06-01). "Wake promoting agents: Search for next generation modafinil, lessons learned: Part III". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 22 (11): 3751–3753. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.04.031. ISSN 0960-894X. PMID 22546675.
- ^ Inocente, Clara; Arnulf, Isabelle; Bastuji, Hélène; Thibault-Stoll, Anne; Raoux, Aude; Reimão, Rubens; Lin, Jian-Sheng; Franco, Patricia (2012). "Pitolisant, an inverse agonist of the histamine H3 receptor: an alternative stimulant for narcolepsy-cataplexy in teenagers with refractory sleepiness". Clinical Neuropharmacology. 35 (2): 55–60. doi:10.1097/WNF.0b013e318246879d. ISSN 1537-162X. PMID 22356925. S2CID 36336966.
- ^ a b "What is SUNOSI® (solriamfetol) Treatment ? | SUNOSI® for Patients". www.sunosi.com. Retrieved 2020-01-03.
- ^ Kim, Dongsoo (2012-02-22). "Practical Use and Risk of Modafinil, a Novel Waking Drug". Environmental Health and Toxicology. 27: e2012007. doi:10.5620/eht.2012.27.e2012007. ISSN 2233-6567. PMC 3286657. PMID 22375280.
- ^ "How WAKIX Works | WAKIX® (pitolisant) tablets". wakix.com. Retrieved 2020-01-03.
- ^ "New Data Presented at World Sleep Congress Demonstrate Early Signs of Efficacy for TAK-925, a Selective Orexin Type-2 Receptor (OX2R) Agonist, in Patients with Narcolepsy Type 1". www.takeda.com. Retrieved 2019-12-06.
- ^ "Thiazole and diphenyl substituted sulfoxides for use in improving cognition functions and against addictions to substances. - Patent EP-3792252-A1 - PubChem". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2022-09-26.