Northern Turkic language
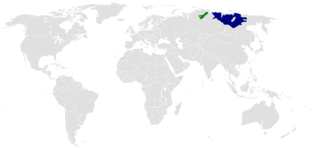
The Dolgan language is a critically endangered Turkic language with 930 speakers,[2] spoken in the Taymyr Peninsula in Russia.[3] The speakers are known as the Dolgans. The word "Dolgan" means 'tribe living on the middle reaches of the river'. This is most likely signifying the geographical location of the Dolgan tribe.[4] Its closest relative is Sakha.
The language is very local and restricted to a certain area and has declined in usage over the years. As of 2010 there are only about 1,050 speakers of the language.[1] The language has expressed a few changes since the beginning of its formation, such as alphabet and phrasing terms. The issue as of recently has become the weak integration of this local language within families with mixed marriages. Instead of speaking either of the parents' local languages, the family incorporates Russian as the more dominant language to ease interfamilial and external communication.[5] This results in children learning the language only slightly or as a second language. Over generations, the language continues to fade.
Classification
Dolgan, along with its close relative Sakha (Yakut), belongs to the North Siberian subbranch of the Turkic language family. Like most other Turkic languages, Dolgan has vowel harmony, agglutinative morphology, subject-object-verb word order, and lacks grammatical gender. Dolgan is linguistically relatively close to its nearest relative Sakha (also known as Yakut), which has led researchers for a long time to account for it as a variety of the latter, cf. Dolgich's (1963: 129) statement in his well-known paper on the origin of the Dolgans: " ... долганский
язык является диалектом якутского языка." ‘[ ...] the Dolgan language is a
dialect of the Yakut language.’. Only in 1985 did Elizaveta I. Ubrjatova account for Dolgan as a separate language, namely in her monograph on the language of the Norilsk Dolgans.
Geographical distribution
Official status
Dolgan is established as a dominant language in the Taymyr Peninsula.
Dialects/Varieties
Three Dolgan subgroups:
All dialects are understood among each other, despite subtle differences. Yakut is also understood among all since it is so similar.[citation needed]
History
The Dolgan language started out having a Latin alphabet in the early 20th century. Over time, the Cyrillic alphabet was implemented instead since it is the same alphabet used by the related language, Yakut. Evenki's influence on Dolgan can explain, in part, why it is considered a separate language from Yakut.[7] Dolgan has made appearances in newspapers, such as the Taymyr, as well as schools starting around the time of the 60s.[3] However, now there are only around 1,050 speakers of the Dolgan language.
Certain words in the language were developed from geographical implications that have been present since the start of the Dolgan language. For instance, the directional terms tās (1. south 2. east) and muora (1. north 2. west) are representative of the corresponding landscapes.[8] Tās is related to the word stone, and the southeast topography of the native region, Taymyr Peninsula, is covered by the Putorana Mountains. Similarly, muora denotes "sea" where the western zone of Taimyr has access to the sea shore.
However, this is not true for all directional terms, nor all words of the Dolgan language. Southwest, uhä, and northeast, allara, have no significance in geographical terms relative to Taymyr.
Grammar
Morphology
The composition of morphological categories in the noun is: case, number, possession, and in the verb is: voice, aspect, mode, time, person and number. Dolgan language exhibits eight grammatical cases. In contrast in the Sakha language (i.e. Yakut), the partitive is used in the possessive declension to address the accusative case, and joint case serves to structure two similar parts of a sentence. Another notable difference from Sakha is that Dolgan does not have comitative case. In conjugation of a verb in the common form of -ааччы, the paradigms of Dolgan inclination were preserved with the word баар.
Phonology
Vowels
Consonants
[9]
Dolgan has the following phonetic characteristics:
- Diphthongisation of the Turkish medium vowels [o, e, ö] in the root syllable
- Labial and palatal vowel harmony in the native words
- Transition of the initial Turkish c- into h- , loss of the uvular x, ҕ: Yakut ; саха ~ Dolgan hака (self)
Vocabulary
- Much of the old Yakut Language was lost.
- Lack of modern political and scientific terminology.
- Change in the meaning of words under the influence of the Turkish semantic system.
- Extensive borrowing from the Russian language.
Writing system
Over time, the language itself has changed and adapted. Even during the time period when it had a Cyrillic alphabet, it changed over the years. The first version of alphabet of the language had the following appearance: А а, Б б, В в, Г г, Д д, Дь дь, Е е, Ё ё, Ж ж, З з, И и, Иэ иэ, Й й, К к, Л л, М м, Н н, Ӈ ӈ, Нь нь, О о, Ө ө, П п, Р р, С с, Т т, У у, Уо уо, Ү ү, Үө үө, Ф ф, Х х, Һ һ, Ц ц, Ч ч, Ш ш, Щ щ, Ъ ъ, Ы ы, Ыа ыа, Ь ь, Э э, Ю ю, Я я.[10]
The current Dolgan alphabet is still Cyrillic and looks as follows:
| А а
|
Б б
|
В в
|
Г г
|
Д д
|
Е е
|
Ё ё
|
Ж ж
|
| З з
|
И и
|
Й й
|
К к
|
Һ һ
|
Л л
|
М м
|
Н н
|
| Ӈ ӈ
|
О о
|
Ө ө
|
П п
|
Р р
|
С с
|
Т т
|
У у
|
| Ү ү
|
Ф ф
|
Х х
|
Ц ц
|
Ч ч
|
Ш ш
|
Щ щ
|
Ъ ъ
|
| Ы ы
|
Ь ь
|
Э э
|
Ю ю
|
Я я
|
|
|
|