 Emblem of the 2016 Summer Olympics[a] | |
| Host city | Rio de Janeiro, Brazil |
|---|---|
| Motto | A New World (Portuguese: Um mundo novo) |
| Nations | 207 (including IOA and EOR teams)[1] |
| Athletes | 11,180 (6,146 men, 5,034 women)[1] |
| Events | 306 in 28 sports (42 disciplines) |
| Opening | 5 August 2016 |
| Closing | 21 August 2016 |
| Opened by | |
| Cauldron | |
| Stadium | Estadio Maracanã |
Summer Winter
2016 Summer Paralympics | |
| Part of a series on |
| 2016 Summer Olympics |
|---|
The 2016 Summer Olympics (Portuguese: Jogos Olímpicos de Verão de 2016),[c] officially the Games of the XXXI Olympiad (Portuguese: Jogos da XXXI Olimpíada) and officially branded as Rio 2016, were an international multi-sport event held from 5 to 21 August 2016 in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, with preliminary events in some sports beginning on 3 August. Rio de Janeiro was announced as the host city at the 121st IOC Session in Copenhagen, Denmark, on 2 October 2009.
11,238 athletes from 207 nations took part in the 2016 Games, including first-time entrants Kosovo, South Sudan, and the Refugee Olympic Team.[3][4] With 306 sets of medals, the Games featured 28 Olympic sports, including rugby sevens and golf, which were added to the Olympic program in 2009. These sporting events took place at 33 venues in the host city and at five separate venues in the Brazilian cities of São Paulo, Belo Horizonte, Salvador, Brasília, and Manaus.
These were the first Olympic Games to be held in South America,[5] as well as the first to be held in a Portuguese-speaking country, the first summer edition to be held entirely in the host country's winter season, the first since 1968 to be held in Latin America (the second being 2018 Summer Youth Olympics in Buenos Aires, Argentina), and the first since 2000 to be held in the Southern Hemisphere.[6] These were also the first Summer Olympics to take place under the International Olympic Committee (IOC) presidency of Thomas Bach.[4]
The United States topped the medal table, winning the most gold medals (46) and the highest number of medals overall (121); the U.S. team also won its 1,000th Summer Olympic gold medal. Great Britain finished second and became the first country to increase its tally of medals in the Summer Olympiad immediately after being the host nation.[7] China finished third in the medal table. Host nation Brazil won seven gold medals and 19 total medals, its best result at any Olympics, finishing in thirteenth place. Bahrain, Fiji, Ivory Coast, Jordan, Kosovo, Puerto Rico, Singapore, Tajikistan, and Vietnam all won their first gold medals, as did the group of Independent Olympic Athletes (from Kuwait).
Bidding process
[edit]

The bidding process for the 2016 Summer Olympics was officially launched on 16 May 2007.[8] The first step for each city was to submit an initial application to the International Olympic Committee by 13 September 2007, confirming their intention to bid. Completed official bid files containing answers to a 25-question IOC form were to be submitted by each city by the deadline of 14 January 2008. On 4 June 2008, two months before the Beijing Olympics, four candidate cities were chosen for the shortlist: Chicago, Madrid, Rio de Janeiro, and Tokyo, which had already hosted the Summer Olympics in 1964. Three cities—Baku, Doha, and Prague—failed to reach the candidature phase. Doha was not promoted, despite scoring higher than the selected candidate city Rio de Janeiro, because of their proposal to host the Olympics in October, outside the IOC's sporting calendar, added with its problems while hosting the 2006 Asian Games, including deaths and illnesses involving athletes and volunteers. Others included lack of infrastructures, including beds for athletes and media reporters at that time.[9]
Nawal El Moutawakel of Morocco headed the 10-member Evaluation Commission, having also chaired the evaluation commission for the 2012 Summer Olympics bids, which was awarded to London, United Kingdom. The commission made on-site inspections in the second quarter of 2009. They issued a comprehensive technical appraisal for IOC members on 2 September, one month before the elections.[10]
Many safeguards were put in place to prevent bidding cities from communicating with or directly influencing the 115 IOC members eligible to vote in the elections. For example, cities could not invite any IOC member to visit, nor could they send anything that could be construed as a gift. Nonetheless, bidding cities invested large sums in their PR and media programs to indirectly influence the IOC members by garnering domestic support and backing from sports media and general international media.
Ultimately, you are communicating with just 115 people and each one has influencers and pressure groups but you are still speaking to no more than about 1,500 people, perhaps 5,000 in the broadest sense. It is not just about getting ads out there but it is about a targeted and very carefully planned campaign.
The final voting was held in Copenhagen on 2 October 2009, with Madrid and Rio de Janeiro considered favorites to secure the Games. Chicago was eliminated after the first round of voting, and Tokyo after the second (The latter city would eventually be awarded the 2020 Summer Olympics in 2013). Rio de Janeiro took a significant lead over Madrid, heading into the final round; the lead was held, and Rio de Janeiro was announced as host of the 2016 Summer Olympics.
| City | NOC | Round 1 | Round 2 | Round 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rio de Janeiro | |
26 | 46 | 66 |
| Madrid | 28 | 29 | 32 | |
| Tokyo | 22 | 20 | — | |
| Chicago | 18 | — | — |
Development and preparation
[edit]On 26 June 2011, it was reported on AroundTheRings.com that Roderlei Generali, the COO of the Rio de Janeiro Organizing Committee for the Olympic Games, resigned just one year after taking the job at ROOC. This came just five months after CCO Flávio Pestana quit for personal reasons.[13] Pestana withdrew later during the 2012 Summer Paralympics, and Renato Ciuchin was then appointed as COO.[14]
Venues and infrastructure
[edit]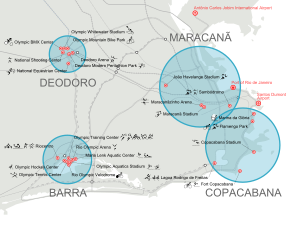
Events took place at eighteen existing venues, nine new venues constructed specifically for the Games, and seven temporary venues.[15]
For the events held in Rio de Janeiro, each event was held in one of four geographically segregated Olympic clusters–Barra, Copacabana, Deodoro, and Maracanã–as was done for the 2007 Pan American Games.[16][17] Several of the venues were located at the Barra Cluster Olympic Park.[15] Nearly half of the athletes could reach their venues in less than 10 minutes, and almost 75 per cent could do so in less than 25 minutes. Of the 34 competition venues, eight underwent some permanent works, seven were totally temporary and nine were constructed as permanent legacy venues.[18]
The largest venue at the Games in terms of seating capacity was the 74,738-seat Maracanã Stadium, which served as the ceremonies venue and site of the football finals.[15] The second largest stadium was the 60,000-seat Estádio Olímpico João Havelange, which hosted track and field events.[15] The athletes' village was said to be the largest in Olympic history. Fittings included about 80,000 chairs, 70,000 tables, 29,000 mattresses, 60,000 clothes hangers, 6,000 television sets and 10,000 smartphones.[19]
Olympic Park
[edit]
The Barra Olympic Park is a cluster of nine sporting venues in Barra da Tijuca, in the west zone of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. The site was formerly occupied by the Autódromo Internacional Nelson Piquet, also known as the Jacarepaguá Formula One circuit.[20]
The nine venues within the Olympic Park were:[21][22]
- Carioca Arena 1 – basketball (capacity: 16,000)
- Carioca Arena 2 – wrestling, judo (capacity: 10,000)
- Carioca Arena 3 – fencing, taekwondo (capacity: 10,000)
- Future Arena – handball (capacity: 12,000)
- Maria Lenk Aquatics Centre – diving, synchronized swimming, water polo (capacity: 5,000)
- Olympic Aquatics Stadium – swimming, water polo play-offs (capacity: 15,000)
- Olympic Tennis Centre – tennis (capacity: 10,000 Main Court)
- Rio Olympic Arena – gymnastics (capacity: 12,000)
- Rio Olympic Velodrome – track cycling (capacity: 5,000)
Football
[edit]As well as the Estádio Olímpico João Havelange and Maracanã and in Rio de Janeiro, football matches took place at five venues in the cities of São Paulo, Belo Horizonte, and the more distant Salvador, Brasília and Manaus.
Urban renovation
[edit]
Rio's historical downtown underwent an urban waterfront revitalization project known as Porto Maravilha, covering 5 km2 (1.9 sq mi) in area. The project aimed to redevelop the port area, increase the city center's attractiveness, and enhance Rio's competitive position in the global economy.[23]
The urban renovation involved 700 km (430 mi) of public networks for water supply, sanitation, drainage, electricity, gas and telecom; 4 km (2.5 mi) of tunnels; 70 km (43 mi) of roads; 650 km2 (250 sq mi) of sidewalks; 17 km (11 mi) of bike path; 15,000 trees; and three sanitation treatment plants. As part of this renovation, a new tram was built from the Santos Dumont Airport to Rodoviária Novo Rio, due to open in April 2016.[24]
The Games required over 200 kilometers of security fencing. A 15,000 square meter warehouse in Barra da Tijuca was used to assemble and supply the furniture and fittings for the Olympic Village. The second warehouse of 90,000 square meters in Duque de Caxias, near the roads that provide access to the venues, contained all the equipment needed for the sporting events.[19]
Medals
[edit]
The medals were produced by the Casa da Moeda do Brasil (the Brazilian mint). The medal design was unveiled on 15 June 2016. They were designed to be environmentally friendly using recycled materials; the bronze and silver medals contained 30% recycled materials. The gold medals were produced using gold that had been mined and extracted according to a set of sustainability criteria, such as being extracted without the use of mercury. The medals feature a wreath design on the front, and in keeping with tradition, the obverse features Nike, the Greek goddess of victory. A wooden carrying box accompanied each medal. Medalists were also awarded a trophy in the shape of the Games' emblem.[25][26]
In May 2017, an Associated Press article disclosed that over 100 athletes who had won medals at the Rio Olympics reported that their medals were showing some damage, including black spots, flaking, or surface degrading. Rio officials offered to replace any defective medals and found problems with 6 to 7 percent of all those awarded.[27]
Torch relay
[edit]

The Olympic flame was lit on 21 April 2016 at the Temple of Hera in Olympia, the traditional start of the Greek phase of the torch relay. The flame was handed over to the Brazilian organisers in a ceremony at the Panathenaic Stadium in Athens on 27 April. A brief stop-off was made in Switzerland to visit the IOC headquarters and the Olympic Museum in Lausanne, as well as the United Nations Office at Geneva.[28]
The torch relay began its journey around Brazil on 3 May at the capital Brasília. The flame visited more than 300 Brazilian cities, including all 26 state capitals and the Brazilian Federal District.[29] The relay ended in Rio de Janeiro on 5 August when the flame was used to light the Olympic cauldron during the opening ceremony.
Volunteers
[edit]Unpaid volunteers performed a variety of tasks before and during the Games. A target of 50,000 volunteers was set as early as 2012. More than 240,000 applications were received when recruitment took place in 2014. The clothing worn by the volunteers included yellow polo shirts and jackets, beige trousers, white socks, and green trainers, which they collected from the Uniform Distribution and Accreditation Centre. Volunteers also wore photo accreditation badges which were allocated to officials, athletes, family members, and media, allowing them to gain access to specific venues and buildings around the site.[30] Many volunteers gave up their roles due to long working hours and insufficient free meals.[31]
Ticketing
[edit]The ticket prices were announced on 16 September 2014, all of which were sold in Brazilian reais (BRL). A total of 7.5 million tickets were to be sold in total, with ticket prices ranging from BRL 40 for many events to BRL 4,600 for the most expensive seats at the opening ceremony. About 3.8 million of these tickets were available for BRL 70 or less.[32][33]
Sustainability
[edit]
As an aspect of its bid, Rio's organizing committee planned to focus on sustainability and environmental protection as a theme of the 2016 Games, going on to dub them a "Green Games for a Blue Planet".[34] As legacy projects, organizers intended to introduce a wider array of public transport options, upgrade the infrastructure of the favelas to provide improved transport and access to utilities, upgrade Rio's sewer system to remediate the level of pollution in the Guanabara Bay,[34][35] and plant 24 million seedlings to offset the expected carbon emissions of the Games. However, some of these projects met with delays or faced economic shortfalls, leading some critics to believe that Rio would not be able to accomplish them.[34][36]
The focus on environmental protection also influenced the implementation of certain Olympic protocols. To reduce emissions, the Olympic cauldron was designed to be smaller than previous iterations, using a kinetic sculpture to enhance its appearance in place of a larger body of flames.[37] The bronze and silver medals, as well as the ribbons on all medals, were designed to incorporate recycled materials.[25][26] The athletes were not presented with flowers during the medal ceremonies, as had been the tradition at previous Olympics (although floral displays were still used as part of the staging of medal presentations). The organizers considered the practice to be wasteful because the flowers were often thrown away and "would struggle to survive in the tropical Brazilian climate" if kept. The podiums were designed using materials that could be recycled to make furniture.[26][38]
The Future Arena, the venue for the handball competitions, was designed as a temporary modular structure whose components could be reconstructed after the Games to build schools.[39] However, as of November 2017, the arena was still standing due to lack of funds to dismantle it and no allocation of funds to do so in the 2018 budget.[40] Portions of the opening ceremony were dedicated to the issue of climate change.[41]
The Games
[edit]Opening ceremony
[edit]
The opening ceremony took place at Maracanã Stadium on 5 August 2016, directed by Fernando Meirelles, Daniela Thomas, and Andrucha Waddington.[42] The ceremony highlighted aspects of Brazilian history and culture, and featured a segment narrated by Fernanda Montenegro and Judi Dench with an appeal to environmental conservation and the prevention of global warming.[41][43] The crowd in the stadium numbered 60,000 and the event was broadcast to an estimated global audience of three billion.[5]
The ceremony included the inaugural presentation of the Olympic Laurel, an honor bestowed by the IOC on those that have made "significant achievements in education, culture, development and peace through sport"; the trophy was awarded to Kenyan athlete Kipchoge Keino.[44] The Games were officially opened by the acting president of Brazil, Michel Temer.[45]
The Olympic cauldron was lit by long-distance runner Vanderlei Cordeiro de Lima,[5] the men's marathon bronze medalist at the 2004 Olympics, who had also received the IOC's Pierre de Coubertin medal for sportsmanship after being attacked by a spectator and losing his lead in the race.[42][46] The cauldron was originally expected to be lit by Brazilian footballer Pelé, but he declined to participate due to health problems.[43][47][48]
Following the opening ceremony, a public cauldron was lit in front of the Candelária Church by Jorge Gomes, a 14-year-old Brazilian athlete who had escaped from poverty to train as a runner.[49][50]
Sports
[edit]



The 2016 Summer Olympic program featured 28 sports encompassing 306 events. The number of events in each of 42 discipline is noted in parentheses.
| 2016 Summer Olympic Sports Programme | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
New sports
[edit]In April 2008, the IOC began accepting applications for two new sports to be introduced to the Olympic programme. Baseball and softball (which were both dropped in 2005), karate, squash, golf, roller sports, and rugby union all applied to be included on the programme. Formal presentations were made to the IOC executive board in June 2009.[51]
In August, the executive board initially gave its approval to rugby sevens—a seven-player version of rugby union—by a majority vote; baseball/softball, roller sports, and squash were removed from contention, leaving golf, karate, and rugby sevens in the running. A final vote was held on 9 October 2009, the closing day of the 121st IOC Session. At this session, a new voting system was in place: a sport now needed only a simple majority from the full IOC committee for approval rather than the two-thirds majority previously required.[52][53]
The 121st IOC Session decided to add rugby sevens and golf to the Rio 2016 Olympic programme.[54] The tally for rugby was 81 in favor, with eight against,[55] and golf was approved by 63 votes to 26.[56] Neither of these two sports was new to the Summer Olympics; rugby last featured in 1924, and golf in 1904.
In May 2012, the International Sailing Federation announced that windsurfing would be replaced by kitesurfing at the 2016 Olympics,[57] but this decision was reversed in November.[58]
Participating National Olympic Committees
[edit]
All 205 National Olympic Committees qualified at least one athlete.[citation needed] The first three nations to qualify athletes for the Games were Germany, Great Britain, and the Netherlands, who each qualified four athletes for the team dressage by winning medals in the team event at the 2014 FEI World Equestrian Games.[59]
As host nation, Brazil received automatic entry for some sports including in all cycling disciplines and six places for weightlifting events.[60][61]
The 2016 Summer Olympics were the first Games in which Kosovo and South Sudan were eligible to participate. Bulgarian and Russian weightlifters were banned from Rio Olympics for numerous anti-doping violations.[62][63]
Kuwait was banned in October 2015 for the second time in five years over government interference in the country's Olympic committee. Kuwaiti athletes instead participated as "Independent Olympic Athletes."[64]


Blue = Participated for the first time in 2016.
Green = Had previously participated.
Yellow circle is host city (Rio de Janeiro)
Number of athletes by National Olympic Committee
[edit]Refugee athletes
[edit]
Due to the European migrant crisis and other reasons, the IOC allowed athletes to compete as Independent Olympians under the Olympic Flag. During the previous Summer Olympic Games, refugees were ineligible to compete because of their inability to represent their home NOCs.[65] On 2 March 2016, the IOC finalized plans for a specific Refugee Olympic Team (ROT); out of 43 refugee athletes deemed potentially eligible, 10 were chosen to form the team.[66]
Independent athletes
[edit]Due to the suspension of the National Olympic Committee of Kuwait, participants from Kuwait were allowed to participate under the Olympic Flag as Independent Olympic Athletes.
In November 2015, Russia was provisionally suspended from all international track and field athletic competitions by the International Association of Athletics Federations (IAAF) following a World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) report into a doping program in the country.[67] The IAAF announced that it would allow individual Russian athletes to apply for "exceptional eligibility" to participate in the Games as "neutral" athletes if it was independently verified that they had not engaged in doping nor in the Russian doping program.[68]
On 24 July 2016, the IOC rejected the IAAF and WADA's recommendations to allow athletes to compete neutrally, stating that the Olympic Charter "does not foresee such 'neutral athletes'" and that it was each country's National Olympic Committee decision on which athletes would be competing.[69] As a result, Russian athletes competed under the Russian flag, although they would compete under a neutral flag in the 2018 Winter Olympics following several developments concerning the doping investigation.
National houses
[edit]During the Games, some countries and continents had a national house. These temporary meeting places for supporters, athletes and other followers were located throughout Rio de Janeiro.[70]
| Nation | Location | Name |
|---|---|---|
| Africa House | Barra da Tijuca | Casa da África |
| Australia | Rio de Janeiro Stock Exchange Convention Center | Casa da Austrália |
| Austria | Botafogo | Casa da Áustria |
| Brazil | Gamboa | Casa do Brasil |
| Colombia | Centro | Casa da Colômbia |
| Czech Republic | Barra da Tijuca | Casa da República Tcheca |
| Denmark | Ipanema | Pavilhão Dinamarquês |
| Finland | Centro | Casa da Finlândia |
| France | Lagoa | Clube da França |
| Germany | Leblon | Casa de Praia da Alemanha |
| Great Britain | Parque Lage, Jardim Botânico | Casa Olímpica da Grã-Bretanha |
| Hungary | Gávea | Casa da Hungria |
| Jamaica | Gávea | Casa da Jamaica |
| Mexico | Centro | Casa do México |
| Netherlands | Lagoa | Holland Heineken House (Casa da Holanda) |
| Portugal | Centro | Casa de Portugal |
| PyeongChang 2018 | Copacabana Beach | Casa de PyeongChang 2018 |
| Qatar | Botafogo | Bayt Quatar |
| Russia | Copacabana | Casa do Time Olímpico do Rússia |
| Slovakia | Barra da Tijuca | Casa Eslovaca |
| Tokyo 2020 | Barra da Tijuca | Casa de Tóquio 2020 |
| Tokyo Metropolitan Government | Paço Imperial | Casa do Governo Metropolitano de Tóquio |
Calendar
[edit]This is currently based on the schedule released on the same day as ticket sales began, 31 March 2015.[71]
- All dates are Brasília Time (UTC–3)
| OC | Opening ceremony | ● | Event competitions | 1 | Gold medal events | EG | Exhibition gala | CC | Closing ceremony |
| August 2016 | 3rd Wed |
4th Thu |
5th Fri |
6th Sat |
7th Sun |
8th Mon |
9th Tue |
10th Wed |
11th Thu |
12th Fri |
13th Sat |
14th Sun |
15th Mon |
16th Tue |
17th Wed |
18th Thu |
19th Fri |
20th Sat |
21st Sun |
Events | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OC | CC | — | |||||||||||||||||||
| Aquatics | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ● | ● | 1 | ● | 1 | ● | 1 | ● | 1 | 46 | ||||||||
| 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | ||||||||||||||
| ● | ● | 1 | ● | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| ● | 1 | 1 | ● | ● | ● | 1 | 1 | 4 | |||||||||||||
| 3 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 1 | 47 | |||||||||||
| ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 5 | |||||||||||
| ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||
| ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 13 | |||||
| Canoeing | ● | ● | 1 | 1 | 2 | 16 | |||||||||||||||
| ● | 4 | ● | 4 | ● | 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| Cycling | 1 | 1 | 2 | 18 | |||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| ● | ● | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ● | ● | ● | 2 | ● | ● | 1 | ● | 1 | ● | 1 | 1 | 6 | |||||||||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 10 | ||||||||||||
| ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||||
| ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||||||
| ● | ● | ● | 1 | ● | ● | ● | 1 | 2 | |||||||||||||
| Gymnastics | ● | ● | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 3 | EG | 18 | ||||||||||
| ● | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||
| 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 14 | ||||||||||||||
| ● | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| ● | ● | ● | ● | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 14 | |||||||||||||
| ● | ● | 1 | ● | ● | 1 | 2 | |||||||||||||||
| ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 10 | ||||||||||
| 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 15 | ||||||||||||
| ● | ● | ● | ● | 1 | 1 | ● | ● | ● | ● | 1 | 1 | 4 | |||||||||
| 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 8 | |||||||||||||||||
| ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | 1 | 1 | 3 | 5 | ||||||||||||
| 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Volleyball | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | 1 | 1 | 4 | |||||||
| ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 15 | |||||||||||
| 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 18 | |||||||||||||
| Daily medal events | 12 | 14 | 14 | 15 | 20 | 19 | 24 | 21 | 22 | 17 | 25 | 16 | 23 | 22 | 30 | 12 | 306 | ||||
| Cumulative total | 12 | 26 | 40 | 55 | 75 | 94 | 118 | 139 | 161 | 178 | 203 | 219 | 242 | 264 | 294 | 306 | |||||
| August 2016 | 3rd Wed |
4th Thu |
5th Fri |
6th Sat |
7th Sun |
8th Mon |
9th Tue |
10th Wed |
11th Thu |
12th Fri |
13th Sat |
14th Sun |
15th Mon |
16th Tue |
17th Wed |
18th Thu |
19th Fri |
20th Sat |
21st Sun |
Events | |
Records
[edit]Twenty-seven world records and ninety-one Olympic records were set during the 2016 Summer Olympics. The records were set in archery, athletics, canoeing, cycling track, modern pentathlon, rowing, shooting, swimming, and weightlifting.
Event scheduling
[edit]
A number of events, most notably in aquatics, beach volleyball and track and field, were scheduled with sessions and matches occurring as late as 10:00 p.m. to midnight BRT. These scheduling practices were influenced primarily by United States broadcast rightsholder NBC, whose substantial rights fees are one of the major sources of revenue for the IOC, who therefore allowed NBC to have influence on event scheduling to maximize U.S. television ratings when possible (on 7 May 2014, NBC agreed to a US$7.75 billion contract extension to air the Olympics through 2032, including US$1.23 billion for Rio 2016),[72][73] as well as the main Brazilian rightsholder Rede Globo. As Brasília time is only one hour ahead of the U.S. Eastern Time Zone, certain marquee events were scheduled to occur during U.S. primetime hours (traditionally 8:00 to 11:00 p.m. ET, 9:00 p.m. to midnight BRT), allowing them to be broadcast live on the east coast as opposed to being delayed. This practice was also beneficial to Globo; a Brazilian critic noted that the network very rarely preempts its primetime telenovelas, as they are among the highest-rated programs in the country.[74][75][76][77]
Closing ceremony
[edit]
The closing ceremony of the 2016 Summer Olympics was held on 21 August 2016 from 20:00 to 22:50 BRT at the Maracanã Stadium.[78] As per traditional Olympic protocol, the ceremony featured cultural presentations from both the current (Brazil) and following (Japan) host countries, as well as closing remarks by IOC president Thomas Bach, who declared the Games closed, and the Games' organizing committee leader Carlos Arthur Nuzman, the official handover of the Olympic flag from Rio de Janeiro mayor Eduardo Paes to Tokyo governor Yuriko Koike, whose city will host the 2020 Summer Olympics, and the extinguishing of the Olympic flame.[79]
The creative director for the ceremony was Rosa Magalhães.[80] Amid heavy rainfall, the ceremony began with interpretive dancers representing various landmarks in the host city. Martinho da Vila then performed a rendition of "Carinhoso" by Pixinguinha. In another segment, introducing the athletes, singer Roberta Sá channeled Carmen Miranda, the fruit-headdress-wearing, mid-century Hollywood diva who endures as a beloved camp figure. The Parade of Flags followed shortly after a choir of 27 children, representing the states of Brazil, sang the Brazilian national anthem.
Cost
[edit]
The Oxford Olympics Study 2016 estimated the out-turn cost of the Rio 2016 Summer Olympics at US$4.6 billion in 2015-dollars. This figure included sports-related costs, that is, (i) operational costs incurred by the organizing committee to stage the Games, of which the largest components were technology, transportation, workforce, and administration costs, while other operational costs included security, catering, ceremonies, and medical services, and (ii) direct capital costs incurred by the host city and country or private investors to build the competition venues, the Olympic village, international broadcast center, and media and press center, which were required to host the Games.[81]
Indirect capital costs were not included, such as for road, rail, or airport infrastructure, for hotel upgrades, or other business investment incurred in preparation for the Games but not directly related to staging the Games. The Rio Olympics' cost of US$4.6 billion compares with costs of US$40–44 billion for Beijing 2008 and US$51 billion for Sochi 2014, the two most expensive Olympics in history. The average cost of the Summer Games since 1960 is US$5.2 billion.[81]
Medal table
[edit]The top ten listed NOCs by the number of gold medals are listed below. Host nation Brazil finished in 13th place with a total of 19 medals (7 gold, 6 silver, and 6 bronze).
* Host nation (Brazil)
| Rank | NOC | Gold | Silver | Bronze | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 46 | 37 | 38 | 121 | |
| 2 | 27 | 23 | 17 | 67 | |
| 3 | 26 | 18 | 26 | 70 | |
| 4 | 19 | 17 | 20 | 56 | |
| 5 | 17 | 10 | 15 | 42 | |
| 6 | 12 | 8 | 21 | 41 | |
| 7 | 10 | 18 | 14 | 42 | |
| 8 | 9 | 3 | 9 | 21 | |
| 9 | 8 | 12 | 8 | 28 | |
| 10 | 8 | 11 | 10 | 29 | |
| 11–86 | Remaining NOCs | 124 | 150 | 181 | 455 |
| Totals (86 entries) | 306 | 307 | 359 | 972 | |
Podium sweeps
[edit]| Date | Sport | Event | Team | Gold | Silver | Bronze |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17 August | Athletics | Women's 100-meter hurdles | Brianna Rollins | Nia Ali | Kristi Castlin |
Broadcasting
[edit]
Olympic Broadcasting Services served as the host broadcaster for the 2016 Games. Produced from a total of seven mobile units, OBS distributed 40,000 hours of television footage and 60,000 hours of digital footage of the Games to its international rightsholders. For the first time in Olympic history, digital-oriented footage exceeded the amount of television-oriented footage. The International Broadcast Centre was constructed in the Barra da Tijuca cluster.[82] NHK and OBS once again filmed portions of the Games, including the opening ceremony and selected events, in 8K resolution video. Additionally, expanding upon a 180-degree trial at the 2016 Winter Youth Olympics, 85 hours of video content were originated in 360-degree virtual reality formats.[83] In the United States, NBC offered 4K content downconverted from the 8K footage and with HDR and Dolby Atmos support, to participating television providers.[84] Owing to their expertise in domestic broadcasts of the new sports introduced in Rio, Golf Channel and Sky New Zealand staff handled the production of the golf and rugby sevens events on behalf of OBS.[82]
In August 2009, the IOC reached a deal to sell domestic broadcast rights for the 2016 Summer Olympics to Grupo Globo. Replacing Record, the deal covers free-to-air coverage on Rede Globo, pay TV, and digital rights to the Games. In turn, Globo sublicensed partial free-to-air rights to Rede Record, along with Rede Bandeirantes. IOC board member Richard Carrión described the agreement as "unprecedented", touting that "by working with Brazil's leading media organizations, we are confident that this represents a great deal for Olympic fans in the region. There will be a huge increase in the amount of Olympic action broadcast, both during and outside Games time, and Brazilians will have more choice of how, when and where they follow their Olympic Games."[85]
Olympic Golden Rings Awards
[edit]
In November 2017, the International Olympic Committee announced the winners of the Golden rings in six categories for the best broadcast coverage of the Games. The Best Olympic Sports Production was awarded to Beach Volleyball, produced by Geoff Johnson and directed by Greg Breakell and Gary Milkis. The production for the cycling road race and Sailing came second and third. The next category was the best Olympic feature, for which TV Globo's show Esporte Espetacular finished third, and CCTV from China feature A Sequel of Love came second. The winner was NBC Olympics for their feature The Most Beautiful Thing. The third category was The Best Athlete Profile, for which RTBF from Belgium collected the third place prize for their profile of Nafi Thiam. TV Globo went one better than the previous category coming second with their profile of Isaquias Queiroz. The winner of the category again was NBC, this time for their piece on Wayde van Niekerk. The Best On-Air Promotion was announced next, with the BBC Sport winning with NBC coming second this time and BNT from Bulgaria finishing third. The Best Olympic Digital Service went to NBC, with ZDF and SporTV/Globosat picking up the second and third places. The Best Olympic Programme was awarded to SporTV/Globosat, while TV Globo and BBC Sport completed the podium.[86]
Marketing
[edit]Mascots
[edit]
On 24 November 2014, the official mascots of the 2016 Summer Olympics and Paralympics were unveiled, created by Sao Paulo-based animation company Birdo.[87] The Olympic mascot Vinicius, named after musician Vinicius de Moraes, represents Brazilian wildlife and carries design traits of cats, monkeys, and birds.[87] According to their fictional backgrounds, the mascots "were both born from the joy of Brazilians after it was announced that Rio would host the Games".[88]
Brand director Beth Lula stated that the mascots were intended to reflect the diversity of Brazil's culture and people.[89] The names of the mascots were determined by a public vote whose results were announced on 14 December 2014. The names, which reference the co-writers of the song "The Girl from Ipanema", won over two other sets of names, tallying 44 percent of 323,327 votes.[90] At the Olympic wrestling events, coaches were given plush dolls of Vinicius to throw into the ring when they wished to challenge a referee's call.[91]
Emblem
[edit]
The official emblem for the 2016 Summer Olympics was designed by Brazilian agency Tatíl Design and was unveiled on 31 December 2010, winning in a competition against 139 agencies.[92] The emblem represents three figures joined at their arms and feet, with the overall shape reflecting that of Sugarloaf Mountain. It was also designed to have a three-dimensional form, which designer Fred Gelli claimed made it the first 3D logo in the history of the Olympics.[93]
The logo has been noted as evoking Henri Matisse's painting Dance. There were also allegations by the Colorado-based Telluride Foundation that the logo had been plagiarized from its own; while also consisting of several figures linked in motion, the Telluride Foundation logo contains four figures. This was not the first time that the foundation had alleged plagiarism of its logo by a Brazilian event; in 2004, the linked figures element had been copied for the logo of Carnival celebrations in Salvador. Gelli defended the allegations, stating that the concept of figures linked in embrace was not inherently original, as it was "an ancient reference" and "in the collective unconscious". Gelli cited Dance as an influence of the logo's concept and stated that the designers had intentionally aimed to make the interpretation of the concept as dissimilar to others as possible.[94]
Concerns and controversies
[edit]The lead-up to the Rio Games was marked by several controversies, including: Brazil's political and economic crisis; the Zika virus epidemic; the significant pollution in the Guanabara Bay; and an ongoing doping scandal involving Russia, which affected the participation of Russian athletes in the Games. However, the Zika virus was not contracted by anyone competing in or attending the Olympics,[95] and the Games went ahead normally with no major incident.[96][97][98]
Political and economic crisis
[edit]
In 2014, Operation Car Wash, an investigation by the Federal Police of Brazil, uncovered unprecedented money laundering and corruption at the state-controlled oil company Petrobras. In early 2015, a series of protests against alleged corruption by the government of President Dilma Rousseff began in Brazil, triggered by revelations that numerous politicians were involved in the Petrobras affair. By early 2016, the scandal had escalated into a full-blown political crisis affecting not only President Rousseff, but also former President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva, resulting in widespread demonstrations involving millions of protesters,[99] both anti- and pro-Rousseff.[100][101] At the same time, Brazil faced its worst economic recession since the 1990s, raising questions about whether the country was adequately prepared to host the Olympic Games against a volatile political and economic backdrop. On 12 May 2016, President Rousseff was stripped of her powers and duties for 180 days after an impeachment vote in the Federal Senate, with Vice President Michel Temer standing in as acting president during the Games.[102]
On 5 October 2017, Brazilian Olympic Committee head Carlos Nuzman was arrested amid a money-laundering investigation into a $2 million payment that was allegedly made to secure votes for the bid to bring the Olympics to Rio. The money was believed to have been paid to former IAAF president Lamine Diack and his son Papa Massata Diack, who was a member of the IOC at the time of the alleged payment, which was three days before the vote in 2009. All three were charged with money laundering, along with the former Rio state governor Sergio Cabral (who was already in prison for money laundering offenses at the time), Brazilian businessman Arthur Soares, and ex-Brazilian Olympic Committee chief Leonardo Gryner. All six were charged with running a criminal organization, money laundering, and violating currency laws in their own native countries.[103] On 4 July 2019, it was reported that Cabral told a judge that the money paid to Diack was used to buy as many as nine votes.[104] Rio mayor Eduardo Paes was also accused of corruption and fraud in relation to the construction of a number of venues for the Games.[105][106]
Zika virus
[edit]
An outbreak of the mosquito-borne Zika virus in Brazil raised fears regarding its potential impact on athletes and visitors. To prevent puddles of stagnant water that allow mosquitoes to breed, organizers announced plans to perform daily inspections of Olympic venues.[107] Zika virus transmission was also attributed to inefficient sewage treatment in the area, an issue that was also in the process of being addressed for the Games.[108]
In May 2016, a group of 150 physicians and scientists sent an open letter to the World Health Organization (WHO), calling upon them to, according to co-author Arthur Caplan, have "an open, transparent discussion of the risks of holding the Olympics as planned in Brazil". The WHO dismissed the request, stating that "cancelling or changing the location of the 2016 Olympics [would] not significantly alter the international spread of Zika virus", and that there was "no public health justification" for postponing them.[109][110][111]
Some athletes did not attend the Games because of the epidemic.[112][113] On 2 September 2016, however, the World Health Organization reported that there were no confirmed cases of Zika among athletes or visitors during the 2016 Olympics.[114]
Environmental problems
[edit]
The Guanabara Bay, whose waters were used for sailing and windsurfing competitions, is heavily polluted. Among the chief causes of the pollution are uncollected trash fed into the bay via polluted rivers and slums along the coast. Pollution of the Guanabara has been a long-term issue. At the Earth Summit in 1992, officials promised they would begin to address the pollution, but previous attempts to do so have been insufficient. As an aspect of their bid for the Games, Rio once again committed to making efforts towards cleaning the bay.[115][116] However, some of these proposed initiatives have faced budgetary issues.[35] Prior to these efforts, only 17% of Rio's sewage was treated;[117] this raw sewage also leaked into the bay. Although Rio mayor Eduardo Paes stated that the city might not be able to reach its goal of having 80% of sewage treated,[118] at least 60% of sewage was treated by March 2016, with a projected goal of 65% of sewage being treated by the start of the Olympics.[119]
Security
[edit]
Rio's crime problems also received renewed attention after it was awarded the 2016 Games; mayor Paes stated that the city was facing "big issues" in heightening security, but that such concerns and issues were presented to the IOC throughout the bidding process.[120]
The governor of Rio de Janeiro also highlighted the fact that London faced security problems, with a terrorist attack occurring just a day after it was awarded the 2012 Summer Olympics. The estimate was that 5,000 men of the National Public Security Force and 22,000 military officers (14,800 Army; 5,900 Navy and 1,300 of the Brazilian Air Force), in addition to the fixed quota of Rio January, would act during the Olympic Games.[121]
On 21 July 2016, two weeks before the scheduled start of the Games, the Brazilian Federal Police broke up an Islamic jihadist terrorist cell named Ansar al-Khilafah Brazil by arresting 12 people.[122]
Russian doping scandal
[edit]
In December 2014, media attention began growing when German broadcaster ARD reported on state-sponsored doping in Russia, comparing it to doping in East Germany. In November 2015, the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) published a report, and the International Association of Athletics Federations (IAAF) suspended Russia indefinitely from world track and field events. The United Kingdom Anti-Doping agency later assisted WADA with testing in Russia. In June 2016, they reported they were unable to fully carry out their work, and noted intimidation by armed Federal Security Service (FSB) agents.[123] After a Russian former lab director made allegations about the 2014 Winter Olympics in Sochi, WADA commissioned an independent investigation led by Richard McLaren, which found corroborating evidence, concluding in a report published in July 2016 that the Ministry of Sport and the FSB had operated a "state-directed failsafe system" using a "disappearing positive [test] methodology" (DPM) from "at least late 2011 to August 2015".[124]
In response to these findings, WADA announced that RUSADA should be regarded as non-compliant with respect to the World Anti-Doping Code, and recommended that Russia be banned from competing in the 2016 Summer Olympics.[125] The IOC rejected the recommendation, stating that the IOC and each sport's international federation would make decisions on each athlete's individual basis.[126][127] A day before the opening ceremony, 278 athletes were cleared to compete under the Russian flag, while 111 were removed because of doping.[128] In contrast, the entire Kuwaiti team was banned from competing under their own flag for a non-doping related matter.[129][130] Unlike the IOC, the International Paralympic Committee voted unanimously to ban the entire Russian team from the 2016 Summer Paralympics, and suspended the Russian Paralympic Committee after it found evidence that the DPM was also in operation at the 2014 Winter Paralympics.[131]
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ The official logo of the 2016 Summer Olympics was made in 3D design, made by Brazilian design company Tàtil Design; it was inspired by Brazil's rich history of festivals and its colorful people; it also symbolizes energy, passion and unity. The selected colours derived from the city's environment, symbolises the sun and Brazil's happy warm and nature.
- ^ As acting president, discharging the powers and duties of the office of President of the Federative Republic of Brazil in place of incumbent President Dilma Rousseff, who was suspended from her duties as President during her impeachment trial.[2]
- ^ The Brazilian Portuguese pronunciation is [ˈʒɔɡuz oˈlĩpikuz dʒi veˈɾɐ̃w dʒi ˈdojz ˈmiw i dʒizeˈsejs], in Brazil's standard pronunciation.
References
[edit]- ^ a b "Rio 2016 Summer Olympics – Results and Video Highlights". Rio2016.com. Rio 2016 Organising Committee for the Olympic and Paralympic Games. 17 April 2018. Archived from the original on 1 August 2012. Retrieved 4 August 2017.
- ^ Gallas, Daniel (12 May 2016). "Michel Temer: The man who now leads Brazil". BBC. Retrieved 12 July 2024.
- ^ "Olympic Athletes". Rio2016.com. Rio 2016 Organising Committee for the Olympic and Paralympic Games. Archived from the original on 21 August 2016. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ^ a b "About Rio 2016 Summer Olympics". Rio 2016 Olympics Wiki. Archived from the original on 8 September 2015. Retrieved 31 October 2015.
- ^ a b c "Rio Olympics 2016: Opening ceremony celebrates Brazil to open Games". BBC Sport. 6 August 2016. Archived from the original on 8 November 2020. Retrieved 15 October 2020.
- ^ February 2014, Laura Poppick 05 (5 February 2014). "Why Winter Olympics Bypass the Southern Hemisphere". livescience.com. Archived from the original on 23 April 2020. Retrieved 30 March 2020.
((cite web)): CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Herbert, Ian (21 August 2016). "How many millions each Olympic medal has really cost Britain". The Independent. Archived from the original on 21 August 2016. Retrieved 16 August 2021.
- ^ "2016 Bid Process Launched". olympic.org (Press release). International Olympic Committee. 16 May 2007. Archived from the original on 15 August 2016. Retrieved 14 February 2017.
- ^ "Four on 2016 Olympics short-list". BBC Sport. 4 June 2008. Archived from the original on 29 August 2008. Retrieved 15 March 2010.
- ^ "The International Olympic Committee (IOC) today released the report of the Evaluation". olympic.org (Press release). IOC. 2 September 2009. Archived from the original on 15 February 2017. Retrieved 14 February 2017.
- ^ "Rings around the world". communicatemagazine.co.uk. 6 May 2009. Archived from the original on 8 October 2011.
- ^ "Past Bid Results". GamesBids.com. Archived from the original on 24 January 2011. Retrieved 31 October 2015.
- ^ "Around the Rings – Articles Archive". aroundtherings.com. Archived from the original on 17 January 2013. Retrieved 31 October 2015.
- ^ "Rio 2016 contrata Renato Ciuchini como Diretor-Executivo Comercial" (in Portuguese). Archived from the original on 4 October 2012.
- ^ a b c d "Sports and Venues" (PDF), Rio de Janeiro 2016 Candidate File (PDF), vol. 2, BOC, 16 February 2009, pp. 10–11, archived from the original (PDF) on 23 May 2013, retrieved 29 June 2015.
- ^ "Introduction" (PDF), Rio de Janeiro 2016 Candidate File (PDF), vol. 1, London, United Kingdom: BOC, 16 February 2009, archived from the original (PDF) on 20 March 2009, retrieved 5 May 2009.
- ^ Rio 2007 Pan Am Games Get Debriefed Ahead Of 2016 Bid, Toronto, Canada: GamesBids, 9 March 2008, archived from the original on 23 October 2008, retrieved 5 May 2009.
- ^ "An introduction to the Venues at the 2016 Rio Games". Rio2016.com. Rio 2016 Organising Committee for the Olympic and Paralympic Games. 23 April 2018. Archived from the original on 1 August 2012. Retrieved 3 March 2020.
- ^ a b Martins, Christina (6 June 2016). "8,400 shuttlecocks, 250 golf carts, 54 boats... the mind-blowing numbers behind the Rio 2016 Games". Rio2016.com. Rio 2016 Organising Committee for the Olympic and Paralympic Games. Archived from the original on 7 July 2016.
- ^ Lewis, Peter (15 September 2013). "Rio Olympics 2016: Brazilian city in a race against time to be ready to play host to the Games". ABC News Australia. Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Archived from the original on 4 August 2016. Retrieved 14 May 2016.
- ^ "Introducing Carioca Arena 1… the new home of Olympic basketball". Rio2016.com. Rio 2016 Organising Committee for the Olympic and Paralympic Games. 12 January 2016. Archived from the original on 10 March 2016. Retrieved 4 March 2016.
- ^ "Barra Region". Portal Brasil 2016. Governo Federal do Brasil. Archived from the original on 20 August 2016. Retrieved 4 March 2016.
- ^ Porto Maravilha Archived 29 August 2012 at the Wayback Machine Rio de Janeiro City Hall. Retrieved 10 August 2012. (in Portuguese).
- ^ "Rio tram starts test running". Railway Gazette. 26 November 2015. Archived from the original on 6 March 2019. Retrieved 1 January 2016.
- ^ a b "Innovative medal design unveiled for Rio 2016". olympic.org. IOC. 15 June 2016. Archived from the original on 3 February 2018. Retrieved 12 August 2016.
- ^ a b c Busbee, Jay (10 August 2016). "Rio mystery solved: Why don't Olympic medal winners get flowers?". Yahoo! Sports. Archived from the original on 10 August 2016. Retrieved 12 August 2016.
- ^ Meredith, Luke; Pells, Eddie (24 May 2017). "Faster, higher, rustier: Medals from Rio Olympics damaged". Associated Press. Archived from the original on 12 June 2017. Retrieved 24 May 2017.
- ^ "Greek fire lights up Rio 2016 Games... Olympic Torch lit in traditional ceremony at Olympia". Rio2016.com. Rio 2016 Organising Committee for the Olympic and Paralympic Games. 21 April 2016. Archived from the original on 24 April 2016. Retrieved 21 April 2016.
- ^ "Goiás will be the first state to receive the Rio 2016 Olympic Flame". Diário Mercantil. 16 April 2015. Archived from the original on 18 April 2015. Retrieved 29 April 2015.
- ^ "Volunteers set to make their mark at Rio 2016". olympic.org. IOC. 5 August 2016. Archived from the original on 6 November 2018. Retrieved 30 December 2016.
- ^ Sims, Alexandra (17 August 2016). "Thousands of Olympic volunteers quit over 'long hours and lack of food'". The Independent. Archived from the original on 1 May 2022. Retrieved 30 December 2016.
- ^ "Prijzen tickets Olympische Spelen 2016 in Rio bekend". olympischespelenrio.nl. 16 September 2014. Archived from the original on 8 October 2014. Retrieved 6 October 2014.
- ^ "Olympic Games ticket prices September 2014" (PDF). Rio2016.com. Rio 2016 Organising Committee for the Olympic and Paralympic Games. 16 September 2014. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 September 2014. Retrieved 6 October 2014.
- ^ a b c "Brazil Made Big Environmental Promises for Its Rio Olympics. Here's Why It Won't Keep Them". The Atlantic. 2 July 2014. Archived from the original on 30 June 2016. Retrieved 13 August 2016.
- ^ a b Balch, Oliver (1 February 2016). "Funding problems hit plan to clean Rio's polluted waterways ahead of Olympics". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 7 May 2016. Retrieved 6 May 2016.
- ^ "Rio has broken its promise of an environmentally-friendly Olympics". Vice News. August 2016. Archived from the original on 14 August 2016. Retrieved 13 August 2016.
- ^ "Diminutive Rio 2016 cauldron complemented by massive kinetic sculpture". Dezeen. 8 August 2016. Archived from the original on 10 August 2016. Retrieved 11 August 2016.
- ^ "Here's why Olympic medalists don't get flowers at the Summer Games in Rio". Mashable. 12 August 2016. Archived from the original on 13 August 2016. Retrieved 12 August 2016.
- ^ "Rio 2016 handball arena will dismantle to become four schools". Dezeen. 25 July 2016. Archived from the original on 12 August 2016. Retrieved 13 August 2016.
- ^ "No Answers Yet for Rio Olympic Park Dismantling". aroundtherings.com. Archived from the original on 12 February 2018. Retrieved 11 February 2018.
- ^ a b "The Rio Opening Ceremony Put Climate Change Front And Center". The Huffington Post. 6 August 2016. Archived from the original on 7 August 2016. Retrieved 7 August 2016.
- ^ a b Gibson, Owen; Watts, Jonathan (6 August 2016). "Rio 2016 opening ceremony a mix of pared patriotism and climate concern". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 12 August 2016. Retrieved 14 October 2020.
- ^ a b Levinson King, Robin (5 August 2016). "Highlights from Rio 2016 Olympic opening ceremony". Toronto Star. Archived from the original on 6 August 2016. Retrieved 8 August 2016.
- ^ "Kip Keino to receive Olympic Laurel distinction". olympic.org. IOC. 4 August 2016. Archived from the original on 25 August 2018. Retrieved 15 August 2016.
- ^ Axon, Rachel (6 August 2016). "No introduction for Brazil's president at start of opening ceremony". USA Today. Archived from the original on 24 December 2017. Retrieved 6 August 2016.
- ^ "Protester ruins marathon". BBC Sport. 29 August 2004. Archived from the original on 8 May 2022. Retrieved 15 October 2020.
- ^ "Emanuel surpreende e oferece sua medalha de ouro para Vanderlei Cordeiro" [Emanuel surprises and offers his gold medal to Vanderlei Cordeiro]. Folha Online (in Portuguese). 1 September 2004. Archived from the original on 5 October 2013. Retrieved 8 August 2012.
- ^ "Mystery Solved: Why Rio Olympics' cauldron is so tiny". Yahoo! Sports. 6 August 2016. Archived from the original on 10 August 2016. Retrieved 6 August 2016.
- ^ Brunhuber, Kim (12 August 2016). "Formerly homeless boy who lit Olympic cauldron now has 'beautiful life'". CBC.ca. Archived from the original on 10 October 2019. Retrieved 22 August 2016.
- ^ Klotz, Fabio (6 August 2016). "Vanderlei Cordeiro de Lima se eterniza como herói e ganha a medalha de ouro" [Vanderlei Cordeiro de Lima immortalizes himself as an Olympic hero and 'wins' gold]. O Dia. Archived from the original on 10 August 2016. Retrieved 21 August 2016..
- ^ "Golf among seven sports seeking inclusion in 2016 Games". ESPN. 25 April 2008. Archived from the original on 22 February 2009. Retrieved 20 August 2008.
- ^ "Olympic Leaders Approve Golf and Rugby for 2016 Summer Games". Fox News Channel. 13 August 2009. Archived from the original on 19 September 2009. Retrieved 1 October 2009.
- ^ "Olympics 2016: IOC Approves Golf And Rugby Sevens To Be Included In Rio De Janeiro Games". Sky (United Kingdom). Archived from the original on 22 May 2011. Retrieved 15 March 2010.
- ^ "121st IOC Session: some much awaited decisions". www.eurolympic.org. 9 October 2009. Archived from the original on 21 May 2015. Retrieved 2 April 2019.
((cite web)): CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ "History of Rugby in the Olympics". World Rugby. 17 July 2019. Archived from the original on 9 February 2018. Retrieved 2 April 2019.
- ^ "Golf receives final approval, will be part of 2016 Olympics". PGATour.com. 8 October 2009. Archived from the original on 2 April 2019. Retrieved 2 April 2019.
- ^ "Kiteboarding to replace windsurfing at 2016 Rio Olympics". BBC Sport. 7 May 2012. Archived from the original on 7 December 2015. Retrieved 10 May 2012.
- ^ "Windsurfing restored to Brazil 2016 Olympics". BBC Sport. 10 November 2012. Archived from the original on 8 January 2016. Retrieved 14 November 2012.
- ^ "Rio Olympics gets 1st qualified athletes". USA Today. Associated Press. 26 August 2014. Archived from the original on 27 August 2014. Retrieved 26 August 2014.
- ^ Hann, Michael (7 May 2014). "UCI and IOC agree qualification quotas for Rio 2016". Reuters. Archived from the original on 3 September 2014. Retrieved 26 August 2014.
- ^ Anderson, Gary (2 February 2014). "Weightlifting qualification criteria for Rio 2016 approved by IOC". insidethegames.biz. Archived from the original on 12 September 2019. Retrieved 26 August 2014.
- ^ "Bulgarian weightlifters banned from Rio Olympics after CAS rejects appeal against ban for doping violations". abc.net.au. Reuters. 29 January 2016. Archived from the original on 6 January 2018. Retrieved 26 July 2016.
- ^ "Strong statement by the IWF Executive Board". IWF. 22 June 2016. Archived from the original on 10 September 2016. Retrieved 4 August 2016.
- ^ "Olympics-Kuwait ban remains in force as ties with IOC deteriorate". Yahoo Sports. 9 December 2015. Archived from the original on 8 January 2016. Retrieved 2 January 2016.
- ^ "Refugees can compete for first time in 2016 Rio Olympics, IOC head says". ESPN.com. 27 October 2015. Archived from the original on 27 October 2015. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- ^ "Rio 2016: Refugee team to compete at Olympics". BBC Sport. 2 March 2016. Archived from the original on 26 March 2016. Retrieved 3 March 2016.
- ^ "Athletics doping: Russia provisionally suspended by IAAF". BBC Sport. 13 November 2015. Archived from the original on 13 November 2015. Retrieved 14 November 2015.
- ^ Ingle, Sean (1 July 2016). "Russian whistleblower Yuliya Stepanova to compete as 'neutral athlete' in Rio". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 12 July 2016. Retrieved 15 July 2016.
- ^ "Background Information to the decision of the IOC Executive Board concerning the participation of Russian athletes in the Olympic Games Rio 2016". olympic.org. IOC. 24 July 2016. Archived from the original on 25 July 2016. Retrieved 27 July 2016.
- ^ "National Houses". Rio2016.com. Rio 2016 Organising Committee for the Olympic and Paralympic Games. Archived from the original on 6 August 2016. Retrieved 10 August 2016.
- ^ "Rio 2016 Olympic Games Ticketing Guide" (PDF). Rio 2016. Rio 2016 Organising Committee for the Olympic and Paralympic Games. March 2015. pp. 28–133. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 April 2015. Retrieved 11 August 2021.
- ^ "Olympics on NBC through 2032". USA Today. 7 May 2014. Archived from the original on 21 January 2020. Retrieved 11 March 2019.
- ^ "Fewer Russians Could Be a Windfall for U.S. Olympic Business". The New York Times. 7 December 2017. Archived from the original on 5 February 2018. Retrieved 5 February 2018.
- ^ "Why all the midnight madness for some Olympians?". CBC News. Archived from the original on 19 August 2016. Retrieved 18 August 2016.
- ^ "Australia's Olympic swimmers can sleep easy at Rio despite late night meets thanks to recovery training". The Courier-Mail. Archived from the original on 17 May 2021. Retrieved 18 August 2016.
- ^ Segal, David (10 June 2016). "Greed, Passion, Lust, Betrayal, and the Olympics in Between". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 13 June 2016. Retrieved 18 August 2016.
- ^ "Swimming, beach volleyball will be on late in Rio". U.S. News & World Report. Archived from the original on 8 January 2016. Retrieved 31 October 2015.
- ^ "Rio 2016 Ingressos – Compre seu ingresso para as Olímpiadas". ingressos.rio2016.com (in Portuguese). Rio 2016 Organising Committee for the Olympic and Paralympic Games. Archived from the original on 24 August 2016. Retrieved 21 August 2016.
- ^ "Rio Olympics 2016: Spectacular closing ceremony as Olympic flag goes to Tokyo". BBC Sport. 22 August 2016. Archived from the original on 27 December 2017. Retrieved 22 August 2016.
- ^ "Rio 2016: Rosa Magalhães deve comandar encerramento". Rio 2016 (in Portuguese). 19 September 2015. Archived from the original on 21 September 2016. Retrieved 21 August 2016.
- ^ a b Flyvbjerg, Bent; Stewart, Allison; Budzier, Alexander (2016). The Oxford Olympics Study 2016: Cost and Cost Overrun at the Games. Oxford: Saïd Business School Working Papers (Oxford: University of Oxford). pp. 18–20. arXiv:1607.04484. doi:10.2139/ssrn.2804554. SSRN 2804554.
- ^ a b "Olympic Broadcasting: Inside the Chief Executive's Office". TV Technology. Archived from the original on 17 October 2016. Retrieved 12 July 2016.
- ^ "Olympics in VR: NBC to Present 85 Hours of Virtual-Reality Content on Samsung Devices". Variety. 30 June 2016. Archived from the original on 3 May 2019. Retrieved 12 July 2016.
- ^ "Rio Olympics: NBC Plans 4K and High Dynamic Range for Opening Ceremony Coverage". The Hollywood Reporter. 26 May 2016. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019. Retrieved 12 July 2016.
- ^ "IOC reaches agreement for 2014 & 2016 broadcast rights in Brazil". olympic.org (Press release). IOC. 27 August 2009. Archived from the original on 16 August 2016. Retrieved 14 February 2017.
- ^ "IOC Announces Golden Rings Awards Winners". olympic.org (Press release). IOC. 7 November 2017. Archived from the original on 6 January 2019. Retrieved 5 January 2019.
- ^ a b "Meet the Rio 2016 Olympic and Paralympic Games mascots and help choose their names". Rio2016.com. Rio 2016 Organising Committee for the Olympic and Paralympic Games. 23 November 2014. Archived from the original on 9 August 2016. Retrieved 25 July 2016.
- ^ Quarrell, Dan (22 July 2016). "2016 Rio Olympics: Biggest stars, dates, schedule, mascots, logo, Usain Bolt 'triple triple', Zika". Eurosport. Archived from the original on 25 July 2016. Retrieved 30 July 2016.
- ^ "Rio 2016: Olympic and Paralympic mascots launched". BBC Sport. 24 November 2014. Archived from the original on 25 November 2014. Retrieved 24 November 2014.
- ^ "Rio 2016 Olympic and Paralympic mascots named Vinicius and Tom by public vote". Rio2016.com. Rio 2016 Organising Committee for the Olympic and Paralympic Games. 14 December 2014. Archived from the original on 8 August 2016. Retrieved 8 August 2016.
- ^ Gordon, Aaron (17 August 2016). "Olympic Wrestling Uses Stuffed Animals for Replay Challenges". Vice Sports. Vice Media. Archived from the original on 17 August 2016. Retrieved 22 August 2016.
- ^ Nudd, Tim (14 August 2012). "Hated the London 2012 Logo? You Might Like Rio 2016 Better Brazil's Tatíl Design tells story of its creation". Adweek. Archived from the original on 17 August 2012. Retrieved 14 August 2012.
- ^ "Rio 2016 motif is "first 3D logo in the history of the Olympics" says designer". Dezeen. 11 August 2016. Archived from the original on 14 August 2016. Retrieved 16 August 2016.
- ^ "Telluride Foundation says Brazil stole its logo for Olympics". The Denver Post. Archived from the original on 10 May 2016. Retrieved 7 May 2016.
- ^ Ramseth, Luke (8 October 2017). "U. study: Olympic athletes in Rio dodged Zika, but not West Nile and other mosquito-borne illnesses". The Salt Lake Tribune. Archived from the original on 6 November 2018. Retrieved 6 November 2018.
- ^ Watts, Jonathan (21 August 2016). "Have the Olympics been worth it for Rio?". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 11 April 2019. Retrieved 11 April 2019.
For politicians and administrators who have staked their careers on these Games, there were no shortage of reasons to declare them a success: tourist numbers were reasonably high (in excess of the 500,000 target, according to the government), sales goals were reached, the infrastructure remained standing, Zika fears proved unfounded and Brazil won more medals than at any previous Games.
- ^ Davies, Wyre (20 August 2016). "Has the Olympics been a success for Brazil?". BBC News. Archived from the original on 11 April 2019. Retrieved 11 April 2019.
Indeed, for the second time in two years, Brazil has shown it can successfully stage a major international sporting jamboree.
- ^ "How do we know that Rio 2016 was a success". olympic.org. IOC. 6 December 2016. Archived from the original on 11 April 2019. Retrieved 11 April 2019.
- ^ Flynn, Daniel; Soto, Alonso (14 March 2016). "Record Brazil protests put Rousseff's future in doubt". Reuters. Archived from the original on 6 November 2020. Retrieved 14 March 2016.
- ^ Segal, David (7 August 2015). "Petrobras Oil Scandal Leaves Brazilians Lamenting a Lost Dream". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 4 March 2017. Retrieved 1 March 2017.
- ^ Grandin, Greg (22 March 2016). "Millennials Are Taking to the Streets to Defend Democracy in Brazil". The Nation. Archived from the original on 4 June 2016. Retrieved 5 June 2016.
- ^ "Processo de impeachment é aberto, e Dilma é afastada por até 180 dias". g1.globo.com (in Portuguese). Rede Globo. 12 May 2016. Archived from the original on 28 July 2016. Retrieved 14 February 2017.
- ^ "Rio Olympics head Carlos Nuzman charged with corruption". BBC News. 19 October 2017. Archived from the original on 7 January 2018. Retrieved 26 December 2017.
- ^ Viga Gaier, Rodrigo (5 July 2019). "Former Rio de Janeiro governor tells judge he paid $2 million bribe to host 2016 Olympics". Reuters. Archived from the original on 5 July 2019. Retrieved 8 July 2019.
- ^ Chade, Jamil (23 April 2017). "Stadium deals, corruption and bribery: the questions at the heart of Brazil's Olympic and World Cup 'miracle'". The Observer. ISSN 0029-7712. Archived from the original on 6 April 2020. Retrieved 6 April 2020.
- ^ Gillen, Nancy (29 March 2020). "Former Rio Mayor Paes accused of corruption during Olympic venue construction". insidethegames.biz. Archived from the original on 6 April 2020. Retrieved 6 April 2020.
- ^ "Zika virus: Olympic venues to be inspected daily before and during Games". BBC Sport. 29 January 2016. Archived from the original on 29 January 2016. Retrieved 30 January 2016.
- ^ Khazan, Olga (31 March 2016). "What Happens When There's Poop in the Water". The Atlantic. Archived from the original on 2 July 2016. Retrieved 30 June 2016.
- ^ ""The Games will go ahead": Tourists have a near-zero chance of getting Zika at the Rio Olympics". Quartz. 12 May 2016. Archived from the original on 26 May 2016. Retrieved 31 May 2016.
- ^ "150 experts say Olympics must be moved or postponed because of Zika". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 2 June 2016. Retrieved 31 May 2016.
- ^ "Zika crisis: WHO rejects 'move Rio Olympics' call". BBC News. 28 May 2016. Archived from the original on 30 May 2016. Retrieved 31 May 2016.
- ^ "Rio 2016: Are tennis players using Zika as an excuse?". CNN. 21 July 2016. Archived from the original on 13 August 2016. Retrieved 13 August 2016.
- ^ "Olympics-Golf-Zika an excuse for top ranked players, says Van Zyl". Yahoo!. Reuters. 2 August 2016. Archived from the original on 16 September 2016. Retrieved 13 August 2016.
- ^ "No Zika cases from Olympics, says WHO". BBC News. 2 September 2016. Archived from the original on 3 September 2016. Retrieved 3 September 2016.
- ^ Romero, Simon; Clarey, Christopher (18 May 2014). "Note to Olympic Sailors: Don't Fall in Rio's Water". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 11 March 2016. Retrieved 6 May 2016.
- ^ Carneiro, Julia (10 January 2014). "Rio's Olympic waters blighted by heavy pollution". BBC News. Archived from the original on 11 January 2014. Retrieved 12 January 2014.
- ^ "German sailor blames infections on water at Rio 2016 Olympic test event". The Guardian. Reuters. 28 August 2015. Archived from the original on 8 January 2016. Retrieved 3 January 2016.
- ^ "'Super bacteria' found in Rio waters where sailors and windsurfers are supposed to compete in the Olympics". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 9 June 2016. Retrieved 6 May 2016.
- ^ "USOC, athletes navigate questions swirling around Rio's contaminated water". The Washington Post. 9 March 2016. Archived from the original on 19 June 2016. Retrieved 30 June 2016.
- ^ "Rio Mayor Promises Crackdown on Violence". CBS News. Associated Press. 19 October 2009. Archived from the original on 15 February 2017. Retrieved 14 February 2017.
- ^ "Terroristas divulgam 'manual' para ataques nos Jogos do Rio" (in Portuguese). Terra. 20 July 2016. Archived from the original on 21 July 2016. Retrieved 25 July 2016.
- ^ Jelmayer, Rogerio; Magalhaes, Luciana (25 July 2016). "Brazil Authorities Arrest 12th Suspect in Alleged Olympics Terror Plot". The Wall Street Journal. Archived from the original on 15 February 2017. Retrieved 14 February 2017.
- ^ "Update on the status of Russia testing" (PDF). wada-ama.org. World Anti-Doping Agency. June 2016. Archived (PDF) from the original on 25 January 2017. Retrieved 24 December 2017.
- ^ "McLaren Independent Investigation Report – Part 1" (PDF). wada-ama.org. World Anti-Doping Agency. 18 July 2016. Archived from the original on 6 December 2017. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "WADA Statement: Independent Investigation confirms Russian State manipulation of the doping control process". wada-ama.org. World Anti-Doping Agency. 18 July 2016. Archived from the original on 3 December 2017. Retrieved 24 December 2017.
- ^ "Decision of the IOC Executive Board concerning the participation of Russian athletes in the Olympic Games Rio 2016". olympic.org (Press release). IOC. 24 July 2016. Archived from the original on 30 December 2017. Retrieved 24 July 2016.
- ^ "IOC sets up 3-person panel to rule on Russian entries". San Diego Tribune. 30 July 2016. Archived from the original on 31 July 2016. Retrieved 31 July 2016.
- ^ "Rio 2016: 270 Russians cleared to compete at Olympic Games". BBC Sport. 4 August 2016. Archived from the original on 4 August 2016.
- ^ Butler, Nick (5 June 2017). "Exclusive: Pound confident Russian athletes will be found guilty of Sochi 2014 doping despite IOC inaction". insidethegames.biz. Archived from the original on 17 September 2017. Retrieved 24 December 2017.
- ^ Weber, Joscha (27 April 2017). "Doping pressure mounts on IOC at German parliament". DW.com. Archived from the original on 2 August 2020. Retrieved 31 March 2020.
- ^ "The IPC suspends the Russian Paralympic Committee with immediate effect". Paralympic.org. IPC. 7 August 2016. Archived from the original on 7 December 2017. Retrieved 24 December 2017.
External links
[edit]- "Rio de Janeiro 2016". Olympics.com. International Olympic Committee.
- Official website (Rio2016.com) at the Wayback Machine (archived 6 August 2016)
| Elected city | ||
|---|---|---|
| Candidate cities | ||
| Applicant cities | ||
| Proposed bids | ||
| Africa |
| |
|---|---|---|
| Americas |
| |
| Asia |
| |
| Europe |
| |
| Oceania | ||
| Others | ||
| Barra Cluster | ||
|---|---|---|
| Copacabana Cluster | ||
| Deodoro Cluster | ||
| Maracanã-Engenho de Dentro Cluster | ||
| Football stadia | ||
| International | |
|---|---|
| National | |
| Other | |












