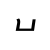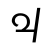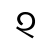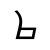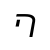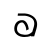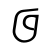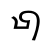Dialect continuum of Sichuan, China
.mw-parser-output .hidden-begin{box-sizing:border-box;width:100%;padding:5px;border:none;font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .hidden-title{font-weight:bold;line-height:1.6;text-align:left}.mw-parser-output .hidden-content{text-align:left}@media all and (max-width:500px){.mw-parser-output .hidden-begin{width:auto!important;clear:none!important;float:none!important))You can help expand this article with text translated from
the corresponding article in Portuguese. (November 2021) Click [show] for important translation instructions.
Machine translation, like
DeepL or
Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting machine-translated text into the English Wikipedia.
Consider
adding a topic to this template: there are already 464 articles in the
main category, and specifying|topic= will aid in categorization.
Do not translate text that appears unreliable or low-quality. If possible, verify the text with references provided in the foreign-language article.
You must provide
copyright attribution in the
edit summary accompanying your translation by providing an
interlanguage link to the source of your translation. A model attribution edit summary is Content in this edit is translated from the existing Portuguese Wikipedia article at [[:pt:Língua qiang]]; see its history for attribution.
You may also add the template ((Translated|pt|Língua qiang)) to the
talk page.
For more guidance, see
Wikipedia:Translation.
Qiang language, called Rma (尔玛) or Rme [1] by its speakers, is a Sino-Tibetan language cluster of the Qiangic branch spoken by approximately 140,000 people in north-central Sichuan Province, China.
Qiang consists of:
Classification
Sims (2016)[4] gives the following classification for the "Qiangish" (or "Rma") languages, which include Northern Qiang and Southern Qiang. Individual dialects are highlighted in italics.
- Qiangish
- Northern Qiang ('upstream' *nu- innovation group)
- NW Heishui: Luhua 芦花镇
- Central Heishui
- Qinglang 晴朗乡
- Zhawo 扎窝乡
- Ciba 慈坝乡
- Shuangliusuo 双溜索乡
- uvular V's innovation group: Zhimulin 知木林乡, Hongyan 红岩乡, Mawo 麻窝乡
- SE Heishui: Luoduo 洛多乡, Longba 龙坝乡, Musu 木苏乡, Shidiaolou 石碉楼乡
- North Maoxian: Taiping 太平乡, Songpinggou 松坪沟乡
- South Songpan: Xiaoxing 小姓乡, Zhenjiangguan 镇江关乡, Zhenping 镇坪乡
- West Maoxian / South Heishui: Weigu 维古乡, Waboliangzi 瓦钵乡梁子, Se'ergu 色尔古镇, Ekou, Weicheng 维城乡, Ronghong, Chibusu, Qugu 曲谷乡 [basis for written language], Wadi 洼底乡, Baixi 白溪乡, Huilong 回龙乡, Sanlong 三龙乡
- Central Maoxian: Heihu 黑虎乡
- SE Maoxian (reflexive marker innovation): Goukou 沟口乡, Yonghe 永和乡
- Southern Qiang (perfective agreement suffixes innovation group)
- 'inward' *ji innovation subgroup
- 'downward' *ɚ innovation subgroup
- Western Lixian: Puxi 蒲溪乡, Xuecheng 薛城镇, Muka 木卡乡, Jiuzi 九子村
- Eastern Lixian: Taoping 桃坪乡, Tonghua 通化乡
Reconstruction
Sims (2017)[5] reconstructs tones for Proto-Rma (alternatively called Proto-Qiangish), proposing that the lack of tones in Northern Qiang is due to Tibetan influence. High tones and low tones are reconstructed for Proto-Rma, as well as for Proto-Prinmi.