Portal maintenance status: (No date set)
|
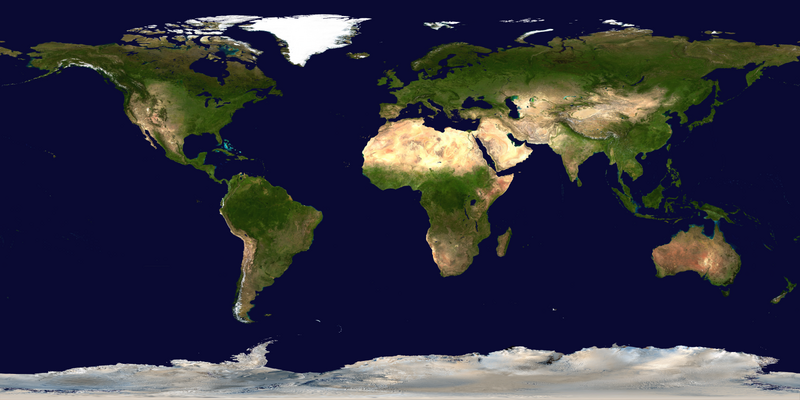
The World Portal

The world is the totality of entities, the whole of reality, or everything that exists. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique while others talk of a "plurality of worlds". Some treat the world as one simple object while others analyze the world as a complex made up of parts.
In scientific cosmology, the world or universe is commonly defined as "[t]he totality of all space and time; all that is, has been, and will be". Theories of modality talk of possible worlds as complete and consistent ways how things could have been. Phenomenology, starting from the horizon of co-given objects present in the periphery of every experience, defines the world as the biggest horizon or the "horizon of all horizons". In philosophy of mind, the world is contrasted with the mind as that which is represented by the mind. Theology conceptualizes the world in relation to God, for example, as God's creation, as identical to God or as the two being interdependent. In religions, there is a tendency to downgrade the material or sensory world in favor of a spiritual world to be sought through religious practice. A comprehensive representation of the world and our place in it, as is found in religions, is known as a worldview. Cosmogony is the field that studies the origin or creation of the world while eschatology refers to the science or doctrine of the last things or of the end of the world.
In various contexts, the term "world" takes a more restricted meaning associated, for example, with the Earth and all life on it, with humanity as a whole or with an international or intercontinental scope. In this sense, world history refers to the history of humanity as a whole and world politics is the discipline of political science studying issues that transcend nations and continents. Other examples include terms such as "world religion", "world language", "world government", "world war", "world population", "world economy", or "world championship". (Full article...)
Selected articles - show another
-
Image 1The global cuisine or world cuisine is a cuisine that is practiced around the world. A cuisine is a characteristic style of cooking practices and traditions, often associated with a specific region, country or culture. To become a global cuisine, a local, regional or national cuisine must spread around the world, its food served worldwide. There have been significant improvements and advances during the 20th century in food preservation, storage, shipping and production, and today many countries, cities and regions have access to their traditional cuisines and many other global cuisines. (Full article...)
-
Image 2
The Scientific Revolution was a series of events that marked the emergence of modern science during the early modern period, when developments in mathematics, physics, astronomy, biology (including human anatomy) and chemistry transformed the views of society about nature. The Scientific Revolution took place in Europe in the second half of the Renaissance period, with the 1543 Nicolaus Copernicus publication De revolutionibus orbium coelestium (On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres) often cited as its beginning.
The era of the Scientific Renaissance focused to some degree on recovering the knowledge of the ancients and is considered to have culminated in Isaac Newton's 1687 publication Principia which formulated the laws of motion and universal gravitation, thereby completing the synthesis of a new cosmology. The subsequent Age of Enlightenment saw the concept of a scientific revolution emerge in the 18th-century work of Jean Sylvain Bailly, who described a two-stage process of sweeping away the old and establishing the new. There continues to be scholarly engagement regarding the boundaries of the Scientific Revolution and its chronology. (Full article...) -
Image 3

Miss Universe is an annual international major beauty pageant that is run by a Thailand and Mexican-based Miss Universe Organization. Along with Miss World, Miss International, and Miss Earth, it is one of the Big Four beauty pageants.
The Miss Universe Organization and its brand, is currently owned by JKN Global Group and Legacy Holding Group USA Inc., an American division of Mexican company Legacy Holding through the joint venture company JKN Legacy Inc. Telemundo has the licensing rights to air the pageant through 2023. The pageant's advocacy is "humanitarian issues and is a voice to affect positive change in the world." (Full article...) -
Image 4

A typical British bank statement header (from a fictitious bank), showing the location of the account's IBAN
The International Bank Account Number (IBAN) is an internationally agreed upon system of identifying bank accounts across national borders to facilitate the communication and processing of cross border transactions with a reduced risk of transcription errors. An IBAN uniquely identifies the account of a customer at a financial institution. It was originally adopted by the European Committee for Banking Standards (ECBS) and since 1997 as the international standard ISO 13616 under the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). The current version is ISO 13616:2020, which indicates the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) as the formal registrar. Initially developed to facilitate payments within the European Union, it has been implemented by most European countries and numerous countries in other parts of the world, mainly in the Middle East and the Caribbean. By July 2023, 86 countries were using the IBAN numbering system.
The IBAN consists of up to 34 alphanumeric characters comprising a country code; two check digits; and a number that includes the domestic bank account number, branch identifier, and potential routing information. The check digits enable a check of the bank account number to confirm its integrity before submitting a transaction. (Full article...) -
Image 5
The Cricket World Cup (officially known as ICC Men's Cricket World Cup) is the international championship of One Day International (ODI) cricket. The event is organised by the sport's governing body, the International Cricket Council (ICC), every four years, with preliminary qualification rounds leading up to a finals tournament. The tournament is one of the world's most viewed sporting events and considered the "flagship event of the international cricket calendar" by the ICC. It is widely considered the pinnacle championship of the sport of cricket.
The first World Cup was organised in England in June 1975, with the first ODI cricket match having been played only four years earlier. However, a separate Women's Cricket World Cup had been held two years before the first men's tournament, and a tournament involving multiple international teams had been held as early as 1912, when a triangular tournament of Test matches was played between Australia, England and South Africa. The first three World Cups were held in England. From the 1987 tournament onwards, hosting has been shared between countries under an unofficial rotation system, with fourteen ICC members having hosted at least one match in the tournament. (Full article...) -
Image 6

The World Economic Forum (WEF) is an international non-governmental organization, think tank, and lobbying organisation based in Cologny, Canton of Geneva, Switzerland. It was founded on 24 January 1971 by German engineer Klaus Schwab.
The foundation, which is mostly funded by its 1,000 member companies – typically global enterprises with more than five billion US dollars in turnover – as well as public subsidies, state that its own mission is "improving the state of the world by engaging business, political, academic, and other leaders of society to shape global, regional, and industry agendas". (Full article...) -
Image 7

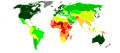
World Muslim population by percentage (Pew Research Center, 2014)
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs, politics, and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. In a modern geopolitical sense, these terms refer to countries in which Islam is widespread, although there are no agreed criteria for inclusion. The term Muslim-majority countries is an alternative often used for the latter sense.
The history of the Muslim world spans about 1,400 years and includes a variety of socio-political developments, as well as advances in the arts, science, medicine, philosophy, law, economics and technology during the Islamic Golden Age. Muslims look for guidance to the Quran and believe in the prophetic mission of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, but disagreements on other matters have led to the appearance of different religious schools of thought and sects within Islam. The Islamic conquests, which culminated in the Caliphate being established across three continents (Asia, Africa, and Europe), enriched the Muslim world, achieving the economic preconditions for the emergence of this institution owing to the emphasis attached to Islamic teachings. In the modern era, most of the Muslim world came under European colonial domination. The nation states that emerged in the post-colonial era have adopted a variety of political and economic models, and they have been affected by secular as well as religious trends. (Full article...)
General images - load new batch
-
Image 2An artist's impression of the Archean, the eon after Earth's formation, featuring round stromatolites, which are early oxygen-producing forms of life from billions of years ago. After the Late Heavy Bombardment, Earth's crust had cooled, its water-rich barren surface is marked by continents and volcanoes, with the Moon still orbiting Earth half as far as it is today, appearing 2.8 times larger and producing strong tides. (from Earth)
-
Image 3"Lucy", the first Australopithecus afarensis skeleton found, was only 1.06 m (3 ft 6 in) tall.
-
Image 5Olmec colossal head, now at the Museo de Antropología de Xalapa
-
Image 6A banded iron formation from the 3.15 Ga Moodies Group, Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa. Red layers represent the times when oxygen was available; gray layers were formed in anoxic circumstances. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 9A schematic view of Earth's magnetosphere with solar wind flowing from left to right (from Earth)
-
Image 10Earth's night-side upper atmosphere appearing from the bottom as bands of afterglow illuminating the troposphere in orange with silhouettes of clouds, and the stratosphere in white and blue. Next the mesosphere (pink area) extends to the orange and faintly green line of the lowest airglow, at about one hundred kilometers at the edge of space and the lower edge of the thermosphere (invisible). Continuing with green and red bands of aurorae stretching over several hundred kilometers. (from Earth)
-
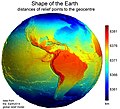
Image 11Earth's western hemisphere showing topography relative to Earth's center instead of to mean sea level, as in common topographic maps (from Earth)
-
Image 12Notre-Dame de Paris, France
-
Image 13Astronaut Buzz Aldrin on the Moon, photographed by Neil Armstrong, 1969 (from History of Earth)
-
Image 14Vitruvian Man by Leonardo da Vinci epitomizes the advances in art and science seen during the Renaissance. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 17Artist's rendition of an oxinated fully-frozen Snowball Earth with no remaining liquid surface water. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 22First airplane, the Wright Flyer, flew on 17 December 1903.
-
Image 23Angkor Wat temple complex, Cambodia, early 12th century
-
Image 24Atomic bombing of Nagasaki, 1945
-
Image 26A 580 million year old fossil of Spriggina floundensi, an animal from the Ediacaran period. Such life forms could have been ancestors to the many new forms that originated in the Cambrian Explosion. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 27A map of heat flow from Earth's interior to the surface of Earth's crust, mostly along the oceanic ridges (from Earth)
-
Image 28A 2012 artistic impression of the early Solar System's protoplanetary disk from which Earth and other Solar System bodies were formed (from Earth)
-
Image 29Standing Buddha from Gandhara, 2nd century CE
-
Image 30Great Pyramids of Giza, Egypt
-
Image 32A reconstruction of Pannotia (550 Ma). (from History of Earth)
-
Image 33A composite image of Earth, with its different types of surface discernible: Earth's surface dominating Ocean (blue), Africa with lush (green) to dry (brown) land and Earth's polar ice in the form of Antarctic sea ice (grey) covering the Antarctic or Southern Ocean and the Antarctic ice sheet (white) covering Antarctica. (from Earth)
-
Image 34Yggdrasil, an attempt to reconstruct the Norse world tree which connects the heavens, the world, and the underworld. (from World)
-
Image 37Change in average surface air temperature and drivers for that change. Human activity has caused increased temperatures, with natural forces adding some variability. (from Earth)
-
Image 38Great Mosque of Kairouan, Tunisia, founded 670 CE
-
Image 40A computer-generated image mapping the prevalence of artificial satellites and space debris around Earth in geosynchronous and low Earth orbit (from Earth)
-
Image 41Artist's impression of the enormous collision that probably formed the Moon (from History of Earth)
-
Image 44A view of Earth with different layers of its atmosphere visible: the troposphere with its clouds casting shadows, a band of stratospheric blue sky at the horizon, and a line of green airglow of the lower thermosphere around an altitude of 100 km, at the edge of space (from Earth)
-
Image 45Lithified stromatolites on the shores of Lake Thetis, Western Australia. Archean stromatolites are the first direct fossil traces of life on Earth. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 46Ajloun Castle, Jordan
-
Image 47Dinosaurs were the dominant terrestrial vertebrates throughout most of the Mesozoic (from History of Earth)
-
Image 48The replicator in virtually all known life is deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA is far more complex than the original replicator and its replication systems are highly elaborate. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 49Obelisk of Axum, Ethiopia
-
Image 50An artist's impression of ice age Earth at glacial maximum. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 51A pillar at Göbekli Tepe
-
Image 52The pale orange dot, an artist's impression of the early Earth which might have appeared orange through its hazy methane rich prebiotic second atmosphere. Earth's atmosphere at this stage was somewhat comparable to today's atmosphere of Titan. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 55Battle during the 1281 Mongol invasion of Japan
-
Image 56Artist's conception of Hadean Eon Earth, when it was much hotter and inhospitable to all forms of life. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 58Trilobites first appeared during the Cambrian period and were among the most widespread and diverse groups of Paleozoic organisms. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 60Tiktaalik, a fish with limb-like fins and a predecessor of tetrapods. Reconstruction from fossils about 375 million years old. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 61Artist's impression of Earth during the later Archean, the largely cooled planetary crust and water-rich barren surface, marked by volcanoes and continents, features already round microbialites. The Moon, still orbiting Earth much closer than today and still dominating Earth's sky, produced strong tides. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 62Shanghai. China urbanized rapidly in the 21st century.
-
Image 63Graph showing range of estimated partial pressure of atmospheric oxygen through geologic time (from History of Earth)
-
Image 64Geologic map of North America, color-coded by age. From most recent to oldest, age is indicated by yellow, green, blue, and red. The reds and pinks indicate rock from the Archean.
-
Image 65Pangaea was a supercontinent that existed from about 300 to 180 Ma. The outlines of the modern continents and other landmasses are indicated on this map. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 68A reconstruction of human history based on fossil data. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 69Peopling of the world, the Southern Dispersal scenario
-
Image 72Artist's impression of a Hadean landscape with the relatively newly formed Moon still looming closely over Earth and both bodies sustaining strong volcanism. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 75Japanese depiction of a Portuguese carrack. European maritime innovations led to proto-globalization.
-
Image 76Earth's axial tilt causing different angles of seasonal illumination at different orbital positions around the Sun (from Earth)
-
Image 77An animation of the changing density of productive vegetation on land (low in brown; heavy in dark green) and phytoplankton at the ocean surface (low in purple; high in yellow) (from Earth)
-
Image 78Tracy Caldwell Dyson, a NASA astronaut, observing Earth from the Cupola module at the International Space Station on 11 September 2010 (from Earth)
-
Image 79Empires of the world in 1898
-
Image 80Last Moon landing: Apollo 17 (1972)
-
Image 81A view of Earth with its global ocean and cloud cover, which dominate Earth's surface and hydrosphere; at Earth's polar regions, its hydrosphere forms larger areas of ice cover. (from Earth)
-
Image 83Benin Bronze head from Nigeria
-
Image 85Earth's land use for human agriculture in 2019 (from Earth)
-
Image 86Fall of the Berlin Wall, 1989
-
Image 87Pale orange dot, an artist's impression of Early Earth, featuring its tinted orange methane-rich early atmosphere (from Earth)
-
Image 88Chloroplasts in the cells of a moss (from History of Earth)
Megacities of the world - show another

Hangzhou is the capital and most populous city of Zhejiang, China. It is located in the northeastern part of the province, sitting at the head of Hangzhou Bay, which separates Shanghai and Ningbo. Hangzhou grew to prominence as the southern terminus of the Grand Canal and has been one of China's most renowned and prosperous cities for much of the last millennium. It is a major economic and e-commerce hub. Hangzhou is classified as a sub-provincial city and forms the core of the Hangzhou metropolitan area, the fourth-largest in China after Guangzhou-Shenzhen Pearl River agglomeration, Shanghai-Suzhou-Wuxi-Changzhou conurbation and Beijing. As of 2022, the Hangzhou metropolitan area was estimated to produce a gross metropolitan product (nominal) of 4 trillion yuan (US$590 billion), making it larger than the economy of Sweden. As of the 2020 Chinese census, it had a total population of 11,936,010 inhabitants. However, its metropolitan area, populated by 13.035 million people over an area of 8,107.9 km2 (3,130.5 sq mi), consists of all urban districts in Hangzhou and 3 urban districts of the city of Shaoxing.
Hangzhou has been repeatedly rated as the best commercial city in mainland China by Forbes and the Chinese city with the highest growth potential by the Economist Intelligence Unit. A study conducted by PwC and China Development Research Foundation ranked Hangzhou first among "Chinese Cities of Opportunity". According to the Globalization and World Cities Research Network (GaWC), the city is classified as a Beta (global second-tier) city, together with Chongqing, Nanjing and Tianjin in China. Hangzhou is also one of the world's top 100 financial centers, according to the Global Financial Centres Index. It boasts the eighth largest GDP among cities in mainland China with a GDP of around 1.8 trillion RMB ($280 billion). Home to the headquarters of large global tech companies such as Alibaba Group, Ant Group, and NetEase, Hangzhou is known for attracting professionals and entrepreneurs who work in information technology. , Hangzhou has the tenth-most Fortune Global 500 headquarters of any city in the world and the fourth-most in China – after Beijing, Shanghai and Shenzhen – within its city limits. According to the 2020 Hurun Global Rich List, Hangzhou ranks 11th in the world and 6th in China (after Beijing, Shanghai, Hong Kong, Shenzhen and Guangzhou) in the number of resident billionaires. (Full article...)Did you know - load new batch

- ... that German cavalry carried steel lances throughout the First World War?
- ... that the Morowali Industrial Park is the largest center of nickel industry in Indonesia, the world's top nickel producer?
- ... that the Bancroft region is the only place in Canada and one of very few places in the world where uranium has been mined from pegmatite rock?
- ... that Max Eisenbud helped make Maria Sharapova the world's highest-paid female athlete for more than a decade?
- ... that John Spencer "exploded two myths" by winning the 1977 World Snooker Championship with a two-piece cue that he had only been using for a couple of months?
- ... that despite lagging attendance at the 1964 New York World's Fair, its organizer rejected nearly every suggestion to increase attendance?
- ... that Dreamtime is one of the world's most famous bouldering routes?
- ... that the 1917 Leeds Convention in Britain passed resolutions calling for the end of the First World War and praising the February Revolution in Russia?
Countries of the world - show another

Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to the east, and the Black Sea to the southeast. It has a predominantly continental climate, and an area of 238,397 km2 (92,046 sq mi) with a population of 19 million people (2023). Romania is the twelfth-largest country in Europe and the sixth-most populous member state of the European Union. Its capital and largest city is Bucharest, followed by Cluj-Napoca, Iași, Timișoara, Constanța, Craiova, Brașov, and Galați.
Europe's second-longest river, the Danube, rises in Germany's Black Forest and flows southeast for 2,857 km (1,775 mi), before emptying into Romania's Danube Delta. The Carpathian Mountains cross Romania from the north to the southwest and include Moldoveanu Peak, at an altitude of 2,544 m (8,346 ft). (Full article...)Related portals
Protected areas of the world - load new batch
-
Image 1

Network of protected areas in Albania (2020)
Despite being a relatively small country, Albania is exceedingly rich in biodiversity. Its ecosystems and habitats support over 5,550 species of vascular and non-vascular plants and more than 15,600 species of coniferous and non-coniferous evergreens, most of which are threatened at global and European levels. The country has made recent efforts to expand its network of protected areas which now include: 11 national parks, 1 marine park, 718 nature monuments, 23 managed nature reserves, 11 protected landscapes, 4 World Heritage Sites, 4 Ramsar sites and other protected areas of various categories, that when combined, account for 21.36% of the territory. Furthermore, a biosphere reserve, 45 important plant areas and 16 important bird areas are found in the country.
Meanwhile, the central government has proclaimed the Coastline and the Tirana Greenbelt as areas of national importance. (Full article...) -
Image 2Protected areas of West Bengal cover 4% of the state area. Forests make up 14% of the geographical area of West Bengal, which is lower than the national average of 33%. West Bengal has a wide variety of fauna, including Bengal tigers, Indian leopards, sloth and Himalayan black bears, chital and sambar (deer), Indian boars, pygmy hogs, Indian elephants, Indian peafowl, great Indian hornbills, Eurasian spoonbills, brahminy ducks, king and Indian cobras, white-lipped pit viper, Indian and reticulated pythons, mugger crocodiles, saltwater crocodiles, gharials, and many more. A huge montane forest, Dooars, is situated in the Northern West Bengal districts of Alipur Duar, Darjeeling, and Kalimpong. Part of the world's largest mangrove forest, Sundarbans, is located in southern West Bengal.
There are 6 national parks and 15 wildlife sanctuaries in West Bengal. (Full article...) -
Image 3Protected areas in the U.S. State of Ohio include national forest lands, Army Corps of Engineers areas, state parks, state forests, state nature preserves, state wildlife management areas, and other areas. (Full article...)
-
Image 4The country of Burundi in Africa has the following national parks and other protected areas. (Full article...)
-
Image 5The Ulyanovsk Oblast in Russia contains about 118 protected natural areas. (Full article...)
-
Image 6

Desert landscape in Qatar
Protected areas of Qatar include:- Al Reem Biosphere Preserve (designated in 2007) is part of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves in the Arab States
- Al Shahaniyah Park in Al-Shahaniya
- Al Thakira Nature Reserve in Al Thakhira
- Al Wabra Wildlife Preservation
- Dahl Al Hammam Park, a sinkhole in Doha (entrance to the hole is now closed to the public)
- Khor Al Adaid Natural Reserve in Khor Al Adaid
- Khor Al Udeid Fish Sanctuary
- Mudhlem Cave in Mukaynis
- Musfer Sinkhole in Salwa
- Ras Abrouq Nature Reserve (also known as Bir Zekreet (Zekreet Beach)) in Ras Abrouq
- Ras Ushairij Gazelle Conservation Park
- Umm Tais National Park
-
Image 7Protected areas of Indonesia comprise both terrestrial and marine environments in any of the six IUCN Protected Area categories. There are over 500 protected areas in Indonesia, of which 54 National Parks cover 16.4 million ha, and another 527 nature and game reserves cover a further 28.3 million ha. The total protected land area represents over 15% of Indonesia's landmass. Marine Protected Areas comprise over 15.7 million ha representing ca. 5% of territorial waters. (Full article...)
-
Image 8This is a list of protected areas of Saudi Arabia, some of which are managed by the Saudi Wildlife Authority.:
- At-Taysiyah Protected Area
- Jabal Shada Nature Reserve
- Majami'al-Hadb Protected Area
- Nafud al-'Urayq
- Raydah Natural Reserve
- 'Uruq Bani Ma'arid
- Saja Umm Ar-Rimth Natural Reserve
- Harrat al-Harrah Protected Area
- Al-Khunfah Natural Reserve
- Ibex Reserve Protected Area
- Mahazat as-Sayd Protected Area
- Umm al-Qamari Islands
- Al-Tubayq Natural Reserve
- Farasan Islands Protected Area
- Jubail Marine Wildlife Sanctuary
- Jabal Aja Protected Area
- Wadi Turabah Nature Reserve
-
Image 9

Andohahela National Park in southern Madagascar
The national parks of Madagascar include all officially recognized protected areas as of 2015. The protected areas network of Madagascar is managed by the Madagascar National Parks Association (PNM-ANGAP). The network includes three types of protected areas: Strict Nature Reserves (IUCN category Ia), National Parks (IUCN category II) and Wildlife Reserves (IUCN category IV). At the 2003 IUCN World Parks Congress in Durban, the Malagasy President, Marc Ravalomanana, announced an initiative to more than triple the area under protection from approximately 17,000 km2 (6,600 sq mi) to over 60,000 km2 (23,000 sq mi) (from 3% to 10% of Madagascar's area). This "Durban Vision", as it has been dubbed, involved broadening the definition of protected areas in the country and legislation has been passed to allow the creation of four new categories of protected area: Natural Parks (IUCN category II), Natural Monuments (IUCN category III), Protected Landscapes (IUCN category V), and Natural Resource Reserves (IUCN category VI). As well as allowing these new objectives for protected areas management, the new legislation also provided for entities other than PNM-ANGAP to manage protected areas, such as government ministries, community associations, NGOs and other civil society organizations, and the private sector. (Full article...) -
Image 11

Entrance to Tanintharyi Nature Reserve.
This list of protected areas of Myanmar includes national parks, wildlife sanctuaries and botanical gardens that were established since 1927. (Full article...) -
Image 12Protected areas of Sri Lanka are administrated by Department of Forest Conservation and Department of Wildlife Conservation of Sri Lanka.There are 501 protected areas in Sri Lanka. The protected areas that fall under supervision of the Department of Forest Conservation include forests defined in National Heritage Wilderness Area Act in 1988, forest reservations, and forests managed for sustainability. Sinharaja Forest Reserve is an example for a National Heritage forest (it is also a World Heritage Site). There are 32 forests categorized as conservation forests including Knuckles Mountain Range. Strict nature reserves, national parks, nature reserves, forest corridors, and sanctuaries recognized under the Flora and Fauna Protection Ordinance are managed by Department of Wildlife Conservation. Total of all protected areas is 1,767,000 ha. Protected areas in Sri Lanka account for 26.5 percent of the total area. This is a higher percentage of protected areas than in all of Asia and much of the World. (Full article...)
-
Image 13This is a list of protected areas of Sierra Leone, including national parks, game reserves, conservation areas, wetlands, and those that are listed as proposed protected areas in the UN Environment Programme World Conservation Monitoring Centre (UNEP WCM) database. (Full article...)
-
Image 14Queensland is the second-largest state in Australia. As at 2020, it contained more than 1,000 protected areas. In August 2023, it was estimated a total of 14.5 million hectares or 8.38% of Queensland's landmass was protected. (Full article...)
-
Image 15The protected areas of Michigan come in an array of different types and levels of protection. Michigan has five units of the National Park Service system. There are 14 federal wilderness areas; the majority of these are also tribal-designated wildernesses. It has one of the largest state forest systems as well having four national forests. The state maintains a large state park system and there are also regional parks, and county, township and city parks. Still other parks on land and in the Great Lakes are maintained by other governmental bodies. Private protected areas also exist in the state, mainly lands owned by land conservancies. (Full article...)
Selected world maps
-
Image 1The world map by Gerardus Mercator (1569), the first map in the well-known Mercator projection
-
Image 2Time zones of the world
-
Image 3Only a few of the largest large igneous provinces appear (coloured dark purple) on this geological map, which depicts crustal geologic provinces as seen in seismic refraction data
-
Image 4Mollweide projection of the world
-
Image 51516 map of the world by Martin Waldseemüller
-
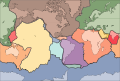
Image 6A plate tectonics map with volcano locations indicated with red circles
-
Image 7United Nations Human Development Index map by country (2016)
-
Image 8The Goode homolosine projection is a pseudocylindrical, equal-area, composite map projection used for world maps.
-
Image 9Index map from the International Map of the World (1:1,000,000 scale)
World records
- List of Olympic records in athletics
- List of world records in athletics
- List of junior world records in athletics
- List of world records in masters athletics
- List of world youth bests in athletics
- List of IPC world records in athletics
- List of world records in canoeing
- List of world records in chess
- List of cycling records
- List of world records in track cycling
- List of world records in finswimming
- List of world records in juggling
- List of world records in rowing
- List of world records in speed skating
- List of world records in swimming
- List of IPC world records in swimming
- List of world records in Olympic weightlifting
Topics
Continents of Earth | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
| Cenozoic Era (present–66.0 Ma) |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesozoic Era (66.0–252 Ma) |
| ||||||||||||
| Paleozoic Era (252–539 Ma) |
| ||||||||||||
| Proterozoic Eon (539 Ma–2.5 Ga) |
| ||||||||||||
| Archean Eon (2.5–4 Ga) | |||||||||||||
| Hadean Eon (4–4.6 Ga) | |||||||||||||
ka = kiloannum (thousands years ago); Ma = megaannum (millions years ago); Ga = gigaannum (billions years ago). See also: Geologic time scale • | |||||||||||||
| City proper | |
|---|---|
| Metropolitan area | |
| Urban area/agglomeration | |
| Historical | |
| Related articles | |
| Locations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Related | ||
| Retrospectively recognized expositions | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIE-recognized Universal expositions | |||||||||||||
| BIE-recognized specialized expositions |
| ||||||||||||
| BIE-recognized horticultural exhibitions (AIPH) | |||||||||||||
| Not BIE- recognized |
| ||||||||||||
†Postponed to 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic | |||||||||||||
| Confederations | |
|---|---|
| World Championships | |
| World Cup | |
| Special events | |
| Presidents |
|
| Awards |
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
Economic classification of countries | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Three-World Model | |||||
| Gross domestic product (GDP) |
| ||||
| Gross national income (GNI) | |||||
| Wages | |||||
| Wealth | |||||
| Other national accounts | |||||
| Human development | |||||
| Digital divide | |||||
| Net international investment position (NIIP) | |||||
| Technological |
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sociological | |||||
| Ecological |
| ||||
| Biological |
| ||||
| Astronomical | |||||
| Eschatological |
| ||||
| Others |
| ||||
| Fictional | |||||
| Organizations | |||||
| Theatres |
| ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Principal participants |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Timeline |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Aspects |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| General |
| ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Participants |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Timeline |
| ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Categories
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus