| Aragonese | |
|---|---|
| aragonés | |
| Pronunciation | [aɾaɣoˈnes] |
| Native to | Spain |
| Region | Aragon; northern and central Huesca and northern Zaragoza |
| Ethnicity | Aragonese |
Native speakers | Active speakers: 10,000–12,000 (2017)[1] Active and passive speakers: 30,000–50,000 (2017)[1] |
Indo-European
| |
Early forms | Old Latin
|
| Dialects |
|
| Latin (Aragonese alphabet) | |
| Official status | |
Recognised minority language in | |
| Regulated by | Academia d'a Luenga Aragonesa |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | an |
| ISO 639-2 | arg |
| ISO 639-3 | arg |
| Glottolog | arag1245 |
| ELP | Aragonese |
| Linguasphere | 51-AAA-d |
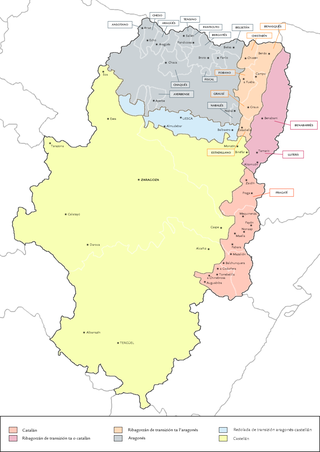 Map of Aragon with the dialects of northern Aragon in grey, blue, and light orange | |
 Aragonese is classified as Definitely Endangered by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger (2010) | |

Aragonese (/ˌærəɡəˈniːz/ ARR-ə-gə-NEEZ; aragonés [aɾaɣoˈnes] in Aragonese) is a Romance language spoken in several dialects by about 12,000 people as of 2011, in the Pyrenees valleys of Aragon, Spain, primarily in the comarcas of Somontano de Barbastro, Jacetania, Alto Gállego, Sobrarbe, and Ribagorza/Ribagorça.[1][2] It is the only modern language which survived from medieval Navarro-Aragonese in a form distinct from Spanish.
Historically, people referred to the language as fabla ('talk' or 'speech'). Native Aragonese people usually refer to it by the names of its local dialects such as cheso (from Valle de Hecho) or patués (from the Benasque Valley).
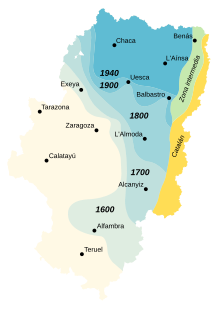
Aragonese, which developed in portions of the Ebro basin, can be traced back to the High Middle Ages. It spread throughout the Pyrenees to areas where languages similar to modern Basque might have been previously spoken. The Kingdom of Aragon (formed by the counties of Aragon, Sobrarbe and Ribagorza) expanded southward from the mountains, pushing the Moors farther south in the Reconquista and spreading the Aragonese language.
The union of the Catalan counties and the Kingdom of Aragon which formed the 12th-century Crown of Aragon did not merge the languages of the two territories; Catalan continued to be spoken in the east and Navarro-Aragonese in the west, with the boundaries blurred by dialectal continuity. The Aragonese Reconquista in the south ended with the cession of Murcia by James I of Aragon to the Kingdom of Castile as dowry for an Aragonese princess.
The best-known proponent of the Aragonese language was Johan Ferrandez d'Heredia, the Grand Master of the Knights Hospitaller in Rhodes at the end of the 14th century. He wrote an extensive catalog of works in Aragonese and translated several works from Greek into Aragonese (the first in medieval Europe).
The spread of Castilian (Spanish), the Castilian origin of the Trastámara dynasty, and the similarity between Castilian (Spanish) and Aragonese facilitated the recession of the latter. A turning point was the 15th-century coronation of the Castilian Ferdinand I of Aragon, also known as Ferdinand of Antequera.
In the early 18th century, after the defeat of the allies of Aragon in the War of the Spanish Succession, Philip V ordered the prohibition of the Aragonese language in schools and the establishment of Castilian (Spanish) as the only official language in Aragon. This was ordered in the Aragonese Nueva Planta decrees of 1707.
In recent times, Aragonese was mostly regarded as a group of rural dialects of Spanish. Compulsory education undermined its already weak position; for example, pupils were punished for using it. However, the 1978 Spanish transition to democracy heralded literary works and studies of the language.

Aragonese is the native language of the Aragonese mountain ranges of the Pyrenees, in the comarcas of Somontano, Jacetania, Sobrarbe, and Ribagorza. Cities and towns in which Aragonese is spoken are Huesca, Graus, Monzón, Barbastro, Bielsa, Chistén, Fonz, Echo, Estadilla, Benasque, Campo, Sabiñánigo, Jaca, Plan, Ansó, Ayerbe, Broto, and El Grado.
It is spoken as a second language by inhabitants of Zaragoza, Huesca, Ejea de los Caballeros, or Teruel. According to recent polls, there are about 25,500 speakers (2011)[2] including speakers living outside the native area. In 2017, the Dirección General de Política Lingüística de Aragón estimated there were 10,000 to 12,000 active speakers of Aragonese.[1]
In 2009, the Languages Act of Aragon (Law 10/2009) recognized the "native language, original and historic" of Aragon. The language received several linguistic rights, including its use in public administration.[3][4] Some of the legislation was repealed by a new law in 2013 (Law 3/2013).[5] [See Languages Acts of Aragon for more information on the subject]
|
Main article: Aragonese dialects |

Aragonese has many historical traits in common with Catalan. Some are conservative features that are also shared with the Asturleonese languages and Galician–Portuguese, where Spanish innovated in ways that did not spread to nearby languages.
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i | u | |
| Mid | e | o | |
| Open | a |
| Labial | Dental | Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ɲ | |||
| Plosive | voiceless | p | t | t͡ʃ | k | |
| voiced | b | d | ɡ | |||
| Fricative | f | θ | s | ʃ | ||
| Approximant | central | j | w | |||
| lateral | l | ʎ | ||||
| Flap | ɾ | |||||
| Trill | r | |||||
Before 2023, Aragonese had three orthographic standards:
During the 16th century, Aragonese Moriscos wrote aljamiado texts (Romance texts in Arabic script), possibly because of their inability to write in Arabic. The language in these texts has a mixture of Aragonese and Castilian traits, and they are among the last known written examples of the Aragonese formerly spoken in central and southern Aragon.[12]
| Sounds and features | Academia de l'Aragonés | Grafía de Uesca (1987) | Grafía SLA |
|---|---|---|---|
| /a/ | a | a | a |
| /b/ | b, v according to Latin etymology Ex: bien, servicio, val, activo, cantaba, debant |
b Ex: bien, serbizio, bal, autibo, cantaba, debán |
b, v according to Medieval etymology, as in Catalan and Occitan Ex: bien, servício, val, activo, cantava, devant |
| /k/ |
|
|
|
| /kw/ | If there is an etymological q, as in Catalan and a bit in Occitan:
|
cu as in Spanish Ex: cuan, cuestión |
If there is an etymological q, as in Catalan and a bit in Occitan:
|
| /tʃ/ | ch Ex: chaminera, minchar, chusticia, cheografía |
ch Ex: chaminera, minchar, chustizia, cheografía |
|
| /d/ | d | d | d |
| /e/ | e | e | e |
| /f/ | f | f | f |
| /ɡ/ |
|
|
|
| /ɡw/ |
|
|
|
| Etymological h (rendered silent after Latin) |
Written according to Latin etymology Ex: historia, hibierno |
Not written Ex: istoria, ibierno |
Written as in Medieval Aragonese and Catalan Ex: história, hivierno |
| /i/ |
|
|
|
| /l/ | l | l | l |
| /ʎ/ | ll | ll | ll |
| /m/ | m | m | m |
| /n/ | n | n | n |
| /ɲ/ | ny as in Medieval Aragonese and Catalan Ex: anyada |
ñ as in Spanish Ex: añada |
ny as in Medieval Aragonese and Catalan Ex: anyada |
| /o/ | o | o | o |
| /p/ | p | p | p |
| /ɾ/ | r | r | r |
| /r/ |
|
|
|
| /s/ | s (also between two vowels, never *ss) | s (also between two vowels, never *ss) | s (also between two vowels, never *ss) |
| /t/ | t | t | t |
| Etymological final -t (silent in Modern Aragonese) |
Written as in Medieval Aragonese, Catalan and Occitan Ex: sociedat, debant, chent |
Not written Ex: soziedá, debán, chen |
Written as in Medieval Aragonese, Catalan and Occitan Ex: sociedat, devant, gent |
| /u, w/ | u | u | u |
| /jʃ/ (Eastern dialects) /ʃ/ (Western dialects) |
ix as unifying grapheme for all dialects Ex: baixo, x as in xoriguer |
x Ex: baxo |
|
| /j/ |
|
|
|
| /θ/ |
|
z Ex: zona, Probenza, fez, zentro, serbizio, realizar, berdaz |
|
| Learned Greco-Roman words | Assimilatory tendencies not written Ex: dialecto, extension, and lexico |
Assimilatory tendencies written Ex: dialeuto, estensión, but lecsico |
Not all assimilatory tendencies written Ex: dialecto, extension, and lexico |
| Accent mark for stress (accented vowel in bold) |
Spanish model, but with the possibility for oxytones to not be accented Ex:
|
Spanish model Ex:
|
Portuguese, Catalan and Occitan model Ex:
|
In 2023, a new orthographic standard has been published by the Academia Aragonesa de la Lengua.[14] This version is close to the Academia de l'Aragonés orthography, but with the following differences: /kw/ is always spelled ⟨cu⟩, e. g. cuan, cuestión (exception is made for some loanwords: quad, quadrívium, quark, quásar, quáter, quórum); /ɲ/ is spelled ⟨ny⟩ or ⟨ñ⟩ by personal preference; final ⟨z⟩ is not written as ⟨tz⟩.
The marginal phoneme /x/ (only in loanwords, e. g. jabugo) is spelled j in the Uesca, Academia de l'Aragonés and Academia Aragonesa de la Lengua standards (not mentioned in the SLA standard). Additionally, the Academia de l'Aragonés and Academia Aragonesa de la Lengua orthographies allow the letter j in some loanwords internationally known with it (e. g. jazz, jacuzzi, which normally have /tʃ/ in the Aragonese pronunciation) and also mention the letters k and w, also used only in loanwords (w may represent /b/ or /w/).
Aragonese grammar has a lot in common with Occitan and Catalan,[15] but also Spanish.
The definite article in Aragonese has undergone dialect-related changes, [clarification needed] with definite articles in Old Aragonese similar to their present Spanish equivalents. There are two main forms:
| Masculine | Feminine | |
|---|---|---|
| Singular | el | la |
| Plural | els/es | las/les |
These forms are used in the eastern and some central dialects.
| Masculine | Feminine | |
|---|---|---|
| Singular | lo/ro/o | la/ra/a |
| Plural | los/ros/os | las/ras/as |
These forms are used in the western and some central dialects.[16]
Neighboring Romance languages have influenced Aragonese. Catalan and Occitan influenced Aragonese for many years. Since the 15th century, Spanish has most influenced Aragonese; it was adopted throughout Aragon as the first language, limiting Aragonese to the northern region surrounding the Pyrenees. French has also influenced Aragonese; Italian loanwords have entered through other languages (such as Catalan), and Portuguese words have entered through Spanish. Germanic words came with the conquest of the region by Germanic peoples during the fifth century, and English has introduced a number of new words into the language.
Words that were part of the Latin second declension—as well as words that joined it later on—are usually masculine:
Words that were part of the Latin first declension are usually feminine:
Some Latin neuter plural nouns joined the first declension as singular feminine nouns:
Words ending in -or are feminine:
The names of fruit trees usually end in -era (a suffix derived from Latin -aria) and are usually feminine:
The genders of river names vary:
Just like most other Occitano-Romance languages, Aragonese has partitive and locative clitic pronouns derived from the Latin inde and ibi: en/ne and bi/i/ie; unlike Ibero-Romance.
Such pronouns are present in most major Romance languages (Catalan en and hi, Occitan ne and i, French en and y, and Italian ne and ci/vi).
En/ne is used for:
Bi/hi/ie is used for:
|
Main article: Aragonese-language literature |
Aragonese was not written until the 12th and 13th centuries; the history Liber Regum,[17] Razón feita d'amor,[17] Libre dels tres reys d'orient,[17] and Vida de Santa María Egipcíaca date from this period;[17][18] there is also an Aragonese version of the Chronicle of the Morea, differing also in its content and written in the late 14th century called Libro de los fechos et conquistas del principado de la Morea.
Since 1500, Spanish has been the cultural language of Aragon; many Aragonese wrote in Spanish, and during the 17th century the Argensola brothers went to Castile to teach Spanish.[19] Aragonese became a popular village language.[12] During the 17th century, popular literature in the language began to appear. In a 1650 Huesca literary contest, Aragonese poems were submitted by Matías Pradas, Isabel de Rodas and "Fileno, montañés".[citation needed]
The 19th and 20th centuries have seen a renaissance of Aragonese literature in several dialects. In 1844, Braulio Foz's novel Vida de Pedro Saputo was published in the Almudévar (southern) dialect. The 20th century featured Domingo Miral's costumbrist comedies and Veremundo Méndez Coarasa's poetry, both in Hecho (western) Aragonese; Cleto Torrodellas' poetry and Tonón de Baldomera's popular writings in the Graus (eastern) dialect and Arnal Cavero's costumbrist stories and Juana Coscujuela's novel A Lueca, historia d'una moceta d'o Semontano, also in the southern dialect.
The 1997 Aragonese law of languages stipulated that Aragonese (and Catalan) speakers had a right to the teaching of and in their own language.[20] Following this, Aragonese lessons started in schools in the 1997–1998 academic year.[20] It was originally taught as an extra-curricular, non-evaluable voluntary subject in four schools.[21] However, whilst legally schools can choose to use Aragonese as the language of instruction, as of the 2013–2014 academic year, there are no recorded instances of this option being taken in primary or secondary education.[21] In fact, the only current scenario in which Aragonese is used as the language of instruction is in the Aragonese philology university course, which is optional, taught over the summer and in which only some of the lectures are in Aragonese.[21]
In pre-school education, students whose parents wish them to be taught Aragonese receive between thirty minutes to one hour of Aragonese lessons a week.[21] In the 2014–2015 academic year there were 262 students recorded in pre-school Aragonese lessons.[21]
The subject of Aragonese now has a fully developed curriculum in primary education in Aragon.[21] Despite this, in the 2014–2015 academic year there were only seven Aragonese teachers in the region across both pre-primary and primary education and none hold permanent positions, whilst the number of primary education students receiving Aragonese lessons was 320.[21]
As of 2017 there were 1068 reported Aragonese language students and 12 Aragonese language instructors in Aragon.[22]
There is no officially approved program or teaching materials for the Aragonese language at the secondary level, and though two non-official textbooks are available (Pos ixo... Materials ta aprender aragonés (Benítez, 2007) and Aragonés ta Secundaria (Campos, 2014)) many instructors create their own learning materials. Further, most schools with Aragonese programs that have the possibility of being offered as an examinative subject have elected not to do so.
As of 2007 it is possible to use Aragonese as a language of instruction for multiple courses; however, no program is yet to instruct any curricular or examinative courses in Aragonese. As of the 2014–2015 academic year there were 14 Aragonese language students at the secondary level.[23]
Aragonese is not currently a possible field of study for a bachelor's or postgraduate degree in any official capacity, nor is Aragonese used as a medium of instruction. A bachelor's or master's degree may be obtained in Magisterio (teaching) at the University of Zaragoza; however, no specialization in Aragonese language is currently available. As such those who wish to teach Aragonese at the pre-school, primary, or secondary level must already be competent in the language by being a native speaker or by other means. Further, prospective instructors must pass an ad hoc exam curated by the individual schools at which they wish to teach in order to prove their competence, as there are no recognized standard competency exams for the Aragonese language.
Since the 1994–1995 academic year, Aragonese has been an elective subject within the bachelor's degree for primary school education at the University of Zaragoza's Huesca campus.[23]
The University of Zaragoza's Huesca campus also offers a Diploma de Especialización (These are studies that require a previous university degree and have a duration of between 30 and 59 ECTS credits.) in Aragonese Philology with 37 ECTS credits.[24]